Abstract
Purpose
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) facilitates the adaptation of normal and tumor tissues to oxygen deprivation. HIF-1 is frequently overexpressed in cancer cells, where it is involved in the upregulation of many genes necessary for survival. EZN-2968 is an antisense oligodeoxynucleotide that specifically targets HIF-1α, one of the subunits of HIF-1. We conducted a trial of EZN-2968 in patients with refractory solid tumors to evaluate antitumor response and to measure modulation of HIF-1α mRNA and protein levels as well as HIF-1 target genes.
Methods
Adult patients with refractory advanced solid tumors were administered EZN-2968 as a 2-h IV infusion at a dose of 18 mg/kg once a week for three consecutive weeks followed by 3-week off; in a 6-week cycle. Tumor biopsies and dynamic contrast enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI) were performed at baseline and after the third dose.
Results
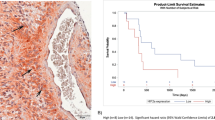
Ten patients were enrolled, of whom all were evaluable for response; one patient with a duodenal neuroendocrine tumor had prolonged stabilization of disease (24 weeks). Reduction in HIF-1α mRNA levels compared to baseline was demonstrated in 4 of 6 patients with paired tumor biopsies. Reductions in levels of HIF-1α protein and mRNA levels of some target genes were observed in two patients. Quantitative analysis of DCE-MRI from two patients revealed changes in K trans and k ep. The trial was closed prematurely when the sponsor suspended development of this agent.
Conclusion
This trial provides preliminary proof of concept for modulation of HIF-1α mRNA and protein expression and target genes in tumor biopsies following the administration of EZN-2968.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Semenza GL (2003) Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 3:721–732
Schindl M, Schoppmann SF, Samonigg H, Hausmaninger H, Kwasny W, Gnant M, Jakesz R, Kubista E, Birner P, Oberhuber G (2002) Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α is associated with an unfavorable prognosis in lymph node-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 8:1831–1837
Shibaji T, Nagao M, Ikeda N, Kanehiro H, Hisanaga M, Ko S et al (2003) Prognostic significance of HIF-1 alpha overexpression in human pancreatic cancer. Anticancer Res 23:4721–4727
Swinson DEB, Jones JL, Cox G, Richardson D, Harris AL, O’Byrne KJ (2004) Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in non small cell lung cancer: relation to growth factor, protease and apoptosis pathways. Int J Cancer 111:43–50
Hu Y, Liu J, Huang H (2013) Recent agents targeting HIF-1 alpha for cancer therapy. J Cell Biochem 114:498–509
Melillo G (2007) Targeting hypoxia cell signaling for cancer therapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev 26:341–352
Aboul-Fadl T (2005) Antisense oligonucleotides: the state of the art. Curr Med Chem 12:2193–2214
Vester B, Wengel J (2004) LNA (locked nucleic acid): high-affinity targeting of complementary RNA and DNA. Biochemistry 43:13233–13241
Raunak, Ravindra Babu B, Sorensen MD, Parmar VS, Harrit NH, Wengel J (2004) Oligodeoxynucleotides containing alpha-L-ribo configured LNA-type C-aryl nucleotides. Org Biomol Chem 2:80–89
Nimesh S, Gupta N, Chandra R (2011) Cationic polymer based nanocarriers for delivery of therapeutic nucleic acids. J Biomed Nanotechnol 7:504–520
Greenberger LM, Horak ID, Filpula D, Sapra P, Westergaard M, Frydenlund HF, Albaek C, Schroder H, Orum H (2008) A RNA antagonist of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha, EZN-2968, inhibits tumor cell growth. Mol Cancer Ther 7:3598–3608
Patnaik A, Chiorean EG, Tolcher A, Papadopoulos K, Beeram M, Kee D, Waddell M, Gilles E, Buchbinder A (2009) EZN-2968, a novel hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) antagonist: results of a phase I, pharmacokinetic (PK), dose-escalation study of daily administration in patients (pts) with advanced malignancies. J Clin Oncol 27:2564
Cohen RB, Olszanski A, Figueroa J, Hurwitz H, Lokiec FM, Rezaï K, Berkowitz N, Buchbinder A (2011) Down-modulation of messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) by EZN-2968, an hypoxia-inducible factor-1(HIF-1α) mRNA antagonist, administered in adult patients with advanced solid tumors [abstract]. In: Proceedings of the 102nd Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research, Orlando, Florida. AACR, Philadelphia (PA), abstract nr LB-407, 2–6 April 2011
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S, Mooney M, Rubinstein L, Shankar L, Dodd L, Kaplan R, Lacombe D, Verweij J (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45:228–247
Park SR, Kinders RJ, Khin S, Hollingshead M, Parchment RE, Tomaszewski JE, Doroshow JH (2012) Validation and fitness testing of a quantitative immunoassay for HIF-1 alpha in biopsy specimens [abstract]. In: Proceedings of the 103rd Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research, Chicago, Illinois. AACR, Philadelphia (PA), abstract nr 3616, 31 March–4 April 2012
Levin AA (1999) A review of the issues in the pharmacokinetics and toxicology of phosphorothioate antisense oligonucleotides. Biochim Biophys Acta 1489:69–84
Zhong H, De Marzo AM, Laughner E, Lim M, Hilton DA, Zagzag D, Buechler P, Isaacs WB, Semenza GL, Simons JW (1999) Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α in common human cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res 59:5830–5835
Talks KL, Turley H, Gatter KC, Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ, Harris AL (2000) The expression and distribution of the hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1α and HIF-2α in normal human tissues, cancers, and tumor-associated macrophages. Am J Pathol 157:411–421
Keith B, Johnson RS, Simon MC (2012) HIF1α and HIF2α: sibling rivalry in hypoxic tumour growth and progression. Nat Rev Cancer 12:9–22
Jeong W, Doroshow JH, Kummar S (2013) United States Food and Drug Administration approved oral kinase inhibitors for the treatment of malignancies. Curr Probl Cancer 37:110–144
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Yvonne, A. Evrard, and Andrea Voth for editorial assistance. This project has been funded in whole or in part with federal funds from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, under Contract No. HHSN261200800001E. The content of this publication does not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the Department of Health and Human Services, nor does mention of trade names, commercial products, or organizations imply endorsement by the US Government.
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, W., Rapisarda, A., Park, S.R. et al. Pilot trial of EZN-2968, an antisense oligonucleotide inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α), in patients with refractory solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 73, 343–348 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2362-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2362-z