Abstract
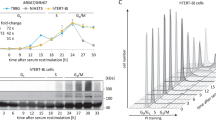
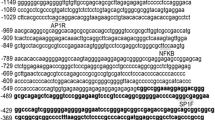
Ki-67 plays a crucial role in cell proliferation as well as maintenance or regulation of cell division. The mechanism governing the Ki-67 gene expression remains unknown. Thus, we cloned the core promoter of the human Ki-67 gene and further investigated its transcriptional regulation. The putative Sp1 binding sites were confirmed by electrophoretic mobility shift assay together with an anti-Sp1 antibody-mediated supershift assay. Deletion mutagenesis and firefly luciferase reporter gene assay demonstrated the essential contribution of Sp1 on transcriptional activation of the Ki-67 gene. In this study, we first confirm that there are three Sp1 binding sites in the Ki-67 core promoter. Two Sp1 sites (one at position −159 to −145 nt and the other at position −14 to +12 nt) are mainly involved in transcriptional regulation of the Ki-67 gene. Overexpression of Sp1 can enhance the Ki-67 promoter activity. However, down-regulation of Sp1 expression using siRNA-Sp1 and mithramycin effectively inhibits the Ki-67 gene transcription. Our results suggest that Sp1 is essential for basal promoter activity of the human Ki-67 gene. Inhibition of the Ki-67 transcriptional activity through abolishment of Sp1 may provide the useful prospect for gene therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Sp1:
-
Specificity protein 1
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
- EMSA:
-
Electrophoretic mobility shift assays
- SV40:
-
Simian virus 40 promoter
- HRP:
-
Horseradish peroxidase
- TBST:
-
Tris-buffered saline Tween-20
References
Duchrow M, Schlueter C, Wohlenberg C, Flad HD, Gerdes J. Molecular characterization of the gene locus of the human cell proliferation-associated nuclear protein defined by monoclonal antibody Ki-67. Cell Prolif. 1996;29:1–12.
MacCallum DE, Hall PA. Biochemical characterization of pKi67 with the identification of a mitotic-specific form associated with hyperphosphorylation and altered DNA binding. Exp Cell Res. 1999;252:186–98.
Schlüter C, Duchrow M, Wohlenberg C, Becker MH, Key G, Flad HD, et al. The cell proliferation associated antigen of antibody Ki-67: a very large, ubiquitous nuclear protein with numerous repeated elements, representing a new kind of cell cycle-maintaining proteins. J Cell Biol. 1993;123:513–22.
MaCallum DE, Hall PA. Biochemical characterization of pKi-67 with the identification of a mitotic-specific form association with hyperphosphorylation and altered DNA binding. Exp Cell Res. 1991;52:186–98.
Kausch I, Jiang H, Ewerdwalbesloh N, Doehn C, Kruger S, Sczakiel G, et al. Inhibition of Ki-67 in a renal cell carcinoma severe combined immunodeficiency disease mouse model is associated with induction of apoptosis and tumour growth inhibition. BJU Int. 2005;95:416–20.
Dynan WS, Tjian R. Isolation of transcription factors that discriminate between different promoters recongnized by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1983;32:669–80.
Dynan WS, Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983;35:79–87.
Suske G. The Sp-family of transcription factors. Gene. 1999;238:291–300.
Kadonaga JT, Carner KR, Masiarz FR, Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987;51:1079–90.
Endl E, Gerdes J. Post-translational modifications of the Ki-67 protein coincide with two major check points during mitosis. J Cell Physiol. 2000;182:371–80.
Scholzen T, Gerdes J. The Ki-67 protein: from the known and the unknown. J Cell Physiol. 2000;182:311–22.
Takagi M, Matsuoka Y, Kurihara T, Yoneda Y. Chmadrin: a novel Ki-67 antigen-related perichromosomal protein possibly implicated in higher order chromatin structure. J Cell Sci. 1999;112:2463–72.
Yang X, Su K, Roos MD, Chang Q, Paterson AJ, Kudlow JE. O-linkage of N-acetylglucosamine to Sp1 activation domain inhibits its transcriptional capability. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2001;98:6611–6.
Su K, Roos MD, Yang X, Han I, Paterson AJ, Kudlow JE. An N-terminal region of Sp1 targets its proteasome dependent degradation in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:15194–202.
Safe S, Abdelrahim M. Sp transcription factor family and its role in cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2005;41:2438–48.
Safe S, Kim K. Nuclear receptor-mediated transactivation through interaction with Sp proteins. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2004;77:1–36.
Bouwman P, Philipsen S. Regulation of the activity of Sp1-related transcription factors. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2002;195:27–38.
Li L, He S, Sun JM, Davie JR. Gene regulation by Sp1 and Sp3. Biochem Cell Biol. 2004;82:460–71.
Barth N, Langmann T, Scholmerich J, Schmitz G, Schaffler A. Identification of regulatory elements in the human adipose most abundant gene transcript-1 (apM-1) promoter: role of SP1/SP3 and TNF-alpha as regulatory pathways. Diabetologia. 2002;45:1425–33.
Wang LW, Wei DY, Huang SY, Peng ZH, Le XD, Wu TT, et al. Transcription factor Sp1 expression is a significant predictor of survival in human gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:6371–80.
Shi Q, Le XD, Abbruzzese JL, Peng ZH, Qian CN, Tang HM, et al. Constitutive Sp1 activity is essential for differential constitutive expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2001;61:4143–54.
Chiefari E, Brunetti A, Arturi F, Bidart JM, Russo D, Schlumberger M, et al. Increased expression of AP2 and Sp1 transcription factors in human thyroid tumours: a role in NIS expression regulation. BMC Cancer. 2002;2:35.
Hosoi Y, Watanabe T, Nakagawa K, Matsumoto Y, Enomoto A, Morita A, et al. Up-regulation of DNA-dependent protein kinase activity and Sp1 in colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol. 2004;25:461–8.
Jang SI, Steinert PM. Loricrin expression in cultured human keratinocytes is controlled by a complex interplay between transcription factors of the Sp1, CREB, AP1, and AP2 families. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:42268–79.
Suzuki T, Kimura A, Nagai R, Horikoshi M. Regulation of interaction of the acetyltransferase region of p300 and the DNA-binding domain of Sp1 on and through DNA binding. Genes Cells. 2000;5:29–41.
Acknowledgments
This project is supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 30873021 and 30972976) and the Science and Technology Department of Jiangsu Province (no. BK 2010177).
Conflicts of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hui Tian and Guo-Wei Qian contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, H., Qian, GW., Li, W. et al. A critical role of Sp1 transcription factor in regulating the human Ki-67 gene expression. Tumor Biol. 32, 273–283 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-010-0119-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-010-0119-4