Abstract
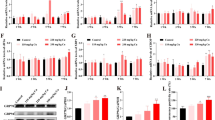
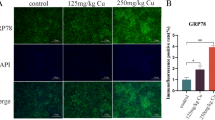
The purpose of this research was to investigate whether copper (Cu) exposure could induce apoptosis via endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) in skeletal muscle of broilers. A total of 240 one-day-old chickens were randomly divided into four groups by free access; the diets are as follows: control diet (Cu 11 mg/kg, control group) and high level of Cu diets (Cu 110 mg/kg, group I; Cu 220 mg/kg, group II; Cu 330 mg/kg, group III). The skeletal muscle tissues were collected on day 49 for further examination. The content of Cu, histopathology, and the expression levels of the genes and proteins related to ERS and apoptosis were detected. Results showed that the Cu levels in skeletal muscle were increased in a dose-dependent manner. Meanwhile, the spaces between the muscle fibers were wider with the increase of Cu content, and the myolysis was observed in group III. Besides, the mRNA expression levels of GRP78, GRP94, eIF2α, ATF6, XBP1, CHOP, Caspase-12, and Caspase3 were markedly increased in treated groups compared with control group, and the protein expression levels of GRP78, Caspase3, Active-Caspase3 and JNK were significantly elevated with the increase of dietary Cu. In summary, these findings suggested that Cu could induce apoptosis through ERS in skeletal muscle of broilers.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gaetke LM, Chow-Johnson HS, Chow CK (2014) Copper: toxicological relevance and mechanisms. Arch Toxicol 88(11):1929–1938. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1355-y
Bonham M, O'Connor JM, Hannigan BM, Strain JJ (2002) The immune system as a physiological indicator of marginal copper status? Br J Nutr 87(5):393–403. https://doi.org/10.1079/bjnbjn2002558
Duncan C, White AR (2012) Copper complexes as therapeutic agents. Metallomics 4(2):127–138. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2mt00174h
Liao J, Yang F, Chen H, Yu W, Han Q, Li Y, Hu L, Guo J, Pan J, Liang Z, Tang Z (2019) Effects of copper on oxidative stress and autophagy in hypothalamus of broilers. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 185:109710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109710
Jiang X, Xiong Z, Liu H, Liu G, Liu W (2017) Distribution, source identification, and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in wetland soils of a river-reservoir system. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24(1):436–444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7775-x
Li S, Zhang Q (2010) Spatial characterization of dissolved trace elements and heavy metals in the upper Han River (China) using multivariate statistical techniques. J Hazard Mater 176(1–3):579–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.11.069
Wu H, Yang F, Li H, Li Q, Zhang F, Ba Y, Cui L, Sun L, Lv T, Wang N, Zhu J (2019) Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of agricultural soil near a smelter in an industrial city in China. Int J Environ Health Res:1–13. doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2019.1584666
Yang F, Cao H, Su R, Guo J, Li C, Pan J, Tang Z (2017) Liver mitochondrial dysfunction and electron transport chain defect induced by high dietary copper in broilers. Poult Sci 96(9):3298–3304. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pex137
Chen H, Kang Z, Qiao N, Liu G, Huang K, Wang X, Pang C, Zeng Q, Tang Z, Li Y (2019) Chronic copper exposure induces hypospermatogenesis in mice by increasing apoptosis without affecting testosterone secretion. Biol Trace Elem Res:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01852-x
Pereira TC, Campos MM, Bogo MR (2016) Copper toxicology, oxidative stress and inflammation using zebrafish as experimental model. J Appl Toxicol 36(7):876–885. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.3303
Maziere C, Auclair M, Djavaheri-Mergny M, Packer L, Maziere JC (1996) Oxidized low density lipoprotein induces activation of the transcription factor NF kappa B in fibroblasts, endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Biochem Mol Biol Int 39(6):1201–1207. https://doi.org/10.1080/15216549600201392
Wang Y, Zhao H, Shao Y, Liu J, Li J, Luo L, Xing M (2018) Copper (II) and/or arsenite-induced oxidative stress cascades apoptosis and autophagy in the skeletal muscles of chicken. Chemosphere 206:597–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.013
Bakalli RI, Pesti GM, Ragland WL, Konjufca V (1995) Dietary copper in excess of nutritional requirement reduces plasma and breast muscle cholesterol of chickens. Poult Sci 74(2):360–365. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.0740360
Wang M, Kaufman RJ (2016) Protein misfolding in the endoplasmic reticulum as a conduit to human disease. Nature 529(7586):326–335. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature17041
Louessard M, Bardou I, Lemarchand E, Thiebaut AM, Parcq J, Leprince J, Terrisse A, Carraro V, Fafournoux P, Bruhat A, Orset C, Vivien D, Ali C, Roussel BD (2017) Activation of cell surface GRP78 decreases endoplasmic reticulum stress and neuronal death. Cell Death Differ 24(9):1518–1529. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2017.35
Wang Y, Wang YL, Huang X, Yang Y, Zhao YJ, Wei CX, Zhao M (2017) Ibutilide protects against cardiomyocytes injury via inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondrial stress pathways. Heart Vessel 32(2):208–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-016-0891-1
Szegezdi E, Logue SE, Gorman AM, Samali A (2006) Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. EMBO Rep 7(9):880–885. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.embor.7400779
Li XN, Zuo YZ, Qin L, Liu W, Li YH, Li JL (2018) Atrazine-xenobiotic nuclear receptor interactions induce cardiac inflammation and endoplasmic reticulum stress in quail (Coturnix coturnix coturnix). Chemosphere 206:549–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.049
Yilmaz E (2017) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and obesity. Adv Exp Med Biol 960:261–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48382-5_11
Rai NK, Tripathi K, Sharma D, Shukla VK (2005) Apoptosis: a basic physiologic process in wound healing. Int J Low Extrem Wounds 4(3):138–144. https://doi.org/10.1177/1534734605280018
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35(4):495–516. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230701320337
Lavrik I, Golks A, Krammer PH (2005) Death receptor signaling. J Cell Sci 118(2):265–267. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.01610%J
Wang C, Youle RJ (2009) The role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Annu Rev Genet 43:95–118. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genet-102108-134850
Mehmet H (2000) Caspases find a new place to hide. Nature 403(6765):29–30. https://doi.org/10.1038/47377
Zhao H, Wang Y, Shao Y, Liu J, Wang S, Xing M (2018) Oxidative stress-induced skeletal muscle injury involves in NF-kappaB/p53-activated immunosuppression and apoptosis response in copper (II) or/and arsenite-exposed chicken. Chemosphere 210:76–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.165
Cao H, Su R, Hu G, Li C, Guo J, Pan J, Tang Z (2016) In vivo effects of high dietary copper levels on hepatocellular mitochondrial respiration and electron transport chain enzymes in broilers. Br Poult Sci 57(1):63–70. https://doi.org/10.1080/00071668.2015.1127895
Su R, Wang R, Cao H, Pan J, Chen L, Li C, Shi D, Tang Z (2011) High copper levels promotes broiler hepatocyte mitochondrial permeability transition in vivo and in vitro. Biol Trace Elem Res 144(1–3):636–646. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-9015-z
Mueller C, Magaki S, Schrag M, Ghosh MC, Kirsch WM (2009) Iron regulatory protein 2 is involved in brain copper homeostasis. J Alzheimers Dis 18(1):201–210. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-2009-1136
Barber RS, Bowland JP, Braude R, Mitchell KG, Porter JW (1961) Copper sulphate and copper sulphide (CuS) as supplements for growing pigs. Br J Nutr 15:189–197. https://doi.org/10.1079/bjn19610024
Liao J, Yang F, Tang Z, Yu W, Han Q, Hu L, Li Y, Guo J, Pan J, Ma F, Ma X, Lin Y (2019) Inhibition of Caspase-1-dependent pyroptosis attenuates copper-induced apoptosis in chicken hepatocytes. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 174:110–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.02.069
Cai LM, Wang QS, Luo J, Chen LG, Zhu RL, Wang S, Tang CH (2019) Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment for children near a large Cu-smelter in Central China. Sci Total Environ 650(Pt 1):725–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.081
Chern YJ, Wong JCT, Cheng GSW, Yu A, Yin Y, Schaeffer DF, Kennecke HF, Morin G, Tai IT (2019) The interaction between SPARC and GRP78 interferes with ER stress signaling and potentiates apoptosis via PERK/eIF2alpha and IRE1alpha/XBP-1 in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis 10(7):504. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1687-x
Wolfson JJ, May KL, Thorpe CM, Jandhyala DM, Paton JC, Paton AW (2008) Subtilase cytotoxin activates PERK, IRE1 and ATF6 endoplasmic reticulum stress-signalling pathways. Cell Microbiol 10(9):1775–1786. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-5822.2008.01164.x
Jin Y, Zhang S, Tao R, Huang J, He X, Qu L, Fu Z (2016) Oral exposure of mice to cadmium (II), chromium (VI) and their mixture induce oxidative- and endoplasmic reticulum-stress mediated apoptosis in the livers. Environ Toxicol 31(6):693–705. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22082
Xu C, Bailly-Maitre B, Reed JC (2005) Endoplasmic reticulum stress: cell life and death decisions. J Clin Invest 115(10):2656–2664. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci26373
Garcia de la Cadena S, Massieu L (2016) Caspases and their role in inflammation and ischemic neuronal death. Focus on caspase-12. Apoptosis 21(7):763–777. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-016-1247-0
Jiang Q, Chen S, Ren W, Liu G, Yao K, Wu G, Yin Y (2017) Escherichia coli aggravates endoplasmic reticulum stress and triggers CHOP-dependent apoptosis in weaned pigs. Amino Acids 49(12):2073–2082. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-017-2492-4
Carlisle RE, Brimble E, Werner KE, Cruz GL, Ask K, Ingram AJ, Dickhout JG (2014) 4-Phenylbutyrate inhibits tunicamycin-induced acute kidney injury via CHOP/GADD153 repression. PLoS One 9(1):e84663. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0084663
Chan JY, Luzuriaga J, Maxwell EL, West PK, Bensellam M, Laybutt DR (2015) The balance between adaptive and apoptotic unfolded protein responses regulates beta-cell death under ER stress conditions through XBP1, CHOP and JNK. Mol Cell Endocrinol 413:189–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2015.06.025
Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, Li E, Xu J, Yankner BA, Yuan J (2000) Caspase-12 mediates endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by amyloid-beta. Nature 403(6765):98–103. https://doi.org/10.1038/47513
Lin CL, Lee CH, Chen CM, Cheng CW, Chen PN, Ying TH, Hsieh YH (2018) Protodioscin induces apoptosis through ROS-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress via the JNK/p38 activation pathways in human cervical cancer cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 46(1):322–334. https://doi.org/10.1159/000488433
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31572585) and National Key R & D Program of China (No. 2016YFD0501205 and No. 2017YFD0502200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All experimental protocols were approved by the Ethics Committee of South China Agricultural University.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, J., Bai, Y., Liao, J. et al. Copper Induces Apoptosis Through Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Skeletal Muscle of Broilers. Biol Trace Elem Res 198, 636–643 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02076-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02076-0