This project is part of the @thi.ng/umbrella monorepo and anti-framework.
Text based canvas, drawing, tables with arbitrary formatting (incl. ANSI/HTML).
STABLE - used in production
Search or submit any issues for this package
- @thi.ng/text-format - Customizable color text formatting with presets for ANSI & HTML
yarn add @thi.ng/text-canvasES module import:
<script type="module" src="https://cdn.skypack.dev/@thi.ng/text-canvas"></script>For Node.js REPL:
const textCanvas = await import("@thi.ng/text-canvas");Package sizes (brotli'd, pre-treeshake): ESM: 5.41 KB
- @thi.ng/api
- @thi.ng/arrays
- @thi.ng/checks
- @thi.ng/errors
- @thi.ng/geom-clip-line
- @thi.ng/math
- @thi.ng/strings
- @thi.ng/text-format
- @thi.ng/transducers
Several demos in this repo's /examples directory are using this package.
A selection:
| Screenshot | Description | Live demo | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
ASCII art raymarching with thi.ng/shader-ast & thi.ng/text-canvas | Demo | Source |
 |
3D wireframe textmode demo | Demo | Source |
 |
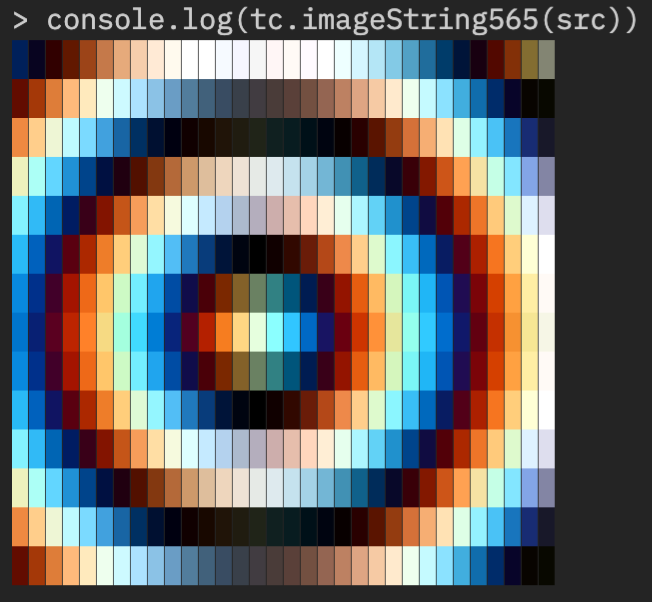
Textmode image warping w/ 16bit color output | Demo | Source |
const c = canvas(width, height, format?, style?);The text canvas stores all characters in a Uint32Array with the lower 16 bits
used for the UTF-16 code and the upper 16 bits for abitrary formatting data.
The package utilizes format identifier constants and formatters from the
@thi.ng/text-format
package,
which are tailored for the included ANSI & HTML formatters, but users are free to
choose use any other system (but then will also need to implement a custom
string formatter impl).
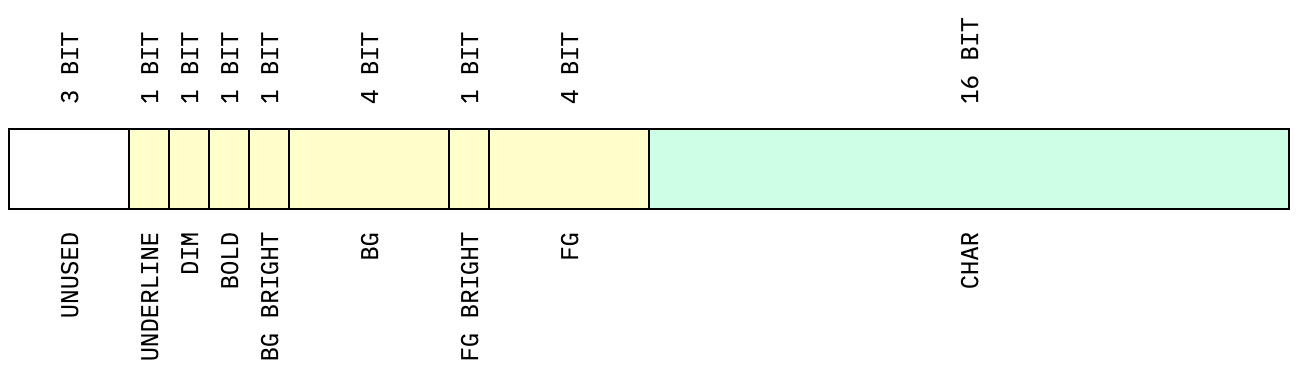
The default format ID layout used by text canvas is as shown:
Most drawing functions accept an optional format arg, but a default
format can also be set via setFormat(canvas, formatID).
The format IDs defined in @thi.ng/text-format are only compatible with these formatters (also supplied by that package):
FMT_ANSI16FMT_HTML_INLINE_CSSFMT_HTML_TACHYONS
All constants and other formatters are also discussed in detail in the @thi.ng/text-format readme.
These color IDs MUST be prefixed with either FG_ (foreground) or BG_
(background):
BLACKREDGREENYELLOWBLUEMAGENTACYANGRAYWHITELIGHT_GRAYLIGHT_REDLIGHT_GREENLIGHT_YELLOWLIGHT_BLUELIGHT_MAGENTALIGHT_CYAN
BOLDDIMUNDERLINE
Format IDs can be combined via the binary OR operator (|), e.g.:
setFormat(canvas, FG_BLACK | BG_LIGHT_CYAN | BOLD | UNDERLINE);Canvas-to-string conversion is completely customizable via the StringFormat
interface.
Currently the following presets are supplied (in the
@thi.ng/text-format
package):
FMT_ANSI16- translate built-in format IDs to 4-bit ANSI escape sequencesFMT_ANSI256- uses all 16 format bits for fg & bg colors (ANSI esc sequences)FMT_ANSI565- uses all 16 format bits for RGB565 fg colors (ANSI esc sequences)FMT_ANSI_RAW- verbatim use of format IDs to ANSI sequencesFMT_HTML_INLINE_CSS- HTML<span>elements with inline CSSFMT_HTML_TACHYONS- HTML<span>elements with Tachyons CSS class namesFMT_HTML565- HTML<span>elements with RGB565 color codingFMT_NONE- dummy formatter outputting plain text only (all format information discarded, e.g. forNO_COLORsupport)
// Terminal
console.log(formatCanvas(canvas, FMT_ANSI16));
// or
console.log(formatCanvas(canvas, FMT_ANSI256));
// Browser
const el = document.createElement("pre");
el.innerHTML = formatCanvas(canvas, FMT_HTML_TACHYONS);Built-in style presets:
STYLE_ASCIISTYLE_THINSTYLE_THIN_ROUNDEDSTYLE_DASHEDSTYLE_DASHED_ROUNDEDSTYLE_DOUBLE
Functions:
beginStyle(canvas, style)endStyle(canvas)
All drawing operations are constrained to the currently active clipping rect (by default full canvas). The canvas maintains a stack of such clipping regions, each newly pushed one being intersected with the previous top-of-stack rect:
beginClip(canvas, x, y, w, h)- push new clip rectendClip(canvas)- restore previous clip rect
┌──────────────────┐
│ A │
│ ╔════════╗─────────┐
│ ║ ║ │
│ ║ A & B ║ │
│ ║ ║ │
└─────────╚════════╝ │
│ B │
└──────────────────┘
-
line -
hline -
vline -
circle -
clear -
fillRect -
strokeRect
blitresizeextractscrollVimage/imageRaw/imageCanvas565/imageString565imageBraille/imageCanvasBraille/imageStringBraille
import { RGB565 } from "@thi.ng/pixel";
import { read } from "@thi.ng/pixel-io-netpbm";
// resize non-proportionally (to compensate
// for character aspect ratio, YMMV)
const img = read(readFileSync("chroma-rings.ppm"))
.resize(32, 32 / 2.25)
.as(RGB565)
// requires an ANSI 24bit compatible terminal
console.log(imageString565(img));textLinetextLinestextColumn(word wrapped)textBox(word wrapped)
The following are string builders only, draw result via text functions:
barHorizontalbarVerticalbarChartHStrbarChartVStr
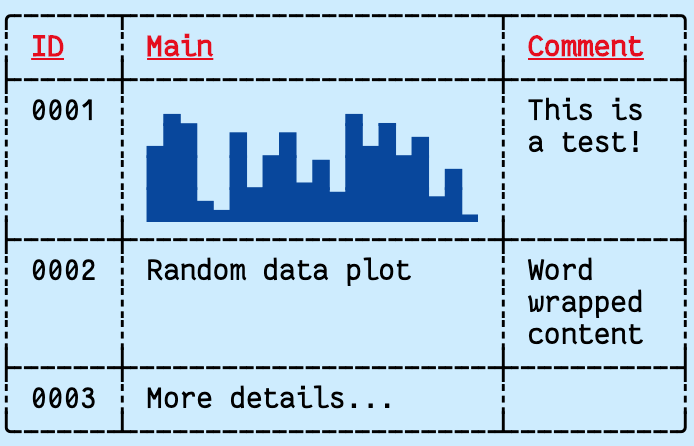
Tables support individual column width, automatic (or user defined) row heights, cell padding, as well as global and per-cell formats and the following border style options:
| Border style | Result |
|---|---|
Border.ALL |
 |
Border.NONE |
 |
Border.H |
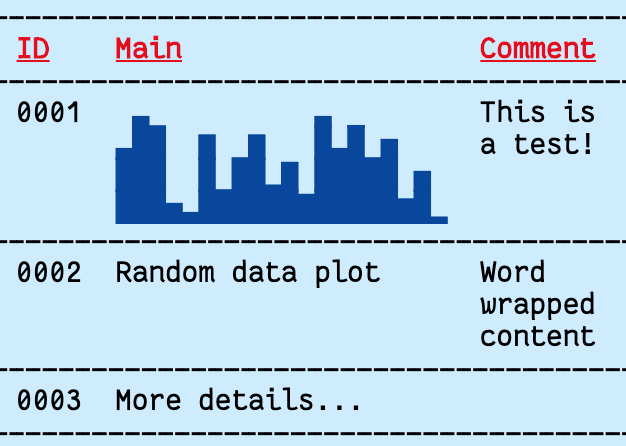 |
Border.V |
 |
Border.FRAME |
 |
Border.FRAME_H |
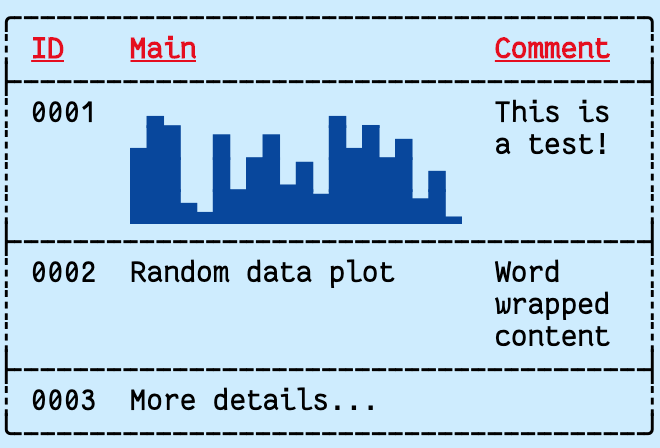 |
Border.FRAME_V |
 |
Table cell contents will be word-wrapped. By default, individual words longer
than the configured cell width will be truncated, but can be forced to wrap by
enabling the hard option (see example below).
import { repeatedly } from "@thi.ng/transducers";
import * as tc from "@thi.ng/text-canvas";
import * as tf from "@thi.ng/text-format";
// generate 20 random values
const data = repeatedly(() => Math.random(), 20)
// format as bar chart string
const chart = tc.barChartHStr(4, data, 0, 1);
// create text canvas
const canvas = new tc.Canvas(64, 20);
// create table
tc.table(
canvas,
0,
0,
{
// column defs
cols: [{ width: 4 }, { width: 20 }, { width: 8 }],
// default cell format
format: tf.FG_BLACK | tf.BG_LIGHT_CYAN,
// default format for header cells (1st row)
formatHead: tf.FG_RED | tf.BG_LIGHT_CYAN | tf.BOLD | tf.UNDERLINE,
// border line style
style: tc.STYLE_DASHED_ROUNDED,
// border mode
border: tc.Border.ALL,
// internal cell padding [h,v]
padding: [1, 0],
// hard word wrap
hard: true,
},
// table contents (row major)
// each cell either a string or RawCell object
[
["ID", "Main", "Comment"],
[
"0001",
{ body: chart, format: tf.FG_BLUE | tf.BG_LIGHT_CYAN },
"This is a test!"
],
["0002", "Random data plot", "Word wrapped content"],
["0003", { body: "More details...", height: 4 }, ""]
]
);
// output as ANSI formatted string
console.log(tc.formatCanvas(canvas, tf.FMT_ANSI16));For even more detailed control, tables can also be pre-initialized prior
to creation of the canvas via
initTable()
and then drawn via
drawTable().
The initTable function returns an object also containing the computed
table size (width, height keys) which can then be used to create a
canvas with the required size...
For convenience, the tableCanvas() function can be used to combine
these steps and to create an auto-sized canvas with the rendered table
as content.
┌───┐
┌──────────────────────┐
│ @thi.ng/text-canvas │
│ wireframe cube │++++++++++
│ │ +++++++++++ ┌───┐
│ x: 0.42 │ ++++│ 6 │
│ y: 0.30 │ ┌───┐ ++++++++ └───┘
└──────────────────────┘++++++++│ 7 │+ +
+ └───┘ └───┘ +
+ + + +
+ + + +
+ + + +
+ + + +
+ + + +
+ + + +
+ + + +
+ + ┌───┐ +
+ + +│ 3 │ +
+ ┌───┐+++ └───┘ +
+ │ 0 │ + +
+ └───┘ + +
+ + + +
+ + + +
+ + + +
+ + + +
+ + ┌───┐
+ + │ 2 │
+ + ++└───┘
+ + +++
+ + ++
+ + +++
++ ++
Code for this above example output (CLI version):
import * as geom from "@thi.ng/geom";
import * as mat from "@thi.ng/matrices";
import * as tc from "@thi.ng/text-canvas";
import * as tf from "@thi.ng/text-format";
const W = 64;
const H = 32;
// create text canvas
const canvas = new tc.Canvas(W, H, tf.BG_BLACK, tf.STYLE_THIN);
// cube corner vertices
const cube = geom.vertices(geom.center(geom.aabb(1))!);
// edge list (vertex indices)
const edges = [
[0, 1], [1, 2], [2, 3], [3, 0], [4, 5], [5, 6],
[6, 7], [7, 4], [0, 4], [1, 5], [2, 6], [3, 7]
];
// animated parameters
let rotx = 0;
let roty = 0;
// 3D transformation matrices
const view = mat.lookAt([], [0, 0, 1], [0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0]);
const proj = mat.perspective([], 90, W / H, 0.1, 10);
const viewp = mat.viewport([], 0, W, H, 0);
setInterval(() => {
tc.clear(canvas, true);
// model rotation matrix
const model = mat.concat(
[],
mat.rotationX44([], rotx += 0.01),
mat.rotationY44([], roty += 0.03)
);
// combined model-view-projection matrix
const mvp = mat.concat([], proj, view, model);
// draw cube instances
// project 3D points to 2D viewport (canvas coords)
const pts = cube.map((p) => mat.project3([], mvp, viewp, p)!);
// draw cube edges
for (let e of edges) {
const a = pts[e[0]];
const b = pts[e[1]];
tc.line(canvas, a[0], a[1], b[0], b[1], "+", tf.FG_WHITE | tf.BG_RED);
}
// draw vertex labels
canvas.format = tf.FG_WHITE | tf.BG_BLUE;
for (let i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
const p = pts[i];
tc.textBox(canvas, p[0] - 1, p[1] - 1, 5, 3, ` ${i} `);
}
tc.textBox(
canvas,
2, 1, 24, -1,
`@thi.ng/text-canvas wireframe cube\n\nx: ${rotx.toFixed(2)}\ny: ${roty.toFixed(2)}`,
{
format: tf.FG_BLACK | tf.BG_LIGHT_CYAN,
padding: [1, 0]
}
);
// draw canvas
console.clear();
// output as ANSI formatted string
console.log(tc.formatCanvas(canvas, tf.FMT_ANSI16));
// output as plain text
// console.log(tc.formatCanvas(canvas));
}, 15);If this project contributes to an academic publication, please cite it as:
@misc{thing-text-canvas,
title = "@thi.ng/text-canvas",
author = "Karsten Schmidt",
note = "https://thi.ng/text-canvas",
year = 2020
}© 2020 - 2023 Karsten Schmidt // Apache License 2.0