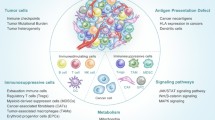
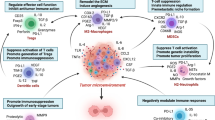
Abstract
Tumor immune escape and the initiation of metastasis are critical steps in malignant progression of tumors and have been implicated in the failure of some clinical cancer immunotherapy. Tumors develop numerous strategies to escape immune surveillance or metastasize: Tumors not only modulate the recruitment and expansion of immunosuppressive cell populations to develop the tumor microenvironment or pre-metastatic niche but also switch the phenotype and function of normal immune cells from a potentially tumor-reactive state to a tumor-promoting state. Immunosuppressive cells facilitate tumor immune escape by inhibiting antitumor immune responses and furthermore promote tumor metastasis by inducing immunosuppression, promoting tumor cell invasion and intravasation, establishing a pre-metastatic niche, facilitating epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and inducing angiogenesis at primary tumor or metastatic sites. Numerous translational studies indicate that it is possible to inhibit tumor immune escape and prevent tumor metastasis by blocking immunosuppressive cells and eliminating immunosuppressive mechanisms that are induced by either immunosuppressive cells or tumor cells. Furthermore, many clinical trials targeting immunosuppressive cells have also achieved good outcome. In this review, we focus on the underlying mechanisms of immunosuppressive cells in promoting tumor immune escape and metastasis, discuss our current understanding of the interactions between immunosuppressive cells and tumor cells in the tumor microenvironment, and suggest future research directions as well as potential clinical strategies in cancer immunotherapy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gajewski TF, Schreiber H, Fu YX (2013) Innate and adaptive immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. Nat Immunol 14:1014–1022
Kitamura T, Qian BZ, Pollard JW (2015) Immune cell promotion of metastasis. Nat Rev Immunol 15:73–86
McAllister SS, Weinberg RA (2014) The tumour-induced systemic environment as a critical regulator of cancer progression and metastasis. Nat Cell Biol 16:717–727
Quail DF, Joyce JA (2013) Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med 19:1423–1437
Vesely MD, Kershaw MH, Schreiber RD, Smyth MJ (2011) Natural innate and adaptive immunity to cancer. Annu Rev Immunol 29:235–271
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674
Gomez Perdiguero E, Geissmann F (2014) Cancer immunology. Identifying the infiltrators. Science 344:801–802
Kim R, Emi M, Tanabe K (2007) Cancer immunoediting from immune surveillance to immune escape. Immunology 121:1–14
Schreiber RD, Old LJ, Smyth MJ (2011) Cancer immunoediting: integrating immunity’s roles in cancer suppression and promotion. Science 331:1565–1570
Vinay DS, Ryan EP, Pawelec G, Talib WH, Stagg J, Elkord E, Lichtor T, Decker WK, Whelan RL, Kumara HM et al. (2015) Immune evasion in cancer: mechanistic basis and therapeutic strategies. Semin Cancer Biol DOI 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.03.004.
Ansell SM, Lesokhin AM, Borrello I, Halwani A, Scott EC, Gutierrez M, Schuster SJ, Millenson MM, Cattry D, Freeman GJ et al (2015) PD-1 blockade with nivolumab in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med 372:311–319
Mittal D, Gubin MM, Schreiber RD, Smyth MJ (2014) New insights into cancer immunoediting and its three component phases—elimination, equilibrium and escape. Curr Opin Immunol 27:16–25
Colonna M (2013) Immunology: an innate regulatory cell. Nature 498:42–43
Wolf D, Wolf AM (2015) CCR 20th Anniversary Commentary: from regulatory T cells to checkpoint monoclonal antibodies-immuno-oncology advances clinical cancer research. Clin Cancer Res 21:2657–2659
von Boehmer H, Daniel C (2013) Therapeutic opportunities for manipulating T(Reg) cells in autoimmunity and cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12:51–63
Facciabene A, Peng X, Hagemann IS, Balint K, Barchetti A, Wang LP, Gimotty PA, Gilks CB, Lal P, Zhang L et al (2011) Tumour hypoxia promotes tolerance and angiogenesis via CCL28 and T(reg) cells. Nature 475:226–230
Han Y, Yang Y, Chen Z, Jiang Z, Gu Y, Liu Y, Xu S, Lin C, Pan Z, Zhou W et al (2014) Human hepatocellular carcinoma-infiltrating CD4(+)CD69(+)Foxp3(−) regulatory T cell suppresses T cell response via membrane-bound TGF-beta1. J Mol Med (Berl) 92:539–550
Thevenot PT, Sierra RA, Raber PL, Al-Khami AA, Trillo-Tinoco J, Zarreii P, Ochoa AC, Cui Y, Del Valle L, Rodriguez PC (2014) The stress-response sensor chop regulates the function and accumulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in tumors. Immunity 41:389–401
Highfill SL, Cui Y, Giles AJ, Smith JP, Zhang H, Morse E, Kaplan RN, Mackall CL (2014) Disruption of CXCR2-mediated MDSC tumor trafficking enhances anti-PD1 efficacy. Sci Transl Med 6:237ra267
Parker KH, Sinha P, Horn LA, Clements VK, Yang H, Li J, Tracey KJ, Ostrand-Rosenberg S (2014) HMGB1 enhances immune suppression by facilitating the differentiation and suppressive activity of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Cancer Res 74:5723–5733
Qian BZ, Pollard JW (2010) Macrophage diversity enhances tumor progression and metastasis. Cell 141:39–51
Noy R, Pollard JW (2014) Tumor-associated macrophages: from mechanisms to therapy. Immunity 41:49–61
Ruffell B, Chang-Strachan D, Chan V, Rosenbusch A, Ho CM, Pryer N, Daniel D, Hwang ES, Rugo HS, Coussens LM (2014) Macrophage IL-10 blocks CD8+ T cell-dependent responses to chemotherapy by suppressing IL-12 expression in intratumoral dendritic cells. Cancer Cell 26:623–637
Liu Y, Cao X (2015) Intratumoral dendritic cells in the anti-tumor immune response. Cell Mol Immunol 12:387–390
Franklin RA, Liao W, Sarkar A, Kim MV, Bivona MR, Liu K, Pamer EG, Li MO (2014) The cellular and molecular origin of tumor-associated macrophages. Science 344:921–925
Liu Y, Cao X (2015) The origin and function of tumor-associated macrophages. Cell Mol Immunol 12:1–4
Alderton GK (2014) Tumour immunology: turning macrophages on, off and on again. Nat Rev Immunol 14:136–137
Steidl C, Lee T, Shah SP, Farinha P, Han G, Nayar T, Delaney A, Jones SJ, Iqbal J, Weisenburger DD et al (2010) Tumor-associated macrophages and survival in classic Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med 362:875–885
Han Y, Chen Z, Yang Y, Jiang Z, Gu Y, Liu Y, Lin C, Pan Z, Yu Y, Jiang M et al (2014) Human CD14+ CTLA-4+ regulatory dendritic cells suppress T-cell response by cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4-dependent IL-10 and indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase production in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 59:567–579
Qian C, Qian L, Yu Y, An H, Guo Z, Han Y, Chen Y, Bai Y, Wang Q, Cao X (2013) Fas signal promotes the immunosuppressive function of regulatory dendritic cells via the ERK/beta-catenin pathway. J Biol Chem 288:27825–27835
Wu C, Zhang Y, Jiang Y, Wang Q, Long Y, Wang C, Cao X, Chen G (2013) Apoptotic cell administration enhances pancreatic islet engraftment by induction of regulatory T cells and tolerogenic dendritic cells. Cell Mol Immunol 10:393–402
Marvel D, Gabrilovich DI (2015) Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment: expect the unexpected. J Clin Invest DOI 10.1172/JCI80005: 1–9.
Upadhyay R, Hammerich L, Peng P, Brown B, Merad M, Brody JD (2015) Lymphoma: immune evasion strategies. Cancers (Basel) 7:736–762
Shields JD, Kourtis IC, Tomei AA, Roberts JM, Swartz MA (2010) Induction of lymphoidlike stroma and immune escape by tumors that express the chemokine CCL21. Science 328:749–752
Gabrilovich DI, Ostrand-Rosenberg S, Bronte V (2012) Coordinated regulation of myeloid cells by tumours. Nat Rev Immunol 12:253–268
Strauss L, Sangaletti S, Consonni FM, Szebeni G, Morlacchi S, Totaro MG, Porta C, Anselmo A, Tartari S, Doni A et al (2015) RORC1 regulates tumor-promoting “emergency” granulo-monocytopoiesis. Cancer Cell 28:253–269
Torroella-Kouri M, Silvera R, Rodriguez D, Caso R, Shatry A, Opiela S, Ilkovitch D, Schwendener RA, Iragavarapu-Charyulu V, Cardentey Y et al (2009) Identification of a subpopulation of macrophages in mammary tumor-bearing mice that are neither M1 nor M2 and are less differentiated. Cancer Res 69:4800–4809
Galli SJ, Borregaard N, Wynn TA (2011) Phenotypic and functional plasticity of cells of innate immunity: macrophages, mast cells and neutrophils. Nat Immunol 12:1035–1044
Fridlender ZG, Sun J, Kim S, Kapoor V, Cheng G, Ling L, Worthen GS, Albelda SM (2009) Polarization of tumor-associated neutrophil phenotype by TGF-beta: “N1” versus “N2” TAN. Cancer Cell 16:183–194
Flavell RA, Sanjabi S, Wrzesinski SH, Licona-Limon P (2010) The polarization of immune cells in the tumour environment by TGFbeta. Nat Rev Immunol 10:554–567
Dumitriu IE, Dunbar DR, Howie SE, Sethi T, Gregory CD (2009) Human dendritic cells produce TGF-beta 1 under the influence of lung carcinoma cells and prime the differentiation of CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol 182:2795–2807
Norian LA, Rodriguez PC, O’Mara LA, Zabaleta J, Ochoa AC, Cella M, Allen PM (2009) Tumor-infiltrating regulatory dendritic cells inhibit CD8+ T cell function via L-arginine metabolism. Cancer Res 69:3086–3094
Papaspyridonos M, Matei I, Huang Y, do Rosario Andre M, Brazier-Mitouart H, Waite JC, Chan AS, Kalter J, Ramos I, Wu Q et al (2015) Id1 suppresses anti-tumour immune responses and promotes tumour progression by impairing myeloid cell maturation. Nat Commun 6:6840
Sato K (2014) Helper T cell diversity and plasticity. Circ J 78:2843–2844
Yaguchi T, Sumimoto H, Kudo-Saito C, Tsukamoto N, Ueda R, Iwata-Kajihara T, Nishio H, Kawamura N, Kawakami Y (2011) The mechanisms of cancer immunoescape and development of overcoming strategies. Int J Hematol 93:294–300
Smith HA, Kang Y (2013) The metastasis-promoting roles of tumor-associated immune cells. J Mol Med (Berl) 91:411–429
Coffelt SB, Kersten K, Doornebal CW, Weiden J, Vrijland K, Hau CS, Verstegen NJ, Ciampricotti M, Hawinkels LJ, Jonkers J et al (2015) IL-17-producing gammadelta T cells and neutrophils conspire to promote breast cancer metastasis. Nature 522:345–348
Chung AS, Wu X, Zhuang G, Ngu H, Kasman I, Zhang J, Vernes JM, Jiang Z, Meng YG, Peale FV et al (2013) An interleukin-17-mediated paracrine network promotes tumor resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nat Med 19:1114–1123
Olkhanud PB, Damdinsuren B, Bodogai M, Gress RE, Sen R, Wejksza K, Malchinkhuu E, Wersto RP, Biragyn A (2011) Tumor-evoked regulatory B cells promote breast cancer metastasis by converting resting CD4(+) T cells to T-regulatory cells. Cancer Res 71:3505–3515
Lee HE, Park DJ, Kim WH, Kim HH, Lee HS (2011) High FOXP3+ regulatory T-cell density in the sentinel lymph node is associated with downstream non-sentinel lymph-node metastasis in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer 105:413–419
Ogawa F, Amano H, Eshima K, Ito Y, Matsui Y, Hosono K, Kitasato H, Iyoda A, Iwabuchi K, Kumagai Y et al (2014) Prostanoid induces premetastatic niche in regional lymph nodes. J Clin Invest 124:4882–4894
Yang P, Li QJ, Feng Y, Zhang Y, Markowitz GJ, Ning S, Deng Y, Zhao J, Jiang S, Yuan Y et al (2012) TGF-beta-miR-34a-CCL22 signaling-induced Treg cell recruitment promotes venous metastases of HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 22:291–303
Dalotto-Moreno T, Croci DO, Cerliani JP, Martinez-Allo VC, Dergan-Dylon S, Mendez-Huergo SP, Stupirski JC, Mazal D, Osinaga E, Toscano MA et al (2013) Targeting galectin-1 overcomes breast cancer-associated immunosuppression and prevents metastatic disease. Cancer Res 73:1107–1117
Zou W (2006) Regulatory T cells, tumour immunity and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol 6:295–307
Sawant A, Hensel JA, Chanda D, Harris BA, Siegal GP, Maheshwari A, Ponnazhagan S (2012) Depletion of plasmacytoid dendritic cells inhibits tumor growth and prevents bone metastasis of breast cancer cells. J Immunol 189:4258–4265
Zhou ZN, Sharma VP, Beaty BT, Roh-Johnson M, Peterson EA, Van Rooijen N, Kenny PA, Wiley HS, Condeelis JS, Segall JE (2014) Autocrine HBEGF expression promotes breast cancer intravasation, metastasis and macrophage-independent invasion in vivo. Oncogene 33:3784–3793
Hernandez L, Smirnova T, Kedrin D, Wyckoff J, Zhu L, Stanley ER, Cox D, Muller WJ, Pollard JW, Van Rooijen N et al (2009) The EGF/CSF-1 paracrine invasion loop can be triggered by heregulin beta1 and CXCL12. Cancer Res 69:3221–3227
Valastyan S, Weinberg RA (2011) Tumor metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell 147:275–292
Alizadeh D, Trad M, Hanke NT, Larmonier CB, Janikashvili N, Bonnotte B, Katsanis E, Larmonier N (2014) Doxorubicin eliminates myeloid-derived suppressor cells and enhances the efficacy of adoptive T-cell transfer in breast cancer. Cancer Res 74:104–118
DeNardo DG, Barreto JB, Andreu P, Vasquez L, Tawfik D, Kolhatkar N, Coussens LM (2009) CD4(+) T cells regulate pulmonary metastasis of mammary carcinomas by enhancing protumor properties of macrophages. Cancer Cell 16:91–102
Liu RY, Zeng Y, Lei Z, Wang L, Yang H, Liu Z, Zhao J, Zhang HT (2014) JAK/STAT3 signaling is required for TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells. Int J Oncol 44:1643–1651
Mazzieri R, Pucci F, Moi D, Zonari E, Ranghetti A, Berti A, Politi LS, Gentner B, Brown JL, Naldini L et al (2011) Targeting the ANG2/TIE2 axis inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by impairing angiogenesis and disabling rebounds of proangiogenic myeloid cells. Cancer Cell 19:512–526
Almand B, Clark JI, Nikitina E, van Beynen J, English NR, Knight SC, Carbone DP, Gabrilovich DI (2001) Increased production of immature myeloid cells in cancer patients: a mechanism of immunosuppression in cancer. J Immunol 166:678–689
Diaz-Montero CM, Salem ML, Nishimura MI, Garrett-Mayer E, Cole DJ, Montero AJ (2009) Increased circulating myeloid-derived suppressor cells correlate with clinical cancer stage, metastatic tumor burden, and doxorubicin-cyclophosphamide chemotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother 58:49–59
Bates GJ, Fox SB, Han C, Leek RD, Garcia JF, Harris AL, Banham AH (2006) Quantification of regulatory T cells enables the identification of high-risk breast cancer patients and those at risk of late relapse. J Clin Oncol 24:5373–5380
Kim SJ, Ha GH, Kim SH, Kang CD (2014) Combination of cancer immunotherapy with clinically available drugs that can block immunosuppressive cells. Immunol Invest 43:517–534
Castelli C, Triebel F, Rivoltini L, Camisaschi C (2014) Lymphocyte activation gene-3 (LAG-3, CD223) in plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs): a molecular target for the restoration of active antitumor immunity. Oncoimmunology 3, e967146
Goldberg MV, Drake CG (2011) LAG-3 in cancer immunotherapy. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 344:269–278
Japp AS, Kursunel MA, Meier S, Malzer JN, Li X, Rahman NA, Jekabsons W, Krause H, Magheli A, Klopf C et al. (2015) Dysfunction of PSA-specific CD8 T cells in prostate cancer patients correlates with CD38 and Tim-3 expression. Cancer Immunol Immunother DOI 10.1007/s00262-015-1752-y
Le Mercier I, Chen W, Lines JL, Day M, Li J, Sergent P, Noelle RJ, Wang L (2014) VISTA regulates the development of protective antitumor immunity. Cancer Res 74:1933–1944
Gertner-Dardenne J, Fauriat C, Orlanducci F, Thibult ML, Pastor S, Fitzgibbon J, Bouabdallah R, Xerri L, Olive D (2013) The co-receptor BTLA negatively regulates human Vgamma9Vdelta2 T-cell proliferation: a potential way of immune escape for lymphoma cells. Blood 122:922–931
Sharma P, Allison JP (2015) The future of immune checkpoint therapy. Science 348:56–61
Korman AJ, Peggs KS, Allison JP (2006) Checkpoint blockade in cancer immunotherapy. Adv Immunol 90:297–339
Brahmer J, Reckamp KL, Baas P, Crino L, Eberhardt WE, Poddubskaya E, Antonia S, Pluzanski A, Vokes EE, Holgado E et al (2015) Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced squamous-cell non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 373:123–135
Hodi FS, O’Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW, Sosman JA, Haanen JB, Gonzalez R, Robert C, Schadendorf D, Hassel JC et al (2010) Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med 363:711–723
Wolchok JD, Kluger H, Callahan MK, Postow MA, Rizvi NA, Lesokhin AM, Segal NH, Ariyan CE, Gordon RA, Reed K et al (2013) Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med 369:122–133
Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Carvajal RD, Sosman JA, Atkins MB et al (2012) Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med 366:2443–2454
Le Mercier I, Lines JL, Noelle RJ (2015) Beyond CTLA-4 and PD-1, the generation Z of negative checkpoint regulators. Front Immunol 6:418
Zhou Q, Munger ME, Veenstra RG, Weigel BJ, Hirashima M, Munn DH, Murphy WJ, Azuma M, Anderson AC, Kuchroo VK et al (2011) Coexpression of Tim-3 and PD-1 identifies a CD8+ T-cell exhaustion phenotype in mice with disseminated acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood 117:4501–4510
Sakuishi K, Ngiow SF, Sullivan JM, Teng MW, Kuchroo VK, Smyth MJ, Anderson AC (2013) TIM3FOXP3 regulatory T cells are tissue-specific promoters of T-cell dysfunction in cancer. Oncoimmunology 2, e23849
Derre L, Rivals JP, Jandus C, Pastor S, Rimoldi D, Romero P, Michielin O, Olive D, Speiser DE (2010) BTLA mediates inhibition of human tumor-specific CD8+ T cells that can be partially reversed by vaccination. J Clin Invest 120:157–167
Woo SRTM, Goldberg MV, Bankoti J, Selby M, Nirschl CJ, Bettini ML, Gravano DM, Vogel P, Liu CL, Tangsombatvisit S et al (2012) Immune inhibitory molecules LAG-3 and PD-1 synergistically regulate T-cell function to promote tumoral immune escape. Cancer Res 72:917–927
Qin H, Lerman B, Sakamaki I, Wei G, Cha SC, Rao SS, Qian J, Hailemichael Y, Nurieva R, Dwyer KC et al (2014) Generation of a new therapeutic peptide that depletes myeloid-derived suppressor cells in tumor-bearing mice. Nat Med 20:676–681
Ali K, Soond DR, Pineiro R, Hagemann T, Pearce W, Lim EL, Bouabe H, Scudamore CL, Hancox T, Maecker H et al (2014) Inactivation of PI(3)K p110delta breaks regulatory T-cell-mediated immune tolerance to cancer. Nature 510:407–411
Killock D (2014) Immunotherapy: PI3Kdelta inhibition lifts the breaks on antitumour immunity. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 11:442
Dimeloe S, Frick C, Fischer M, Gubser PM, Razik L, Bantug GR, Ravon M, Langenkamp A, Hess C (2014) Human regulatory T cells lack the cyclophosphamide-extruding transporter ABCB1 and are more susceptible to cyclophosphamide-induced apoptosis. Eur J Immunol 44:3614–3620
Ni X, Langridge T, Duvic M (2015) Depletion of regulatory T cells by targeting CC chemokine receptor type 4 with mogamulizumab. Oncoimmunology 4, e1011524
Twyman-Saint Victor C, Rech AJ, Maity A, Rengan R, Pauken KE, Stelekati E, Benci JL, Xu B, Dada H, Odorizzi PM et al (2015) Radiation and dual checkpoint blockade activate non-redundant immune mechanisms in cancer. Nature 520:373–377
Rech AJ, Mick R, Martin S, Recio A, Aqui NA, Powell DJ Jr, Colligon TA, Trosko JA, Leinbach LI, Pletcher CH et al (2012) CD25 blockade depletes and selectively reprograms regulatory T cells in concert with immunotherapy in cancer patients. Sci Transl Med 4:134ra162
De Palma M, Lewis CE (2013) Macrophage regulation of tumor responses to anticancer therapies. Cancer Cell 23:277–286
Fang H, Declerck YA (2013) Targeting the tumor microenvironment: from understanding pathways to effective clinical trials. Cancer Res 73:4965–4977
Restifo NP, Dudley ME, Rosenberg SA (2012) Adoptive immunotherapy for cancer: harnessing the T cell response. Nat Rev Immunol 12:269–281
Vanneman M, Dranoff G (2012) Combining immunotherapy and targeted therapies in cancer treatment. Nat Rev Cancer 12:237–251
Bonapace L, Coissieux MM, Wyckoff J, Mertz KD, Varga Z, Junt T, Bentires-Alj M (2014) Cessation of CCL2 inhibition accelerates breast cancer metastasis by promoting angiogenesis. Nature 515:130–133
Qian BZ, Li J, Zhang H, Kitamura T, Zhang J, Campion LR, Kaiser EA, Snyder LA, Pollard JW (2011) CCL2 recruits inflammatory monocytes to facilitate breast-tumour metastasis. Nature 475:222–225
Spranger S, Bao R, Gajewski TF (2015) Melanoma-intrinsic beta-catenin signalling prevents anti-tumour immunity. Nature 523:231–235
Kohrt HE, Colevas AD, Houot R, Weiskopf K, Goldstein MJ, Lund P, Mueller A, Sagiv-Barfi I, Marabelle A, Lira R et al (2014) Targeting CD137 enhances the efficacy of cetuximab. J Clin Invest 124:2668–2682
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from National Key Basic Research Program of China (2014CB542100, 2011CB965202).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Cao, X. Immunosuppressive cells in tumor immune escape and metastasis. J Mol Med 94, 509–522 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-015-1376-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-015-1376-x