This project is part of the @thi.ng/umbrella monorepo and anti-framework.
Sparse & bitwise adjacency matrices, lists and selected traversal algorithms for directed & undirected graphs.
The following types all implement the IGraph
interface and
support both directed & undirected graphs:
- Breadth-First Search
- Depth-First Search
- Floyd-Warshall (global shortest paths search)
- Minimum Spanning Tree
STABLE - used in production
Search or submit any issues for this package
- @thi.ng/dgraph - Type-agnostic directed acyclic graph (DAG) & graph operations
yarn add @thi.ng/adjacencyES module import:
<script type="module" src="https://cdn.skypack.dev/@thi.ng/adjacency"></script>For Node.js REPL:
const adjacency = await import("@thi.ng/adjacency");Package sizes (brotli'd, pre-treeshake): ESM: 2.74 KB
One project in this repo's /examples directory is using this package:
| Screenshot | Description | Live demo | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
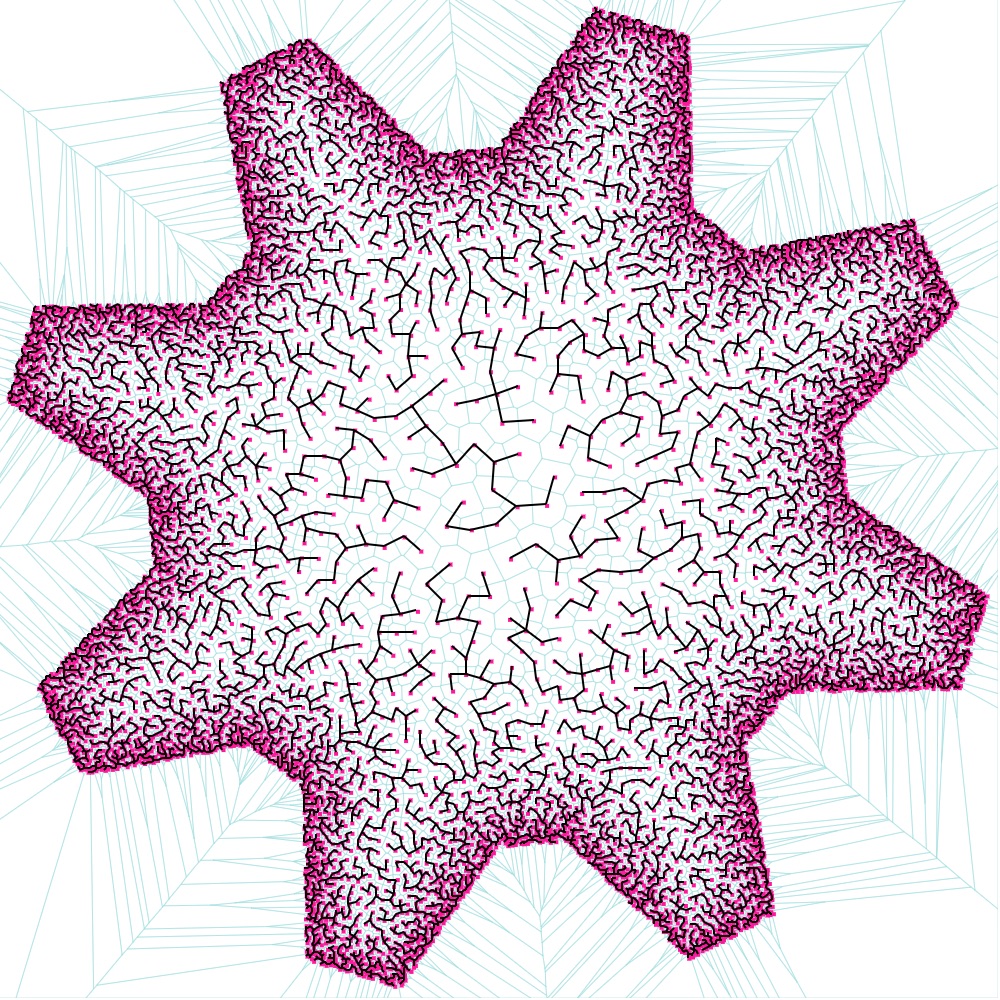 |
Poisson-disk shape-aware sampling, Voronoi & Minimum Spanning Tree visualization | Demo | Source |
TODO
import { defAdjBitMatrix, type Edge } from "@thi.ng/adjacency";
// relationships
const rels = {
a: ["b", "c"],
b: ["d"],
c: ["d", "e"],
e: ["a", "d", "b"],
};
// form set of unique node IDs
const nodeIDs = [
...new Set(Object.entries(rels).flatMap(([id, rels]) => [id, ...rels])),
];
// the current adjacency matrix impls only support numeric node IDs
// therefore, we first map node names to numeric IDs
const index = new Map(nodeIDs.map((id, i) => [id, i]));
// transform relationships into sequence of edges (aka `[from,to]` tuples)
const edges = Object.entries(rels).flatMap(([id, rels]) =>
rels.map((x) => <Edge>[index.get(id), index.get(x)])
);
// build adjacency matrix, treat as undirected graph
// edges can also be added/removed later
const graph = defAdjBitMatrix(nodeIDs.length, edges, true);
// graph queries
console.log("edges:", graph.numEdges(), "verts:", graph.numVertices());
// edges: 8 verts: 5
// check if vertex/node is present in graph
// (this is implementation specific and for the bitmatrix backed version here
// only true if the vertex has at least 1 edge...)
console.log(graph.hasVertex(index.get("d")!));
// true
// are `a` and `d` connected?
console.log(graph.hasEdge(index.get("a")!, index.get("d")!));
// false
// number of connected nodes for `a`
// (in directed graphs, there's also possibility to distinguish between in/out/inout)
console.log(graph.degree(index.get("a")!));
// 3
// neighbors of `a` (with reverse lookup of node names)
console.log(graph.neighbors(index.get("a")!).map((x) => nodeIDs[x]));
// [ 'b', 'c', 'e' ]
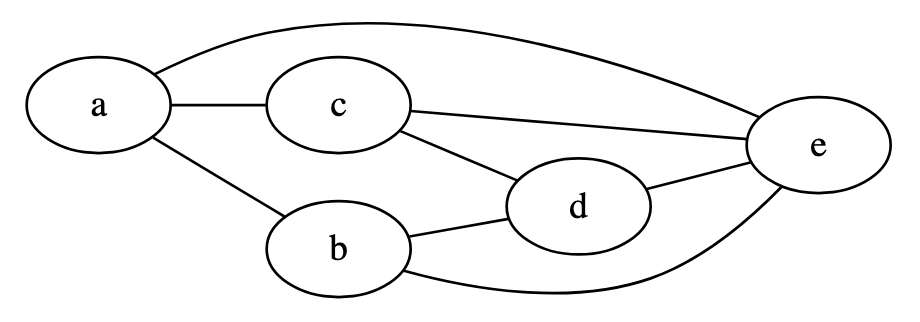
// serialize to GraphViz DOT format (see result visualization below)
console.log(graph.toDot(nodeIDs));
// graph g {
// "d"--"e";
// "c"--"d";
// "c"--"e";
// "b"--"d";
// "b"--"e";
// "a"--"b";
// "a"--"c";
// "a"--"e";
// }
// resize to new capacity & add add/remove vertices/edges
graph.resize(10);
graph.addEdge(4, 5);
graph.removeEdge(0, 1);GraphViz visualization of the above example graph:
- Karsten Schmidt (Main author)
- Igor Loskutov
If this project contributes to an academic publication, please cite it as:
@misc{thing-adjacency,
title = "@thi.ng/adjacency",
author = "Karsten Schmidt and others",
note = "https://thi.ng/adjacency",
year = 2018
}© 2018 - 2023 Karsten Schmidt // Apache License 2.0