Abstract
Purpose
Sonidegib (Odomzo) selectively inhibits smoothened and suppresses the growth of hedgehog pathway-dependent tumors. A population pharmacokinetic (PK) analysis of sonidegib in healthy subjects and patients with advanced solid tumors was conducted to characterize PK, determine variability, and estimate covariate effects.
Methods
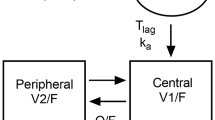
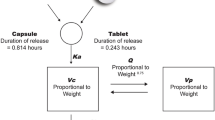
PK data from five phase 1 or 2 studies (N = 436) in the dose range from 100 to 3000 mg were analyzed using NONMEM. A two-compartment base model with first-order absorption, lag time, linear elimination, and bioavailability that decreased with dose was updated to describe the PK of sonidegib. Covariate analyses were performed and were incorporated into the population PK full model.
Results
The base and full models were robust with a good fit to the study data. Population-predicted geometric means (inter-individual variability, CV%) of apparent oral clearance, apparent volume of distribution at steady state, accumulation ratio, and elimination half-life were 9.5 L/h (71.4 %), 9163 L (74.9 %), 21 (131 %) and 29.6 days (109 %). Clinically relevant covariate effects were: A high-fat meal increased sonidegib bioavailability fivefold, healthy volunteers had threefold higher clearance, sonidegib bioavailability decreased with increasing dose levels, and PPI coadministration reduced sonidegib bioavailability by 30 %. Sonidegib PK was not significantly impacted by baseline age, weight, total bilirubin, alanine aminotransferase, albumin, creatinine clearance, gender, and ethnicity (Western countries versus Japanese).
Conclusion
No dose adjustment is needed for mild hepatic impairment, mild and moderate renal impairment, age, weight, gender, or ethnicity. This population PK model adequately characterizes sonidegib PK characteristics and can be used for various simulations and applications.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
di Magliano MP, Hebrok M (2003) Hedgehog signaling in cancer formation and maintenance. Nat Rev Cancer 3(12):903–911
McMahon AP, Ingham PW, Tabin CJ (2003) Developmental roles and clinical significance of hedgehog signaling. Curr Top Dev Biol 53:1–114
Teglund S, Toftgard R (2010) Hedgehog beyond medulloblastoma and basal cell carcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta 1805(2):181–208
Pan S et al (2010) Discovery of NVP-LDE225, a potent and selective smoothened antagonist. ACS Med Chem Lett 1(3):130–134
Buonamici S et al (2010) Interfering with resistance to smoothened antagonists by inhibition of the PI3K pathway in medulloblastoma. Sci Transl Med 2(51):5170
Rodon J et al (2014) A phase I, multicenter, open-label, first-in-human, dose-escalation study of the oral smoothened inhibitor Sonidegib (LDE225) in patients with advanced solid tumours. Clin Cancer Res 20(7):1900–1909
Slade I et al (2011) Heterogeneity of familial medulloblastoma and contribution of germline PTCH1 and SUFU mutations to sporadic medulloblastoma. Fam Cancer 10(2):337–342
Zurawel RH et al (2000) Analysis of PTCH/SMO/SHH pathway genes in medulloblastoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 27(1):44–51
Xie J et al (1998) Activating Smoothened mutations in sporadic basal-cell carcinoma. Nature 391(6662):90–92
Reifenberger J et al (2005) Somatic mutations in the PTCH, SMOH, SUFUH and TP53 genes in sporadic basal cell carcinomas. Br J Dermatol 152(1):43–51
Ling G et al (2001) PATCHED and p53 gene alterations in sporadic and hereditary basal cell cancer. Oncogene 20(53):7770–7778
Novartis (2015) ODOMZO® (sonidegib) capsules, for oral use: US Prescribing Information. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/. Accessed 27 July 2015
Migden MR et al (2015) Treatment with two different doses of sonidegib in patients with locally advanced or metastatic basal cell carcinoma (BOLT): a multicenter, randomised, double-blind phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 16(6):716–728
Zollinger M et al (2014) Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of (1)(4)C-sonidegib (LDE225) in healthy volunteers. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 74(1):63–75
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation Data on File (2015)
Zhou J, Hurh E, Emotte C, Winter S, Quinlan M, Austin T, Kalambakas S, Wang Y (2014) Evaluation of CYP3A4 endogenous biomarkers in a sonidegib drug-drug interaction study with rifampicin and ketoconazole in healthy subjects. In: American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics Annual Meeting, 2014. abstract LBI-021
Hu C, Zhang J, Zhou H (2011) Confirmatory analysis for phase III population pharmacokinetics. Pharm Stat 10(1):14–26
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1972) Drug elimination and apparent volume of distribution in multicompartment systems. J Pharm Sci 61(6):952–954
Gastonguay M (2011) full covariate models as an alternative to methods relying on statistical significance for inferences about covariate effects: a review of methodology and 42 case studies. In: Abstracts of the Annual Meeting of the Population Approach Group in Europe 2011. A16
Acknowledgments
The studies and analysis reported here were sponsored and funded by Novartis Pharma AG, Basel, Switzerland. Medical writing support was provided by Articulate Science LLC and Evelyn Harvey, Novartis Ireland Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goel, V., Hurh, E., Stein, A. et al. Population pharmacokinetics of sonidegib (LDE225), an oral inhibitor of hedgehog pathway signaling, in healthy subjects and in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 77, 745–755 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-016-2982-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-016-2982-1