Abstract.
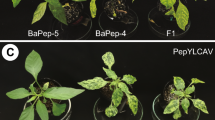
Resistance against both Potato virus Y (PVY) and Tobacco etch virus (TEV) was identified in the wild tomato relative Lycopersicon hirsutum PI247087. Analysis of the segregation ratio in F2/F3 and BC1 interspecific progenies indicated that a single recessive gene, or two very tightly linked recessive loci, are involved in resistance to both potyviruses. This locus was named pot-1. Using amplified fragment length polymorphism markers and a set of L. hirsutum introgression lines, pot-1 was mapped to the short arm of tomato chromosome 3, in the vicinity of the recessive py-1 locus for resistance to corky root rot. Because of the occurrence of phenotypically similar genes in pepper (Capsicum spp.), the comparative genetics of resistance to potyviruses between tomato and pepper was investigated. Unlike most of the comparative genetic studies on resistance genes, pot-1 was tightly flanked by the same restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) markers than the pvr2/pvr5 locus for resistance to PVY and TEV from pepper. These results may indicate that recessive resistance genes against potyviruses evolve less rapidly than the majority of the dominant genes cloned so far, and consequently may belong to a different family of resistance genes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parrella, .G., Ruffel, .S., Moretti, .A. et al. Recessive resistance genes against potyviruses are localized in colinear genomic regions of the tomato (Lycopersicon spp.) and pepper (Capsicum spp.) genomes. Theor Appl Genet 105, 855–861 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-002-1005-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-002-1005-2