Summary
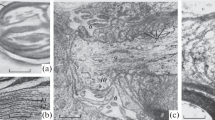
Analysis of the plasmalemma of frog dorsal root ganglion cells by freeze-fracture demonstrates regional differences in the distribution of intramembranous particles. Although P-face particles are distributed rather uniformly, the E-face particle concentration at the cell body (∼300 μm−2) is much lower than that at the axon hillock (∼900 μm−2), proximal initial segment (∼1000 μm−2), or intermediate portion of the initial segment (∼800 μm−2). The particle concentrations in the latter regions approach that at the node of Ranvier and, moreover, particle size analysis reveals that the E-face particles, like those at the node, include a large number that are 10 nm or more in diameter. Thin sections reveal patches of a dense undercoating on the cytoplasmic surface of the axolemma in some regions of the initial segment but not the axon hillock. It is concluded from these results that the axon hillock and the initial segment of dorsal root ganglion cells have some of the structural characteristics of the node of Ranvier.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Black, J. A., Foster, R. E. &Waxman, S. G. (1983) Freeze-fracture ultrastructure of developing and adult non-myelinated ganglion cell axolemma in the retinal nerve fibre layer.Journal of Neurocytology 12, 201–12.
Devor, M. &Obermayer, M. (1984) Membrane differentiation in rat dorsal root ganglia and possible consequence for back pain.Neuroscience Letters 51, 341–6.
Dichter, M. A. &Fischbach, G. D. (1977) The action potential of chick dorsal root ganglion neurons maintained in cell culture.Journal of Physiology 267, 281–98.
Henkart, M., Landis, D. M. D. &Reese, T. S. (1976) Similarity of junctions between plasma membranes and endoplasmic reticulum in muscle and neurons.Journal of Cell Biology 70, 338–47.
Heyer, E. J. &Macdonald, R. L. (1982) Calcium- and sodium-dependent action potentials of mouse spinal cord and dorsal root ganglion neurons in cell culture.Journal of Neurophysiology 47, 641–55.
Ito, M. (1957) The electrical activity of spinal ganglion cells investigated with intracellular microelectrodes.Japanese Journal of Physiology 7, 297–323.
Ito, M. (1959) An analysis of potentials recorded intracellularly from the spinal ganglion cell.Japanese Journal of Physiology 9, 20–31.
Karnovsky, M. (1971) Use of ferrocyanide-reduced osmium tetroxide in electron microscopy. InAbstracts of Papers, 11th Annual Meeting of the American Society for Cell Biology p. 146.
Koketsu, K., Cerf, J. A. &Nishi, S. (1959) Further observations on activity of frog spinal ganglion cells in sodium-free solutions.Journal of Neurophysiology 27, 693–703.
Kostyuk, P. G., Veselovsky, N. S. &Tsyndrenko, A. Y. (1981a) Ionic currents in the somatic membrane of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. I. Sodium currents.Neuroscience 6, 2423–30.
Kostyuk, P. G., Veselovsky, N. S. &Fedulova, S. A. (1981b) Ionic currents in the somatic membrane of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. II. Calcium currents.Neuroscience 6, 2431–8.
Kostyuk, P. G., Veselovsky, N. S. &Fedulova, S. A. (1981c) Ionic currents in the somatic membrane of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. III. Potassium currents.Neuroscience 6, 2439–44.
Kristol, C., Sandri, C. &Akert, K. (1978) Intramembranous particles at the nodes of Ranvier of the cat spinal cord: a morphometric study.Brain Research 142, 391–400.
Lieberman, A. R. (1976) Sensory ganglia. InThe Peripheral Nerve (edited byLandon, D. N.), pp. 188–278. London: Chapman and Hall.
Matsuda, Y., Yoshida, S. &Tonesawa, T. (1978) Tetrodotoxin sensitivity and Ca component of action potentials in mouse dorsal root ganglion cells cultured in vitro.Brain Research 154, 69–82.
Pannese, E. (1981) The satellite cells of the sensory ganglia.Advances in Anatomy, Embryology and Cell Biology 65, 1–111.
Peters, A., Palay, S. L. &Webster, H. De F. (1976)The fine structure of the nervous system. The neurons and supporting cells. Philadelphia, London, Toronto: Saunders.
Quick, D. C. &Waxman, S. G. (1977) Specific staining of the axon membrane at nodes of Ranvier with ferric ion and ferrocyanide.Journal of the Neurological Sciences 31, 1–11.
Rambourg, A., Clermont, Y. &Beaudet, A. (1983) Ultrastructural features of six types of neurons in rat dorsal root ganglia.Journal of Neurocytology 12, 47–66.
Rosenbluth, J. (1962) Subsurface cisterns and their relationship to the neuronal plasma membrane.Journal of Cell Biology 13, 405–19.
Rosenbluth, J. (1974) Substructure of amphibian motor endplate.Journal of Cell Biology 62, 755–66.
Rosenbluth, J. (1976) Intramembranous particle distribution at the node of Ranvier and adjacent axolemma in myelinated axons of the frog brain.Journal of Neurocytology 5, 731–45.
Rosenbluth, J. (1983) Structure of the node of Ranvier. InStructure and Function in Excitable Cells (edited byChang, D. C., Tasaki, I., Adelmań, W. J. &Leuchtag, H. R.), pp. 25–52. New York: Plenum Publishing Corporation.
Sato, M. &Austin, G. (1961) Intracellular potentials of mammalian dorsal root ganglion cells.Journal of Neurophysiology 24, 569–82.
Smith, T. G. (1983) Sites of action potential generation in cultured vertebrate neurons.Brain Research 288, 381–3.
Stolinski, C., Breathnach, A. S., Martin, B., Thomas, P. K., King, R. G. M. &Gabriel, G. (1981) Associated particle aggregates in juxtaparanodal axolemma and adaxonal Schwann cell membrane of rat peripheral nerve.Journal of Neurocytology 10, 679–91.
Tao-Cheng, J.-H. &Rosenbluth, J. (1980) Nodal and paranodal membrane structure in complementary freeze-fracture replicas of amphibian peripheral nerves.Brain Research 199, 249–65.
Tao-Cheng, J.-H. &Rosenbluth, J. (1984) Extranodal particle accumulations in the axolemma of myelinated frog optic axons.Brain Research 38, 289–300.
Waxman, S. G. &Foster, R. E. (1980) Ionic channel distribution and heterogeneity of the axon membrane in myelinated fibers.Brain Research Reviews 2, 205–34.
Yoshida, S. &Matsuda, Y. (1979) Studies on sensory neurons of the mouse with intracellular recording and horseradish peroxidase-injection techniques.Journal of Neurophysiology 42, 1134–45.
Yoshida, S., Matsuda, Y. &Samejima, A. (1978) Tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium and calcium components of action potentials in dorsal root ganglion cells of the adult mouse.Journal of Neurophysiology 41, 1096–106.
Zenker, W. &Högel, E. (1976) The prebifurcation section of the axon of the rat spinal ganglion cell.Cell and Tissue Research 165, 345–63.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsumoto, E., Rosenbluth, J. Plasma membrane structure at the axon hillock, initial segment and cell body of frog dorsal root ganglion cells. J Neurocytol 14, 731–747 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01170825
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01170825