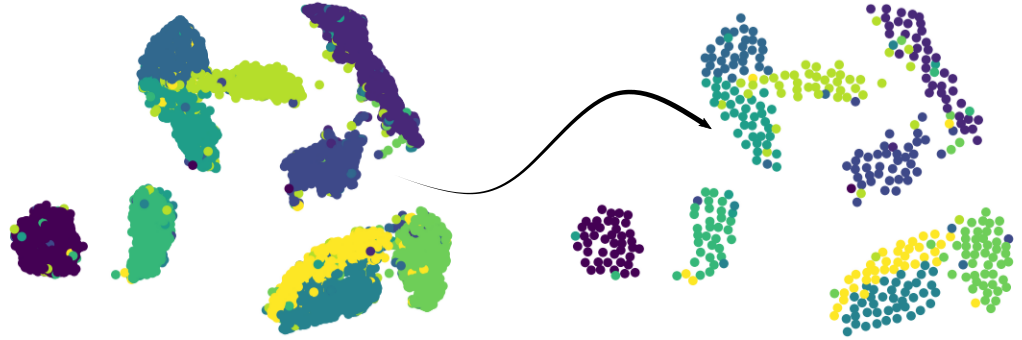
Scatter plot-based representations of dimensionality reduction (such as t-SNE and UMAP) can help us to understand various patterns in high-dimensional datasets. However, due to the huge size of datasets in practical applications, these representations often result in cluttered layouts. With SADIRE, you can reduce the size of the dataset while preserving the context and structural relations imposed by dimensionality reduction techniques.
- SADIRE uses a QuadTree for selecting representative data points, we chose Pyqtree for this matter:
- Pyqtree
@article{MarcilioJr2020_SADIRE,
author = "Marcílio-Jr, W. E. and Eler, D. M.",
year = "2020",
title = "SADIRE: a context-preserving sampling technique for dimensionality reduction visualizations",
journal = "Journal of Visualization",
pages = "999--1013"
}SADIRE samples from a 2D representation of a multidimensional dataset. It was designed to preserve the relationship imposed by a dimensionality reduction technique.
Load a dataset and reduce
iris_data = load_iris()
X, y = iris_data.data, iris_data.targetReduce to 2D
reducer = umap.UMAP(random_state=0)
embedding = reducer.fit_transform(X)Use SADIRE
import sadire
"""
SADIRE uses the concept of windows to select samples and remove redundancy.
* alpha is the size of the window
* beta is the size of each block (or superpixel) in a window
The greater are these parameters, more scattered will be the representative data points.
Using alpha = 2 or 3 and beta between 4 and 10 works fine for the datasets we have tested.
Please, see the paper for more details.
"""
model = sadire.SADIRE(alpha=1, beta=3)SADIRE returns the representative indices
samples = model.fit_transform(embedding)See SADIRE on the MNIST dataset on top.
Please, if you have any questions feel free to contact me at wilson_jr@outlook.com