This project is part of the @thi.ng/umbrella monorepo.
Highly customizable 1D cellular automata, shared env, multiple rules, arbitrary sized/shaped neighborhoods, short term memory, cell states etc..
The generic implementation provided by this package enables many novel and unusual CA setups as well as coevolution of multiple CAs within a shared environment.
This library also forms the core of C-SCAPE, a generative art project by the author. Visit the project site to get a better impression and overview of the multitude of possible results (still nothing more than a small glimpse only)...
Cell neighborhoods are defined via an arbitrary number of 2D offset vectors [x, y], where x coordinates are horizontal offsets and positive y coordinates
are used to refer to previous generations (e.g. 0 = current gen, 1 = T-1, 2 =
T-2 etc.) and thereby providing a form of short term memory for that specific
automata. Negative y coords will lead to cells being ignored.
Automata rules are encoded as JS BigInt values and are considered anisotropic
by default. If isotropy is desired, it has to be explicitly pre-encoded (out of
scope of this library). There's also built-in optional support for position
independent neighborhood encoding, only considering the number/count of non-zero
cells. An encoded rule ID and its overall magnitude is directly related and
dependent on the size and shape of its kernel config, e.g.:
kernel = [[-2, 1], [-1, 0], [0, 0], [1, 0], [2, 1]]This example kernel defines a 5-cell neighborhood with a max. short term memory of one additional previous generation (i.e. the [-2,1] and [2,1] offsets)
The rules related to this kernel have a 32 bit address space (4 billion
possibilities), due to 2^5 = 32 and each kernel offset being assigned a distinct
bit value by default, i.e. first kernel offset = 2^0, second kernel offset =
2^1, third = 2^2, fourth = 2^3, fifth = 2^4. Via the positional config option,
this behavior can be overridden per kernel, to achieve position-independent
kernels (with much smaller rule spaces).
Given the following example cell matrix with the center cell highlighted with
caret (^):
T-1: 2 0 1 2 1
T-0: 0 1 0 3 0
^
The above example kernel will select the following values and assign bit positions (for all non-zero cell states) to compute a summed ID:
| k index | offset | cell value | encoded |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | [-2, 1] |
2 | 2^0 = 1 |
| 1 | [-1, 0] |
1 | 2^1 = 2 |
| 2 | [0, 0] |
0 | 0 |
| 3 | [1, 0] |
3 | 2^3 = 8 |
| 4 | [2, 1] |
1 | 2^4 = 16 |
Final encoded neighborhood sum: 1 + 2 + 8 + 16 = 27
To determine if a the current cell should be active or not in the next generation, we now use that encoded sum as bit position to test a single bit of the automata's rule ID, i.e. here we're testing bit 27. If that corresponding bit is set in the rule ID, the cell's state will be increased by 1.
Each automata config can define a max. number of possible cell states (aka age).
Once a cell reaches the configured numStates, it automatically resets to zero.
This is by default, but can be overridden via the reset option. Conversely, if
the corresponding bit is not set in the rule ID, the cell state will be zeroed
too.
By default the environment is configured to be toroidal, i.e. both left/right
sides of the env are connected. The behavior can be controlled via a ctor arg
and/or at runtime via the wrap property.
The mask array can be used to select different CA configurations for each cell
in the environment. Because this mask array is initialized to zero, only the
first CA configuration will be used for all cells in the environment by default.
It's the user's responsibility to manage the mask and select/enable other (if
any) CA configs for individual cells (usually cell ranges). The values stored in
this array correspond to the indices of the CA configurations given at
construction.
Due to using Uint8Arrays for storage, only up to 256 cell states are
supported. The same limit applies to the number of CA configs given.
STABLE - used in production
Search or submit any issues for this package
- @thi.ng/lsys - Functional, extensible L-System architecture w/ support for probabilistic rules
- @thi.ng/pixel - Typedarray integer & float pixel buffers w/ customizable formats, blitting, drawing, convolution
yarn add @thi.ng/cellularES module import:
<script type="module" src="https://cdn.skypack.dev/@thi.ng/cellular"></script>For Node.js REPL:
# with flag only for < v16
node --experimental-repl-await
> const cellular = await import("@thi.ng/cellular");
Package sizes (gzipped, pre-treeshake): ESM: 1.24 KB
import { MultiCA1D } from "@thi.ng/cellular";
import { defIndexed, intBuffer } from "@thi.ng/pixel";
import { asPPM } from "@thi.ng/pixel-io-netpbm";
import { writeFileSync } from "fs";
const WIDTH = 512;
const HEIGHT = 512;
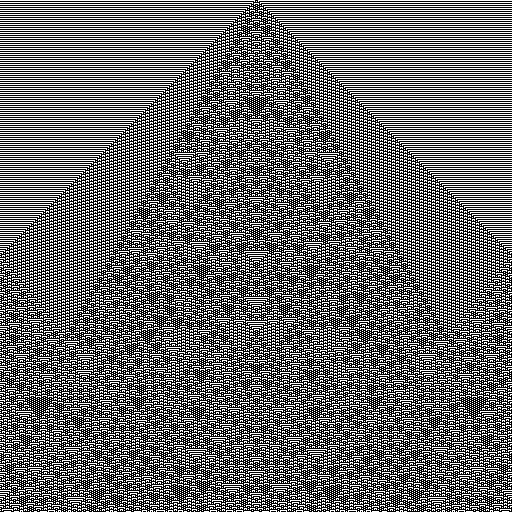
// define standard 1D Wolfram CA (3-neighborhood, 2 states)
const ca = new MultiCA1D(
[
{
rule: 73,
// kernel can be imported as `WOLFRAM3`
kernel: [[-1, 0],[0, 0],[1, 0]],
states: 2,
reset: false,
},
],
WIDTH
);
// seed a single cell in center
ca.current[WIDTH/2] = 1;
// create image with indexed color model (2 cell states => 2 colors)
const img = intBuffer(WIDTH, HEIGHT, defIndexed([0xff000000, 0xffffffff]));
// compute the CA for entire image
ca.updateImage(img.data, HEIGHT);
// write as PPM file
writeFileSync("export/out.ppm", asPPM(img));Result:
import { multiColorGradient, srgb } from "@thi.ng/color";
// create CA with 2 rules/kernels (5-neighborhoods) and 64 states (max age)
const ca = new MultiCA1D(
[
{
rule: 0x73ed2ac2,
// kernel can be imported as `WOLFRAM5`
kernel: [[-2, 0], [-1, 0], [0, 0], [1, 0], [2, 0]],
states: 64,
},
{
rule: 0xef14e4ca,
// kernel can be imported as `WOLFRAM5`
kernel: [[-2, 0], [-1, 0], [0, 0], [1, 0], [2, 0]],
states: 64,
}
],
WIDTH
);
// seed cells with 10% noise
ca.setNoise("cells", 0.1);
// set mask to stripe pattern to select both CAs
ca.setPattern("mask", WIDTH / 4, WIDTH / 2, 1, 0, WIDTH / 8);
// alternatively apply noise to the mask to create
// more uniformly hybrid/mixed results
// ca.setNoise("mask", 0.5);
// create color gradient to visualize the different cell states
// and wrap as indexed color model for pixel buffer below...
// references:
// https://docs.thi.ng/umbrella/color/modules.html#multiColorGradient
// https://docs.thi.ng/umbrella/pixel/modules.html#defIndexed
const fmt = defIndexed(
multiColorGradient(
{
num: ca.numStates,
stops: [
[0, srgb(1, 0, 0.5)],
[0.02, srgb(0.8, 1, 1)],
[1, srgb(1, 0.5, 0)],
],
},
false
)
);
// create image / pixel buffer using above indexed color model
const img = intBuffer(WIDTH, HEIGHT, fmt);
// compute CA for full image
ca.updateImage(img.data, HEIGHT);
// export as PPM image
writeFileSync("export/out.ppm", asPPM(img));| 1st CA only | 2nd CA only |
|---|---|
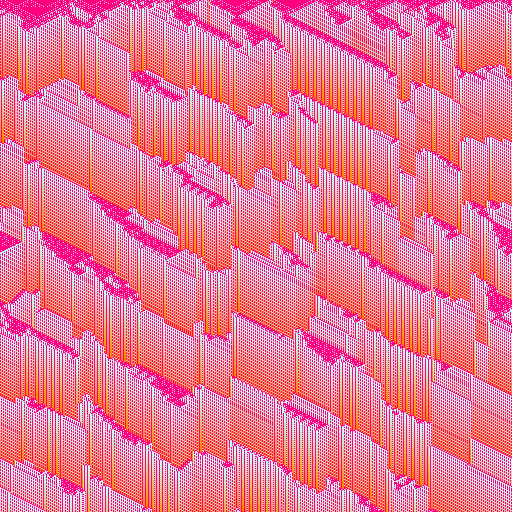 |
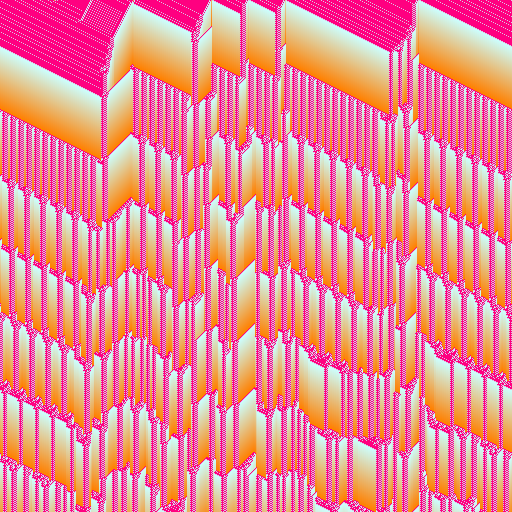 |
| Hybrid (stripe pattern) | Hybrid (noise) |
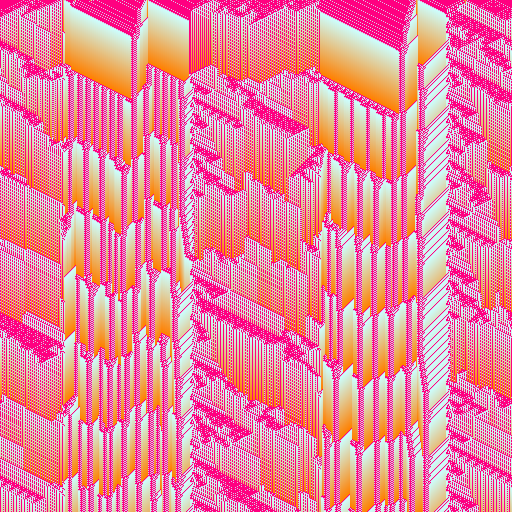 |
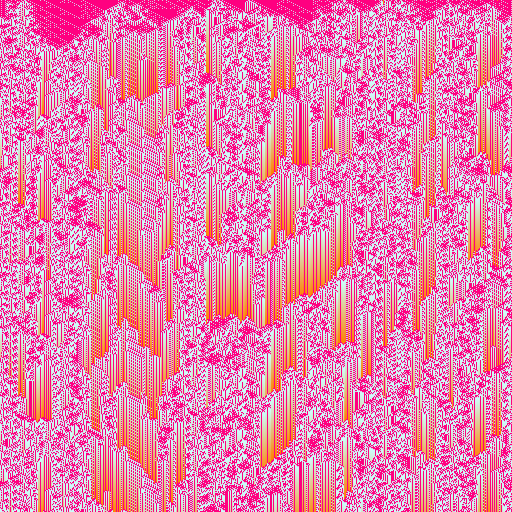 |
Karsten Schmidt
If this project contributes to an academic publication, please cite it as:
@misc{thing-cellular,
title = "@thi.ng/cellular",
author = "Karsten Schmidt",
note = "https://thi.ng/cellular",
year = 2022
}© 2022 Karsten Schmidt // Apache Software License 2.0