Abstract
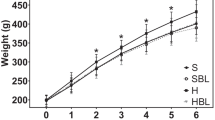
It has been proposed that isoflavones and probiotics possess specific biological activities that enable them to affect lipid metabolism. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of a soy product fermented with Enterococcus faecium and Lactobacillus jugurti and supplemented with isoflavones on the plasma lipid and glucose profiles, and on the retroperitoneal (RET) and epididymal (EPI) adipose tissue adipocyte areas in juvenile rats. Male Wistar rats were subjected to 6-week experimental diets: (1) cholesterol-enriched diet (rat chow) plus fermented soy product supplemented with isoflavones, (2) cholesterol-enriched diet plus unfermented placebo, (3) cholesterol-enriched diet plus placebo supplemented with isoflavones, (4) standard diet (rat chow), or (5) cholesterol-enriched diet. Soy products affected adipose tissue in a regional-specific manner and may be responsible for the observed increase in RET adipocyte area (μ2): (1) 12757.00 ± 286.25; (2) 13269.00 ± 326.87 or (3) 13050.00 ± 226.85 versus (4) 8714.92 ± 262.41 or (5) 8892.70 ± 131.79 or decrease in EPI adipocyte area (μ2): (1) 7759.00 ± 108.89 and (2) 7481.90 ± 111.21 compared with the control group (4) 8346.60 ± 158.89. The effect on epididymal adipose tissue was probably due to isoflavones. Probiotics significantly raised the plasma level of HDL cholesterol. Fermented soy product supplemented with isoflavones did not promote changes in the glucose and triglyceride plasma levels. This product may offer a new approach for improving or preventing lipid metabolism abnormalities by decreasing visceral adipocyte area, adjusting cholesterol-mediated loss of RET adipose tissue (lipoatrophy), and increasing the HDL cholesterol plasma level.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Gawad IA, El-Sayed EM, Hafez SA, El-Zeini HM, Saleh FA (2005) Int Dairy J 15:37–44
Williams RR, Hopkins PN, Hunt SC, Wu LL, Hasstedt SJ, Lalouel JM, Ash KO, Stults BM, Kuida H (1990) Arch Intern Med 150:582–588
Gordon DJ, Jl Probstfield, Garrison RJ (1989) Circulation 79:8–15
Castelli WP, Garrison RJ, Wilson PWF, Abbott RD, Kalousdian S, Kannel WB (1986) J Am Med Assoc 256:2835–2838
Lee YK, Salminem S (1995) Trends Food Sci Technol 6:241–245
Fuller R (1989) J Appl Bacteriol 66:365–378
Scheinbach S (1998) Biotechnol Adv 16(3):581–608
Liong MT (2007) Nutr Rev 65(7):316–328
Simons LA, Amansec SG, Conway P (2006) Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 16(8):531–535
Ali AA, Velasquez MT, Hansen CT, Mohamed SJ, Bathena SJ (2004) J Nutr Biochem 15:583–590
Pereira DI, Gibson GR (2002) Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 37(4):259–281
Krause BR, Hartman AD (1984) J Lipid Res 25:97–110
Farkas J, Angel A, Avigan MI (1973) J Lipid Res 14:344–356
Quintão E, Grundy SM, Ahrens EH (1971) J Lipid Res 12:233–247
Islam KK, Knight BL, Frayn KN, Patel DD, Gibbons GF (2005) Biochim Biophys Acta 1734(3):259–268
Farmakalidis E, Hathcock JN, Murphy PA (1985) Food Chem Toxicol 23:741–745
Nazz A, Yellayi S, Zakroczymski M, Bunick D, Doerge DR, Lubahn DB, Helferich WG, Cooke PS (2003) The soy isoflavone genistein decreases adipose deposition in mice. Endocrinology 144(8):3315–3320
Dieudonne MN, Leneveu MC, Giudicelli Y, Pecquery R (2004) Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 286(3):C655–661
Manzoni MSJ, Rossi EA, Carlos IZ, Vendramini RC, Duarte ACGO, Dâmaso AR (2005) Nutrition 21:1018–1024
National Research Council (1985) Guide for care and use of laboratory animals. National Academy of Sciences, Washington
Rossi EA, Vendramini RC, Carlos IZ, Ueiji IS, Squinzari MM, Silva SI Jr, Valdez GF (2000) Arq Bras Cardiol 74(3):213–216
Rossi EA, Rosier I, Damaso AR, Carlos IZ, Vendramini RC, Abdala DSP, Talarico VH, Minto DF (2004) Aliment Nutr 15(2):93–99
Rossi EA, Vendramini RC, Carlos IZ, de Oliveira MG, de Valdez GF (2003) Arch Latinoam Nutr 53(1):47–51
Hirsch J, Gallian E J (1968) Lipid Res 9:110–119
Tchkonia T, Lenburg M, Thomou T, Giorgadze M, Frampton G, Pirtskhalava T, Cartwright A, Cartwright M, Flanagam J, Karagiannides I, Gerry N, Forse RA, Tchoukalova Y, Jensen MD, Pothoulakis C, Kirkland JL (2007) Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 292(1):E298–E307
Tchkonia T, Giorgadze M, Pirtskhalava T, Thomou T, DePonte M, Koo Forse RA, Chinnappan D, Martin-Ruiz C, von Zglinicki T, Kirkland JL (2006) Diabetes 55(9):2571–2578
Pedersen SB, Borglum JD, Eriksen EF, Richelsen B (1991) Biochim Biophys Acta 1093(1):80–86
Cooke PS, Heine PA, Taylor JA, Lubahn DB (2001) Mol Cell Endocrinol 178:147–154
Haffner SM (2007) Am J Med 120 (9 Suppl 1):S10–S17
Giorgino F, Laviola L, Eriksson JW (2005) Acta Physiol Scand 183(1):13–30
Frayn KN (2002) Diabetologia 45:1201–1210
Nagasawa A, Fukui K, Kojima M, Kishida K, Maeda N, Nagaretani H, Hibuse T, Nishizawa H, Kihara S, Waki M, Takamatsu K, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y (2003) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 311:909–914
Chen JR, Chiou SF, Suetsuna K, Yang HY, Yang SC (2003) Nutrition 19:676–680
Zulet MA, Barber A, Garcin H, Higueret P, Martínez JF (1999) J Am Coll Nutr 18(1):36–42
Feoli AM, Roehrig C, Rotta LN, Kruger AH, Souza KB, Kessler AM, Renz SV, Brusque AM, Souza DO, Perry ML (2003) Nutrition 19:789–793
Calleja L, Trallero MC, Carrizona C, Méndez MT, Palacios-Alaiz E, Osada J (2000) Atherosclerosis 152:69–78
Agerholm-Larsen L, Raben A, Haulrik N, Hansen AS, Manders M, Astrup A (2000) Eur J Clin Nutr 54(4):288–297
Agerholm-Larsen L, Bell ML, Grunwald GK, Astrup A (2000) The effect of a probiotic milk product on plasma cholesterol: a meta-analysis of short-term interventions studies. Eur J Clin Nutr 54(11):856–860
Hlivak P, Odraska J, Ferencik M, Ebringer L, Jahnova E, Mikes Z (2005) Bratisl Lek Listy 106(2):67–72
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo, Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jovenasso Manzoni, M.S., Rossi, E.A., Carlos, I.Z. et al. Fermented soy product supplemented with isoflavones affects adipose tissue in a regional-specific manner and improves HDL-cholesterol in rats fed on a cholesterol-enriched diet. Eur Food Res Technol 227, 1591–1597 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-008-0883-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-008-0883-1