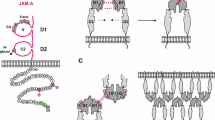
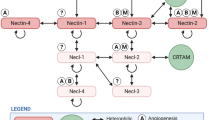
Abstract
Cell–cell adhesive processes are central to the physiology of multicellular organisms. A number of cell surface molecules contribute to cell–cell adhesion, and the dysfunction of adhesive processes underlies numerous developmental defects and inherited diseases. The nectins, a family of four immunoglobulin superfamily members (nectin-1 to -4), interact through their extracellular domains to support cell–cell adhesion. While both homophilic and heterophilic interactions among the nectins are implicated in cell–cell adhesion, cell-based and biochemical studies suggest heterophilic interactions are stronger than homophilic interactions and control a range of physiological processes. In addition to interactions within the nectin family, heterophilic associations with nectin-like molecules, immune receptors, and viral glycoproteins support a wide range of biological functions, including immune modulation, cancer progression, host-pathogen interactions and immune evasion. We review current structural and molecular knowledge of nectin recognition processes, with a focus on the biochemical and biophysical determinants of affinity and selectivity that drive distinct nectin associations. These proteins and interactions are discussed as potential targets for immunotherapy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yap AS, Brieher WM, Gumbiner BM (1997) Molecular and functional analysis of cadherin-based adherens junctions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 13:119–146
Takai Y, Ikeda W, Ogita H, Rikitake Y (2008) The immunoglobulin-like cell adhesion molecule nectin and its associated protein afadin. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 24:309–342
Takai Y, Miyoshi J, Ikeda W, Ogita H (2008) Nectins and nectin-like molecules: roles in contact inhibition of cell movement and proliferation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9(8):603–615
Harris TJ, Tepass U (2010) Adherens junctions: from molecules to morphogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11(7):502–514
Sakisaka T, Takai Y (2004) Biology and pathology of nectins and nectin-like molecules. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16(5):513–521
Rikitake Y, Mandai K, Takai Y (2012) The role of nectins in different types of cell–cell adhesion. J Cell Sci 125:3713–3722
Shimono Y, Rikitake Y, Mandai K, Mori M, Takai Y (2012) Immunoglobulin superfamily receptors and adherens junctions. Subcell Biochem 60:137–170
Chothia C, Jones EY (1997) The molecular structure of cell adhesion molecules. Annu Rev Biochem 66:823–862
Taylor ME, Drickamer K (2007) Paradigms for glycan-binding receptors in cell adhesion. Curr Opin Cell Biol 19(5):572–577
Brasch J, Harrison OJ, Honig B, Shapiro L (2012) Thinking outside the cell: how cadherins drive adhesion. Trends Cell Biol 22(6):299–310
Patel SD, Chen CP, Bahna F, Honig B, Shapiro L (2003) Cadherin-mediated cell–cell adhesion: sticking together as a family. Curr Opin Struct Biol 13(6):690–698
Halbleib JM, Nelson WJ (2006) Cadherins in development: cell adhesion, sorting, and tissue morphogenesis. Genes Dev 20(23):3199–3214
Takai Y, Nakanishi H (2003) Nectin and afadin: novel organizers of intercellular junctions. J Cell Sci 116:17–27
Shapiro L, Weis WI (2009) Structure and biochemistry of cadherins and catenins. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 1(3):a003053
Shimoyama Y, Tsujimoto G, Kitajima M, Natori M (2000) Identification of three human type-II classic cadherins and frequent heterophilic interactions between different subclasses of type-II classic cadherins. Biochem J 349:159–167
Katsamba P, Carroll K, Ahlsen G, Bahna F, Vendome J, Posy S, Rajebhosale M, Price S, Jessell TM, Ben-Shaul A et al (2009) Linking molecular affinity and cellular specificity in cadherin-mediated adhesion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(28):11594–11599
Straub BK, Rickelt S, Zimbelmann R, Grund C, Kuhn C, Iken M, Ott M, Schirmacher P, Franke WW (2011) E-N-cadherin heterodimers define novel adherens junctions connecting endoderm-derived cells. J Cell Biol 195(5):873–887
Mizoguchi A, Nakanishi H, Kimura K, Matsubara K, Ozaki-Kuroda K, Katata T, Honda T, Kiyohara Y, Heo K, Higashi M et al (2002) Nectin: an adhesion molecule involved in formation of synapses. J Cell Biol 156(3):555–565
Yagi T, Takeichi M (2000) Cadherin superfamily genes: functions, genomic organization, and neurologic diversity. Genes Dev 14(10):1169–1180
Chan CJ, Andrews DM, Smyth MJ (2012) Receptors that interact with nectin and nectin-like proteins in the immunosurveillance and immunotherapy of cancer. Curr Opin Immunol 24(2):246–251
Fuchs A, Colonna M (2006) The role of NK cell recognition of nectin and nectin-like proteins in tumor immunosurveillance. Semin Cancer Biol 16(5):359–366
Delpeut S, Noyce RS, Siu RW, Richardson CD (2012) Host factors and measles virus replication. Curr Opin Virol 2(6):773–783
Noyce RS, Richardson CD (2012) Nectin 4 is the epithelial cell receptor for measles virus. Trends Microbiol 20(9):429–439
Geraghty RJ, Krummenacher C, Cohen GH, Eisenberg RJ, Spear PG (1998) Entry of alphaherpesviruses mediated by poliovirus receptor-related protein 1 and poliovirus receptor. Science 280(5369):1618–1620
Mandai K, Nakanishi H, Satoh A, Obaishi H, Wada M, Nishioka H, Itoh M, Mizoguchi A, Aoki T, Fujimoto T et al (1997) Afadin: a novel actin filament-binding protein with one PDZ domain localized at cadherin-based cell-to-cell adherens junction. J Cell Biol 139(2):517–528
Rubinstein R, Ramagopal UA, Nathenson SG, Almo SC, Fiser A (2013) Functional classification of immune regulatory proteins. Structure 21(5):766–776
Biederer T (2006) Bioinformatic characterization of the SynCAM family of immunoglobulin-like domain-containing adhesion molecules. Genomics 87(1):139–150
Okabe N, Shimizu K, Ozaki-Kuroda K, Nakanishi H, Morimoto K, Takeuchi M, Katsumaru H, Murakami F, Takai Y (2004) Contacts between the commissural axons and the floor plate cells are mediated by nectins. Dev Biol 273(2):244–256
Togashi H, Kominami K, Waseda M, Komura H, Miyoshi J, Takeichi M, Takai Y (2011) Nectins establish a checkerboard-like cellular pattern in the auditory epithelium. Science 333(6046):1144–1147
Inagaki M, Irie K, Ishizaki H, Tanaka-Okamoto M, Miyoshi J, Takai Y (2006) Role of cell adhesion molecule nectin-3 in spermatid development. Genes Cells 11(9):1125–1132
Tachibana K, Nakanishi H, Mandai K, Ozaki K, Ikeda W, Yamamoto Y, Nagafuchi A, Tsukita S, Takai Y (2000) Two cell adhesion molecules, nectin and cadherin, interact through their cytoplasmic domain-associated proteins. J Cell Biol 150(5):1161–1176
Ikeda W, Nakanishi H, Miyoshi J, Mandai K, Ishizaki H, Tanaka M, Togawa A, Takahashi K, Nishioka H, Yoshida H et al (1999) Afadin: a key molecule essential for structural organization of cell–cell junctions of polarized epithelia during embryogenesis. J Cell Biol 146(5):1117–1132
Tanaka-Okamoto M, Hori K, Ishizaki H, Itoh Y, Onishi S, Yonemura S, Takai Y, Miyoshi J (2011) Involvement of afadin in barrier function and homeostasis of mouse intestinal epithelia. J Cell Sci 124:2231–2240
Satoh-Horikawa K, Nakanishi H, Takahashi K, Miyahara M, Nishimura M, Tachibana K, Mizoguchi A, Takai Y (2000) Nectin-3, a new member of immunoglobulin-like cell adhesion molecules that shows homophilic and heterophilic cell–cell adhesion activities. J Biol Chem 275(14):10291–10299
Aoki J, Koike S, Asou H, Ise I, Suwa H, Tanaka T, Miyasaka M, Nomoto A (1997) Mouse homolog of poliovirus receptor-related gene 2 product, mPRR2, mediates homophilic cell aggregation. Exp Cell Res 235(2):374–384
Ozaki-Kuroda K, Nakanishi H, Ohta H, Tanaka H, Kurihara H, Mueller S, Irie K, Ikeda W, Sakai T, Wimmer E et al (2002) Nectin couples cell–cell adhesion and the actin scaffold at heterotypic testicular junctions. Curr Biol 12(13):1145–1150
Bouchard MJ, Dong Y, McDermott BM Jr, Lam DH, Brown KR, Shelanski M, Bellvé AR, Racaniello VR (2000) Defects in nuclear and cytoskeletal morphology and mitochondrial localization in spermatozoa of mice lacking nectin-2, a component of cell–cell adherens junctions. Mol Cell Biol 20(8):2865–2873
Inagaki M, Irie K, Ishizaki H, Tanaka-Okamoto M, Morimoto K, Inoue E, Ohtsuka T, Miyoshi J, Takai Y (2005) Roles of cell-adhesion molecules nectin 1 and nectin 3 in ciliary body development. Development 132(7):1525–1537
Yoshida T, Miyoshi J, Takai Y, Thesleff I (2010) Cooperation of nectin-1 and nectin-3 is required for normal ameloblast function and crown shape development in mouse teeth. Dev Dyn 239(10):2558–2569
Morita H, Nandadasa S, Yamamoto TS, Terasaka-Iioka C, Wylie C, Ueno N (2010) Nectin-2 and N-cadherin interact through extracellular domains and induce apical accumulation of F-actin in apical constriction of Xenopus neural tube morphogenesis. Development 137(8):1315–1325
Harrison OJ, Vendome J, Brasch J, Jin X, Hong S, Katsamba PS, Ahlsen G, Troyanovsky RB, Troyanovsky SM, Honig B, Shapiro L (2012) Nectin ectodomain structures reveal a canonical adhesive interface. Nat Struct Mol Biol 19(9):906–915
Samanta D, Ramagopal UA, Rubinstein R, Vigdorovich V, Nathenson SG, Almo SC (2012) Structure of Nectin-2 reveals determinants of homophilic and heterophilic interactions that control cell–cell adhesion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(37):14836–14840
Narita H, Yamamoto Y, Suzuki M, Miyazaki N, Yoshida A, Kawai K, Iwasaki K, Nakagawa A, Takai Y et al (2011) Crystal Structure of the cis-Dimer of Nectin-1: implications for the architecture of cell–cell junctions. J Biol Chem 286(14):12659–12669
Reymond N, Fabre S, Lecocq E, Adelaïde J, Dubreuil P, Lopez M (2001) Nectin4/PRR4, a new afadin-associated member of the nectin family that trans-interacts with nectin1/PRR1 through V domain interaction. J Biol Chem 276(46):43205–43215
Momose Y, Honda T, Inagaki M, Shimizu K, Irie K, Nakanishi H, Takai Y (2002) Role of the second immunoglobulin-like loop of nectin in cell–cell adhesion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 293(1):45–49
Yasumi M, Shimizu K, Honda T, Takeuchi M, Takai Y (2003) Role of each immunoglobulin-like loop of nectin for its cell–cell adhesion activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 302(1):61–66
Miyahara M, Nakanishi H, Takahashi K, Satoh-Horikawa K, Tachibana K, Takai Y (2000) Interaction of nectin with afadin is necessary for its clustering at cell–cell contact sites but not for its cis dimerization or trans interaction. J Biol Chem 275(1):613–618
Chan CJ, Martinet L, Gilfillan S, Souza-Fonseca-Guimaraes F, Chow MT, Town L, Ritchie DS, Colonna M, Andrews DM, Smyth MJ (2014) The receptors CD96 and CD226 oppose each other in the regulation of natural killer cell functions. Nat Immunol 15(5):431–438
Seth S, Maier MK, Qiu Q, Ravens I, Kremmer E, Förster R, Bernhardt G (2007) The murine pan T cell marker CD96 is an adhesion receptor for CD155 and nectin-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 364(4):959–965
Bottino C, Castriconi R, Pende D, Rivera P, Nanni M, Carnemolla B, Cantoni C, Grassi J, Marcenaro S, Reymond N et al (2003) Identification of PVR (CD155) and Nectin-2 (CD112) as cell surface ligands for the human DNAM-1 (CD226) activating molecule. J Exp Med 198(4):557–567
Yu X, Harden K, Gonzalez LC, Francesco M, Chiang E, Irving B, Tom I, Ivelja S, Refino CJ, Clark H et al (2009) The surface protein TIGIT suppresses T cell activation by promoting the generation of mature immunoregulatory dendritic cells. Nat Immunol 10(1):48–57
Pende D, Bottino C, Castriconi R, Cantoni C, Marcenaro S, Rivera P, Spaggiari GM, Dondero A, Carnemolla B, Reymond N et al (2005) PVR (CD155) and Nectin-2 (CD112) as ligands of the human DNAM-1 (CD226) activating receptor: involvement in tumor cell lysis. Mol Immunol 42(4):463–469
Tahara-Hanaoka S, Shibuya K, Onoda Y, Zhang H, Yamazaki S, Miyamoto A, Honda S, Lanier LL, Shibuya A (2004) Functional characterization of DNAM-1 (CD226) interaction with its ligands PVR (CD155) and nectin-2 (PRR-2/CD112). Int Immunol 16(4):533–538
Stanietsky N, Simic H, Arapovic J, Toporik A, Levy O, Novik A, Levine Z, Beiman M, Dassa L, Achdout H et al (2009) The interaction of TIGIT with PVR and PVRL2 inhibits human NK cell cytotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(42):17858–17863
Lenschow DJ, Walunas TL, Bluestone JA (1996) CD28/B7 system of T cell costimulation. Annu Rev Immunol 14:233–258
Chen L (2004) Co-inhibitory molecules of the B7-CD28 family in the control of T-cell immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 4(5):336–347
Joller N, Hafler JP, Brynedal B, Kassam N, Spoerl S, Levin SD, Sharpe AH, Kuchroo VK (2011) Cutting edge: TIGIT has T cell-intrinsic inhibitory functions. J Immunol 186(3):1338–1342
Levin SD, Taft DW, Brandt CS, Bucher C, Howard ED, Chadwick EM, Johnston J, Hammond A, Bontadelli K, Ardourel D et al (2011) Vstm3 is a member of the CD28 family and an important modulator of T-cell function. Eur J Immunol 41(4):902–915
Joller N, Lozano E, Burkett PR, Patel B, Xiao S, Zhu C, Xia J, Tan TG, Sefik E, Yajnik V et al (2014) Treg cells expressing the coinhibitory molecule TIGIT selectively inhibit proinflammatory Th1 and Th17 cell responses. Immunity 40(4):569–581
Takano A, Ishikawa N, Nishino R, Masuda K, Yasui W, Inai K, Nishimura H, Ito H, Nakayama H, Miyagi Y et al (2009) Identification of nectin-4 oncoprotein as a diagnostic and therapeutic target for lung cancer. Cancer Res 69(16):6694–6703
Pavlova NN, Pallasch C, Elia AE, Braun CJ, Westbrook TF, Hemann M, Elledge SJ (2013) A role for PVRL4-driven cell–cellinteractions in tumorigenesis. Elife 2:e00358
Fabre-Lafay S, Monville F, Garrido-Urbani S, Berruyer-Pouyet C, Ginestier C, Reymond N, Finetti P, Sauvan R, Adélaïde J, Geneix J et al (2007) Nectin-4 is a new histological and serological tumor associated marker for breast cancer. BMC Cancer 7:73
Oshima T, Sato S, Kato J, Ito Y, Watanabe T, Tsuji I, Hori A, Kurokawa T, Kokubo T (2013) Nectin-2 is a potential target for antibody therapy of breast and ovarian cancers. Mol Cancer 12:60
Lakshmikanth T, Burke S, Ali TH, Kimpfler S, Ursini F, Ruggeri L, Capanni M, Umansky V, Paschen A, Sucker A et al (2009) NCRs and DNAM-1 mediate NK cell recognition and lysis of human and mouse melanoma cell lines in vitro and in vivo. J Clin Invest 119(5):1251–1263
Shibuya A, Campbell D, Hannum C, Yssel H, Franz-Bacon K, McClanahan T, Kitamura T, Nicholl J, Sutherland GR, Lanier LL, Phillips JH (1996) DNAM-1, a novel adhesion molecule involved in the cytolytic function of T lymphocytes. Immunity 4(6):573–581
Carlsten M, Björkström NK, Norell H, Bryceson Y, van Hall T, Baumann BC, Hanson M, Schedvins K, Kiessling R, Ljunggren HG, Malmberg KJ (2007) DNAX accessory molecule-1 mediated recognition of freshly isolated ovarian carcinoma by resting natural killer cells. Cancer Res 67(3):1317–1325
Iguchi-Manaka A, Kai H, Yamashita Y, Shibata K, Tahara-Hanaoka S, Honda S, Yasui T, Kikutani H, Shibuya K, Shibuya A (2008) Accelerated tumor growth in mice deficient in DNAM-1 receptor. J Exp Med 205(13):2959–2964
Hafler JP, Maier LM, Cooper JD, Plagnol V, Hinks A, Simmonds MJ, Stevens HE, Walker NM, Healy B, Howson JM (2009) CD226 Gly307Ser association with multiple autoimmune diseases. Genes Immun 10(1):5–10
Lipson EJ, Drake CG (2011) Ipilimumab: an anti-CTLA-4 antibody for metastatic melanoma. Clin Cancer Res 17(22):6958–6962
Sharma P, Wagner K, Wolchok JD, Allison JP (2011) Novel cancer immunotherapy agents with survival benefit: recent successes and next steps. Nat Rev Cancer 11(11):805–812
Sarnaik AA, Weber JS (2009) Recent advances using anti-CTLA-4 for the treatment of melanoma. Cancer J 15(3):169–173
Callahan MK, Wolchok JD, Allison JP (2010) Anti-CTLA-4 antibody therapy: immune monitoring during clinical development of a novel immunotherapy. Semin Oncol 37(5):473–484
Lipson EJ, Bodell MA, Kraus ES, Sharfman WH (2014) Successful administration of Ipilimumab to two kidney transplantation patients with metastatic melanoma. J Clin Oncol (Epub ahead of print)
Stengel KF, Harden-Bowles K, Yu X, Rouge L, Yin J, Comps-Agrar L, Wiesmann C, Bazan JF, Eaton DL, Grogan JL (2012) Structure of TIGIT immunoreceptor bound to poliovirus receptor reveals a cell–celladhesion and signaling mechanism that requires cis-trans receptor clustering. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(14):5399–5404
Liu J, Qian X, Chen Z, Xu X, Gao F, Zhang S, Zhang R, Qi J, Gao GF, Yan J (2012) Crystal structure of cell adhesion molecule nectin-2/CD112 and its binding to immune receptor DNAM-1/CD226. J Immunol 188(11):5511–5520
Lopez M, Cocchi F, Menotti L, Avitabile E, Dubreuil P, Campadelli-Fiume G (2000) Nectin2alpha (PRR2alpha or HveB) and nectin2delta are low-efficiency mediators for entry of herpes simplex virus mutants carrying the Leu25Pro substitution in glycoprotein D. J Virol 74(3):1267–1274
Manoj S, Jogger CR, Myscofski D, Yoon M, Spear PG (2004) Mutations in herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D that prevent cell entry via nectins and alter cell tropism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(34):12414–12421
Spear PG, Manoj S, Yoon M, Jogger CR, Zago A, Myscofski D (2006) Different receptors binding to distinct interfaces on herpes simplex virus gD can trigger events leading to cell fusion and viral entry. Virology 344(1):17–24
Noyce RS, Bondre DG, Ha MN, Lin LT, Sisson G, Tsao MS, Richardson CD (2011) Tumor cell marker PVRL4 (nectin 4) is an epithelial cell receptor for measles virus. PLoS Pathog 7(8):e1002240
Mühlebach MD, Mateo M, Sinn PL, Prüfer S, Uhlig KM, Leonard VH, Navaratnarajah CK, Frenzke M, Wong XX, Sawatsky B et al (2011) Adherens junction protein nectin-4 is the epithelial receptor for measles virus. Nature 480(7378):530–533
Zhang N, Yan J, Lu G, Guo Z, Fan Z, Wang J, Shi Y, Qi J, Gao GF (2011) Binding of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D to nectin-1 exploits host cell adhesion. Nat Commun 2:577
Di Giovine P, Settembre EC, Bhargava AK, Luftig MA, Lou H, Cohen GH, Eisenberg RJ, Krummenacher C, Carfi A (2011) Structure of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D bound to the human receptor nectin-1. PLoS Pathog 7(9):e1002277
Zhang X, Lu G, Qi J, Li Y, He Y, Xu X, Shi J, Zhang CW, Yan J, Gao GF (2013) Structure of measles virus hemagglutinin bound to its epithelial receptor nectin-4. Nat Struct Mol Biol 20(1):67–72
Sözen MA, Suzuki K, Tolarova MM, Bustos T, Fernández Iglesias JE, Spritz RA (2001) Mutation of PVRL1 is associated with sporadic, non-syndromic cleft lip/palate in northern Venezuela. Nat Genet 29(2):141–142
Suzuki K, Hu D, Bustos T, Zlotogora J, Richieri-Costa A, Helms JA, Spritz RA (2000) Mutations of PVRL1, encoding a cell–celladhesion molecule/herpesvirus receptor, in cleft lip/palate-ectodermal dysplasia. Nat Genet 25(4):427–430
Bustos T, Simosa V, Pinto-Cisternas J, Abramovits W, Jolay L, Rodriguez L, Fernandez L, Ramela M (1991) Autosomal recessive ectodermal dysplasia: I. An undescribed dysplasia/malformation syndrome. Am J Med Genet 41(4):398–404
Zlotogora J (1994) On the inheritance of the split hand/split foot malformation. Am J Med Genet 53(1):29–32
Zlotogora J, Zilberman Y, Tenenbaum A, Wexler MR (1987) Cleft lip and palate, pili torti, malformed ears, partial syndactyly of fingers and toes, and mental retardation: a new syndrome? J Med Genet 24(5):291–293
Brancati F, Fortugno P, Bottillo I, Lopez M, Josselin E, Boudghene-Stambouli O, Agolini E, Bernardini L, Bellacchio E, Iannicelli M et al (2010) Mutations in PVRL4, encoding cell adhesion molecule nectin-4, cause ectodermal dysplasia-syndactyly syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 87(2):265–273
Brancati F, Agolini E, Fortugno P (2013) Nectinopathies: an emerging group of ectodermal dysplasia syndromes. G Ital Dermatol Venereol 148(1):59–64
Logue MW, Schu M, Vardarajan BN, Buros J, Green RC, Go RC, Griffith P, Obisesan TO, Shatz R, Borenstein A et al (2011) A comprehensive genetic association study of Alzheimer disease in African Americans. Arch Neurol 68(12):1569–1579
Takei N, Miyashita A, Tsukie T, Arai H, Asada T, Imagawa M, Shoji M, Higuchi S, Urakami K, Kimura H et al (2009) Genetic association study on in and around the APOE in late-onset Alzheimer disease in Japanese. Genomics 93(5):441–448
Lachke SA, Higgins AW, Inagaki M, Saadi I, Xi Q, Long M, Quade BJ, Talkowski ME, Gusella JF, Fujimoto A et al (2012) The cell adhesion gene PVRL3 is associated with congenital ocular defects. Hum Genet 131(2):235–250
Acknowledgments
We thank Vladimir Vigdorovich for helpful comments and discussions. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grants GM094662 and GM094665 (to SCA). The Albert Einstein Cancer Center is supported by NIH P30CA013330.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samanta, D., Almo, S.C. Nectin family of cell-adhesion molecules: structural and molecular aspects of function and specificity. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 72, 645–658 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1763-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1763-4