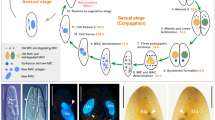
Abstract
The protein trap is a powerful tool for genetic and biochemical studies of gene function in the animal kingdom. Although the original protein trap was developed for flies, it can be easily adapted to other multicellular organisms, both known models and ones with an unsequenced genome. The protein trap has been successfully applied to the fruit fly, crustaceans Parhyale hawaiensis, zebrafish, and insect and animal cell cultures. This approach is based on the integration into genes of an artificial exon that carries DNA encoding a fluorescent marker, standardized immunoepitopes, an integrase docking site, and splice acceptor and donor sites. The protein trap for cell cultures additionally contains an antibiotic resistance gene, which facilitates the selection of trapped clones. Resulting chimeric tagged mRNAs can be interfered by dsRNA against GFP (iGFPi—in vivo GFP interference), or the chimeric proteins can be efficiently knocked down by deGradFP technology. Both RNA and protein knockdowns produce a strong loss of function phenotype in tagged cells. The fluorescent and protein affinity tags can be used for tagged protein localisation within the cell and for identifying their binding partners in their native complexes. Insertion into protein trap integrase docking sites allows the replacement of trap contents by any new constructs, including other markers, cell toxins, stop-codons, and binary expression systems such as GAL4/UAS, LexA/LexAop and QF/QUAS, that reliably reflect endogenous gene expression. A distinctive feature of the protein trap approach is that all manipulations with a gene or its product occur only in the endogenous locus, which cannot be achieved by any other method.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shimomura O, Johnson FH, Saiga Y (1962) Extraction, purification and properties of aequorin, a bioluminescent protein from the luminous hydromedusan, Aequorea. J Cell Comp Physiol 59:223–239
Prasher DC, Eckenrode VK, Ward WW, Prendergast FG, Cormier MJ (1992) Primary structure of the Aequorea victoria green-fluorescent protein. Gene 111(2):229–233
Chalfie M, Tu Y, Euskirchen G, Ward WW, Prasher DC (1994) Green fluorescent protein as a marker for gene expression. Science 263(5148):802–805
Wang S, Hazelrigg T (1994) Implications for bcd mRNA localization from spatial distribution of exu protein in Drosophila oogenesis. Nature 369(6479):400–403
Chudakov DM, Matz MV, Lukyanov S, Lukyanov KA (2010) Fluorescent proteins and their applications in imaging living cells and tissues. Physiol Rev 90(3):1103–1163
Giepmans BN, Adams SR, Ellisman MH, Tsien RY (2006) The fluorescent toolbox for assessing protein location and function. Science 312(5771):217–224
Stepanenko OV, Verkhusha VV, Kuznetsova IM, Turoverov KK (2007) Fluorescent proteins: physical-chemical properties and application in cell biology. Tsitologiia 49(5):395–420
Sineshchekova OO, Kawate T, Vdovychenko OV, Sato TN (2004) Protein-trap version 2.1: screening for expressed proteins in mammalian cells based on their localizations. BMC Cell Biol 5:8
Cutler SR, Ehrhardt DW, Griffitts JS, Somerville CR (2000) Random GFP:cDNA fusions enable visualization of subcellular structures in cells of Arabidopsis at a high frequency. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(7):3718–3723
Misawa K, Nosaka T, Morita S, Kaneko A, Nakahata T, Asano S, Kitamura T (2000) A method to identify cDNAs based on localization of green fluorescent protein fusion products. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(7):3062–3066
Morin X, Daneman R, Zavortink M, Chia W (2001) A protein trap strategy to detect GFP-tagged proteins expressed from their endogenous loci in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(26):15050–15055
Balciunas D, Davidson AE, Sivasubbu S, Hermanson SB, Welle Z, Ekker SC (2004) Enhancer trapping in zebrafish using the Sleeping Beauty transposon. BMC Genom 5(1):62
Engineer CB, Fitzsimmons KC, Schmuke JJ, Dotson SB, Kranz RG (2005) Development and evaluation of a Gal4-mediated LUC/GFP/GUS enhancer trap system in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol 5:9
Yeh E, Gustafson K, Boulianne GL (1995) Green fluorescent protein as a vital marker and reporter of gene expression in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(15):7036–7040
Quiñones-Coello AT, Petrella LN, Ayers K, Melillo A, Mazzalupo S, Hudson AM, Wang S, Castiblanco C, Buszczak M, Hoskins RA, Cooley L (2007) Exploring strategies for protein trapping in Drosophila. Genetics 175(3):1089–1104
Zheng XH, Hughes SH (1999) An avian sarcoma/leukosis virus-based gene trap vector for mammalian cells. J Virol 73(8):6946–6952
Jarvik JW, Adler SA, Telmer CA, Subramaniam V, Lopez AJ (1996) CD-tagging: a new approach to gene and protein discovery and analysis. Biotechniques 20(5):896–904
Smith DJ (1997) Mini-exon epitope tagging for analysis of the protein coding potential of genomic sequence. Biotechniques 23(1):116–120
Clyne PJ, Brotman JS, Sweeney ST, Davis G (2003) Green fluorescent protein tagging Drosophila proteins at their native genomic loci with small P elements. Genetics 165(3):1433–1441
Pastor-Pareja JC, Xu T (2011) Shaping cells and organs in Drosophila by opposing roles of fat body-secreted Collagen IV and perlecan. Dev Cell 21(2):245–256
Morin X (2003) In vivo protein trapping in Drosophila. Brief Funct Genom Proteom 2(2):137–141
Aleksic J, Lazic R, Müller I, Russell SR, Adryan B (2009) Biases in Drosophila melanogaster protein trap screens. BMC Genom 10:249
Bellen HJ, Levis RW, He Y, Carlson JW, Evans-Holm M, Bae E, Kim J, Metaxakis A, Savakis C, Schulze KL, Hoskins RA, Spradling AC (2011) The Drosophila gene disruption project: progress using transposons with distinctive site specificities. Genetics 188(3):731–743
Bellen HJ, Levis RW, Liao G, He Y, Carlson JW, Tsang G, Evans-Holm M, Hiesinger PR, Schulze KL, Rubin GM, Hoskins RA, Spradling AC (2004) The BDGP gene disruption project: single transposon insertions associated with 40% of Drosophila genes. Genetics 167(2):761–781
Venken KJ, Bellen HJ (2005) Emerging technologies for gene manipulation in Drosophila melanogaster. Nat Rev Genet 6(3):167–178
Lowe N, Rees JS, Roote J, Ryder E, Armean IM, Johnson G, Drummond E, Spriggs H, Drummond J, Magbanua JP, Naylor H, Sanson B, Bastock R, Huelsmann S, Trovisco V, Landgraf M, Knowles-Barley S, Armstrong JD, White-Cooper H, Hansen C, Phillips RG, Lilley KS, Russell S, St Johnston D, U. D. P. T. S. Consortium (2014) Analysis of the expression patterns, subcellular localisations and interaction partners of Drosophila proteins using a pigP protein trap library. Development 141(20):3994–4005
Lichty JJ, Malecki JL, Agnew HD, Michelson-Horowitz DJ, Tan S (2005) Comparison of affinity tags for protein purification. Protein Expr Purif 41(1):98–105
Neumüller RA, Wirtz-Peitz F, Lee S, Kwon Y, Buckner M, Hoskins RA, Venken KJ, Bellen HJ, Mohr SE, Perrimon N (2012) Stringent analysis of gene function and protein-protein interactions using fluorescently tagged genes. Genetics 190(3):931–940
Rees JS, Lowe N, Armean IM, Roote J, Johnson G, Drummond E, Spriggs H, Ryder E, Russell S, St Johnston D, Lilley KS (2011) In vivo analysis of proteomes and interactomes using parallel affinity capture (iPAC) coupled to mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteom 10(6):M110.002386
Rothbauer U, Zolghadr K, Tillib S, Nowak D, Schermelleh L, Gahl A, Backmann N, Conrath K, Muyldermans S, Cardoso MC, Leonhardt H (2006) Targeting and tracing antigens in live cells with fluorescent nanobodies. Nat Methods 3(11):887–889
Hacker U, Nystedt S, Barmchi MP, Horn C, Wimmer EA (2003) piggyBac-based insertional mutagenesis in the presence of stably integrated P elements in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(13):7720–7725
Thibault ST, Singer MA, Miyazaki WY, Milash B, Dompe NA, Singh CM, Buchholz R, Demsky M, Fawcett R, Francis-Lang HL, Ryner L, Cheung LM, Chong A, Erickson C, Fisher WW, Greer K, Hartouni SR, Howie E, Jakkula L, Joo D, Killpack K, Laufer A, Mazzotta J, Smith RD, Stevens LM, Stuber C, Tan LR, Ventura R, Woo A, Zakrajsek I, Zhao L, Chen F, Swimmer C, Kopczynski C, Duyk G, Winberg ML, Margolis J (2004) A complementary transposon tool kit for Drosophila melanogaster using P and piggyBac. Nat Genet 36(3):283–287
Spradling AC, Stern DM, Kiss I, Roote J, Laverty T, Rubin GM (1995) Gene disruptions using P transposable elements: an integral component of the Drosophila genome project. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(24):10824–10830
Kontarakis Z, Pavlopoulos A, Kiupakis A, Konstantinides N, Douris V, Averof M (2011) A versatile strategy for gene trapping and trap conversion in emerging model organisms. Development 138(12):2625–2630
Venken KJ, Schulze KL, Haelterman NA, Pan H, He Y, Evans-Holm M, Carlson JW, Levis RW, Spradling AC, Hoskins RA, Bellen HJ (2011) MiMIC: a highly versatile transposon insertion resource for engineering Drosophila melanogaster genes. Nat Methods 8(9):737–743
Metaxakis A, Oehler S, Klinakis A, Savakis C (2005) Minos as a genetic and genomic tool in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 171(2):571–581
Nagarkar-Jaiswal S, Lee PT, Campbell ME, Chen K, Anguiano-Zarate S, Gutierrez MC, Busby T, Lin WW, He Y, Schulze KL, Booth BW, Evans-Holm M, Venken KJ, Levis RW, Spradling AC, Hoskins RA, Bellen HJ (2015) “A library of MiMICs allows tagging of genes and reversible, spatial and temporal knockdown of proteins in Drosophila. Elife 4:e05338
Gohl DM, Silies MA, Gao XJ, Bhalerao S, Luongo FJ, Lin CC, Potter CJ, Clandinin TR (2011) A versatile in vivo system for directed dissection of gene expression patterns. Nat Methods 8(3):231–237
Diao F, Ironfield H, Luan H, Shropshire WC, Ewer J, Marr E, Potter CJ, Landgraf M, White BH (2015) Plug-and-play genetic access to drosophila cell types using exchangeable exon cassettes. Cell Rep 10(8):1410–1421
Gnerer JP, Venken KJ, Dierick HA (2015) Gene-specific cell labeling using MiMIC transposons. Nucleic Acids Res 43(8):e56
Buszczak M, Paterno S, Lighthouse D, Bachman J, Planck J, Owen S, Skora AD, Nystul TG, Ohlstein B, Allen A, Wilhelm JE, Murphy TD, Levis RW, Matunis E, Srivali N, Hoskins RA, Spradling AC (2007) The carnegie protein trap library: a versatile tool for Drosophila developmental studies. Genetics 175(3):1505–1531
Kelso RJ, Buszczak M, Quiñones AT, Castiblanco C, Mazzalupo S, Cooley L (2004) Flytrap, a database documenting a GFP protein-trap insertion screen in Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D418–D420
Lye CM, Naylor HW, Sanson B (2014) Subcellular localisations of the CPTI collection of YFP-tagged proteins in Drosophila embryos. Development 141(20):4006–4017
Dorogova NV, Nerusheva OO, Omelyanchuk LV (2009) Structural organization and dynamics of the endoplasmic reticulum during spermatogenesis of Drosophila melanogaster: studies using PDI-GFP chimera protein. Biochem Moscow Suppl Ser A 3:55. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990747809010073
Rohrbaugh M, Clore A, Davis J, Johnson S, Jones B, Jones K, Kim J, Kithuka B, Lunsford K, Mitchell J, Mott B, Ramos E, Tchedou MR, Acosta G, Araujo M, Cushing S, Duffy G, Graves F, Griffin K, Gurudatta BV, Jackson D, Jaimes D, Jamison K, Kelley D, Kilgore M, Laramore D, Le T, Mazhar B, Mazhar MM, McCrary B, Miller T, Moreland C, Mullins A, Munye E, Okoorie S, Pittman E, Roberts N, Rose D, Rowland A, Shagarabi A, Smith J, Stallworth T, Stroud N, Sung E, Sung K, Takenaka N, Torre E, Veira J, Vu K, Wagstaff W, Wood AM, Wu K, Yang J, Corces VG (2013) Identification and characterization of proteins involved in nuclear organization using Drosophila GFP protein trap lines. PLoS ONE 8(1):e53091
Nerusheva OO, Dorogova NV, Gubanova NV, Yudina OS, Omelyanchuk LV (2009) A GFP trap study uncovers the functions of Gilgamesh protein kinase in Drosophila melanogaster spermatogenesis. Cell Biol Int 33(5):586–593
Hsu HJ, Drummond-Barbosa D (2017) A visual screen for diet-regulated proteins in the Drosophila ovary using GFP protein trap lines. Gene Expr Patterns 23–24:13–21
Roignant JY, Carré C, Mugat B, Szymczak D, Lepesant JA, Antoniewski C (2003) Absence of transitive and systemic pathways allows cell-specific and isoform-specific RNAi in Drosophila. RNA 9(3):299–308
Ni JQ, Zhou R, Czech B, Liu LP, Holderbaum L, Yang-Zhou D, Shim HS, Tao R, Handler D, Karpowicz P, Binari R, Booker M, Brennecke J, Perkins LA, Hannon GJ, Perrimon N (2011) A genome-scale shRNA resource for transgenic RNAi in Drosophila. Nat Methods 8(5):405–407
Caussinus E, Kanca O, Affolter M (2011) Fluorescent fusion protein knockout mediated by anti-GFP nanobody. Nat Struct Mol Biol 19(1):117–121
Rothbauer U, Zolghadr K, Muyldermans S, Schepers A, Cardoso MC, Leonhardt H (2008) A versatile nanotrap for biochemical and functional studies with fluorescent fusion proteins. Mol Cell Proteom 7(2):282–289
Haseloff J, Siemering KR, Prasher DC, Hodge S (1997) Removal of a cryptic intron and subcellular localization of green fluorescent protein are required to mark transgenic Arabidopsis plants brightly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94(6):2122–2127
Rouwendal GJ, Mendes O, Wolbert EJ, Douwe de Boer A (1997) Enhanced expression in tobacco of the gene encoding green fluorescent protein by modification of its codon usage. Plant Mol Biol 33(6):989–999
Allen BG, Weeks DL (2005) Transgenic Xenopus laevis embryos can be generated using phiC31 integrase. Nat Methods 2(12):975–979
Groth AC, Fish M, Nusse R, Calos MP (2004) Construction of transgenic Drosophila by using the site-specific integrase from phage phiC31. Genetics 166(4):1775–1782
Groth AC, Olivares EC, Thyagarajan B, Calos MP (2000) A phage integrase directs efficient site-specific integration in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(11):5995–6000
Lister JA (2010) Transgene excision in zebrafish using the phiC31 integrase. Genesis 48(2):137–143
Minorikawa S, Nakayama M (2011) Recombinase-mediated cassette exchange (RMCE) and BAC engineering via VCre/VloxP and SCre/SloxP systems. Biotechniques 50(4):235–246
Farruggio AP, Bhakta MS, Calos MP (2017) Use of the DICE (dual integrase cassette exchange) system. Methods Mol Biol 1642:69–85
Kuehle J, Turan S, Cantz T, Hoffmann D, Suerth JD, Maetzig T, Zychlinski D, Klein C, Steinemann D, Baum C, Bode J, Schambach A (2014) Modified lentiviral LTRs allow Flp recombinase-mediated cassette exchange and in vivo tracing of “factor-free” induced pluripotent stem cells. Mol Ther 22(5):919–928
Pristovšek N, Nallapareddy S, Grav LM, Hefzi H, Lewis NE, Rugbjerg P, Hansen HG, Lee GM, Andersen MR, Kildegaard HF (2019) Systematic evaluation of site-specific recombinant gene expression for programmable mammalian cell engineering. ACS Synth Biol 8(4):758–774
Turan S, Kuehle J, Schambach A, Baum C, Bode J (2010) Multiplexing RMCE: versatile extensions of the Flp-recombinase-mediated cassette-exchange technology. J Mol Biol 402(1):52–69
Turan S, Zehe C, Kuehle J, Qiao J, Bode J (2013) Recombinase-mediated cassette exchange (RMCE)—a rapidly-expanding toolbox for targeted genomic modifications. Gene 515(1):1–27
Pavlopoulos A, Oehler S, Kapetanaki MG, Savakis C (2007) The DNA transposon Minos as a tool for transgenesis and functional genomic analysis in vertebrates and invertebrates. Genome Biol 8(Suppl 1):S2
Sasakura Y, Oogai Y, Matsuoka T, Satoh N, Awazu S (2007) Transposon mediated transgenesis in a marine invertebrate chordate: ciona intestinalis. Genome Biol 8(Suppl 1):S3
Kawakami K (2007) Tol2: a versatile gene transfer vector in vertebrates. Genome Biol 8(Suppl 1):S7
Sato Y, Kasai T, Nakagawa S, Tanabe K, Watanabe T, Kawakami K, Takahashi Y (2007) Stable integration and conditional expression of electroporated transgenes in chicken embryos. Dev Biol 305(2):616–624
Shibano T, Takeda M, Suetake I, Kawakami K, Asashima M, Tajima S, Taira M (2007) Recombinant Tol2 transposase with activity in Xenopus embryos. FEBS Lett 581(22):4333–4336
Urasaki A, Mito T, Noji S, Ueda R, Kawakami K (2008) Transposition of the vertebrate Tol2 transposable element in Drosophila melanogaster. Gene 425(1–2):64–68
Clark KJ, Balciunas D, Pogoda HM, Ding Y, Westcot SE, Bedell VM, Greenwood TM, Urban MD, Skuster KJ, Petzold AM, Ni J, Nielsen AL, Patowary A, Scaria V, Sivasubbu S, Xu X, Hammerschmidt M, Ekker SC (2011) In vivo protein trapping produces a functional expression codex of the vertebrate proteome. Nat Methods 8(6):506–515
Trinh LA, Hochgreb T, Graham M, Wu D, Ruf-Zamojski F, Jayasena CS, Saxena A, Hawk R, Gonzalez-Serricchio A, Dixson A, Chow E, Gonzales C, Leung HY, Solomon I, Bronner-Fraser M, Megason SG, Fraser SE (2011) A versatile gene trap to visualize and interrogate the function of the vertebrate proteome. Genes Dev 25(21):2306–2320
Kawakami K, Takeda H, Kawakami N, Kobayashi M, Matsuda N, Mishina M (2004) A transposon-mediated gene trap approach identifies developmentally regulated genes in zebrafish. Dev Cell 7(1):133–144
Balciunas D, Wangensteen KJ, Wilber A, Bell J, Geurts A, Sivasubbu S, Wang X, Hackett PB, Largaespada DA, McIvor RS, Ekker SC (2006) Harnessing a high cargo-capacity transposon for genetic applications in vertebrates. PLoS Genet 2(11):e169
Sivasubbu S, Balciunas D, Davidson AE, Pickart MA, Hermanson SB, Wangensteen KJ, Wolbrink DC, Ekker SC (2006) Gene-breaking transposon mutagenesis reveals an essential role for histone H2afza in zebrafish larval development. Mech Dev 123(7):513–529
Trinh LA, Fraser SE (2013) Enhancer and gene traps for molecular imaging and genetic analysis in zebrafish. Dev Growth Differ 55(4):434–445
Bialkowska A, Zhang XY, Reiser J (2005) Improved tagging strategy for protein identification in mammalian cells. BMC Genom 6:113
Kontarakis Z, Konstantinides N, Pavlopoulos A, Averof M (2011) Reconfiguring gene traps for new tasks using iTRAC. Fly (Austin) 5(4):352–355
Funding
This study was supported by the ICG SB RAS budget Project No. 0324-2019- 0042.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fedorova, S.A., Dorogova, N.V. Protein trap: a new Swiss army knife for geneticists?. Mol Biol Rep 47, 1445–1458 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-05181-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-05181-z