Abstract.
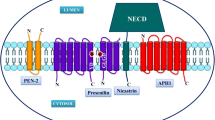
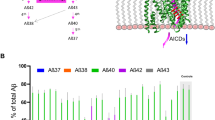
Presenilin-2 (PS2) is one of three genes [amyloid precursor protein (APP), presenilin-1 (PS1) and PS2] shown to cause familial Alzheimer's disease (FAD), and is highly homologous to PS1. Currently demonstrated functions of PS2 include interactions with APP and Aβ, and participation in apoptotic pathways. PS2 FAD mutations influence APP processing in a manner predicted to promote amyloid formation and also enhance the proapoptotic effect of wild-type PS2. Other possible functions of PS2 are related to its homology to Notch pathway genes in Caenorhabditis elegans, suggesting it may have a developmental role. PS2-associated AD is the most reminiscent of the sporadic form of the disease in terms of older age of onset and longer disease duration. Since PS2 mutations are incompletely penetrant and age of onset in carriers is highly variable (40 – 88 years), elucidation of PS2 mechanisms may reveal factors which modify AD and are therapeutically relevant to sporadic AD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Renbaum, P., Levy-Lahad, E. Monogenic determinants of familial Alzheimer's disease: presenilin-2 mutations. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 54, 910–919 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s000180050220
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s000180050220