JFrog Frogbot is a Git bot that scans your Git repositories for security vulnerabilities.
- It scans pull requests immediately after they are opened but before they are merged. This process notifies you if the pull request is about to introduce new vulnerabilities to your code. This unique capability ensures the code is scanned and can be fixed even before vulnerabilities are introduced into the codebase.
- It scans the Git repository periodically and creates pull requests with fixes for detected vulnerabilities.
- Software Composition Analysis (SCA): Scan your project dependencies for security issues. For selected security issues, get leverage-enhanced CVE data from our JFrog Security Research team. Frogbot uses JFrog's vast vulnerabilities database, to which we continuously add new component vulnerability data. Also included is VulnDB, the industry's most comprehensive security database, to further extend the range of vulnerabilities detected and fixed by Frogbot.
- Validate Dependency Licenses: Ensure that the licenses for the project's dependencies are in compliance with a predefined list of approved licenses.
- Static Application Security Testing (SAST): Provides fast and accurate security-focused engines that detect zero-day security vulnerabilities on your source code sensitive operations, while minimizing false positives.
- CVE Vulnerability Contextual Analysis: This feature uses the code context to eliminate false positive reports on vulnerable dependencies that are not applicable to the code. For CVE vulnerabilities that are applicable to your code, Frogbot will create pull request comments on the relevant code lines with full descriptions regarding the security issues caused by the CVE. Vulnerability Contextual Analysis is currently supported for Python, JavaScript, and Java code.
- Secrets Detection: Detect any secrets left exposed inside the code. to stop any accidental leak of internal tokens or credentials.
- Infrastructure as Code scans (IaC): Scan Infrastructure as Code (Terraform) files for early detection of cloud and infrastructure misconfigurations.
NOTE: SAST, Vulnerability Contextual Analysis, Secrets Detection and Infrastructure as Code scans require the JFrog Advanced Security Package.
Set up Frogbot on your preferred CI server:
Optional - set up a FREE JFrog Environment in the Cloud
Frogbot requires a JFrog environment to scan your projects. If you don't have an environment, we can set up a free environment in the cloud for you. Just run one of the following commands in your terminal to set up an environment in less than a minute.
The commands will do the following:
- Install JFrog CLI on your machine.
- Create a FREE JFrog environment in the cloud for you.
For macOS and Linux, use curl
curl -fL "https://getcli.jfrog.io?setup" | sh
For Windows, use PowerShell
powershell "Start-Process -Wait -Verb RunAs powershell '-NoProfile iwr https://releases.jfrog.io/artifactory/jfrog-cli/v2-jf/[RELEASE]/jfrog-cli-windows-amd64/jf.exe -OutFile $env:SYSTEMROOT\system32\jf.exe'" ; jf setup
After the setup is complete, you'll receive an email with your JFrog environment connection details, which can be stored as secrets in Git.
Advanced - Customize advanced settings with frogbot-config.yml
Scanning pull requests
General
Frogbot uses JFrog Xray (version 3.29.0 and above is required) to scan your pull requests. It adds the scan results as a comment on the pull request. If no new vulnerabilities are found, Frogbot will also add a comment, confirming this.
The following features use the package manager used for building the project:
- Software Composition Analysis (SCA)
- Vulnerability Contextual Analysis
How to use Pull Request scanning?
GitHub
After you create a new pull request, the maintainer of the Git repository can trigger Frogbot to scan the pull request from the pull request UI.
NOTE: The scan output will include only new vulnerabilities added by the pull request. Vulnerabilities that aren't new, and existed in the code before the pull request was created, will not be included in the report. In order to include all of the vulnerabilities in the report, including older ones that weren't added by this PR, use the includeAllVulnerabilities parameter in the frogbot-config.yml file.
The Frogbot GitHub scan workflow is:
-
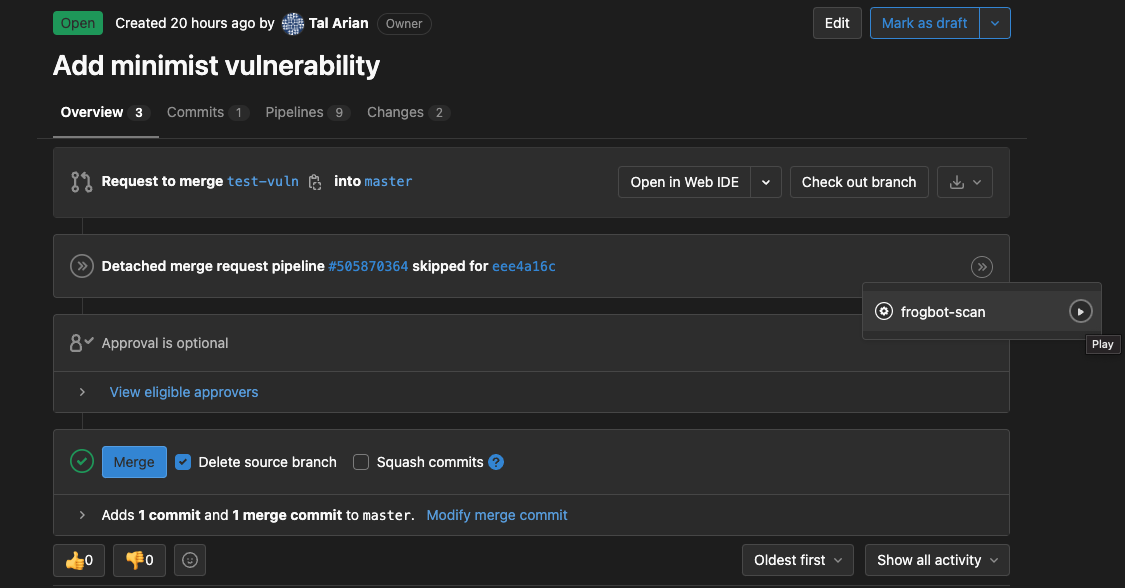
The developer opens a pull request.
-
The Frogbot workflow automatically gets triggered and a GitHub environment named
frogbotbecomes pending for the maintainer's approval.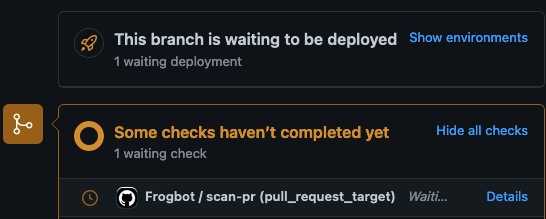
-
The maintainer of the repository reviews the pull request and approves the scan:

-
Frogbot can be triggered again following new commits, by repeating steps 2 and 3.
GitLab
After you create a new merge request, the maintainer of the Git repository can trigger Frogbot to scan the merge request from the merge request UI.
NOTE: The scan output will include only new vulnerabilities added by the merge request. Vulnerabilities that aren't new, and existed in the code before the merge request was created, will not be included in the report. In order to include all of the vulnerabilities in the report, including older ones that weren't added by this merge request, use the includeAllVulnerabilities parameter in the frogbot-config.yml file.
The Frogbot GitLab flow is as follows:
- The developer opens a merge request.
- The maintainer of the repository reviews the merge request and approves the scan by triggering the manual frogbot-scan job.
- Frogbot is then triggered by the job, it scans the merge request and adds a comment with the scan results.
- Frogbot can be triggered again following new commits, by triggering the frogbot-scan job again.
Azure Repos
After you create a new pull request, Frogbot will automatically scan it.
NOTE: The scan output will include only new vulnerabilities added by the pull request. Vulnerabilities that aren't new, and existed in the code before the pull request was created, will not be included in the report. In order to include all the vulnerabilities in the report, including older ones that weren't added by this PR, use the includeAllVulnerabilities parameter in the frogbot-config.yml file.
The Frogbot Azure Repos scan workflow is:
- The developer opens a pull request.
- Frogbot scans the pull request and adds a comment with the scan results.
- Frogbot can be triggered again following new commits, by adding a comment with the
rescantext.
Bitbucket Server
After you create a new pull request, Frogbot will automatically scan it.
NOTE: The scan output will include only new vulnerabilities added by the pull request. Vulnerabilities that aren't new, and existed in the code before the pull request was created, will not be included in the report. In order to include all of the vulnerabilities in the report, including older ones that weren't added by this PR, use the includeAllVulnerabilities parameter in the frogbot-config.yml file.
The Frogbot scan on Bitbucket Server workflow:
- The developer opens a pull request.
- Frogbot scans the pull request and adds a comment with the scan results.
- Frogbot can be triggered again following new commits, by adding a comment with the
rescantext.
👮 Security note for pull requests scanning
When installing Frogbot using JFrog Pipelines, Jenkins, and Azure DevOps, Frogbot will not wait for a maintainer's approval before scanning newly opened pull requests. Using Frogbot with these platforms is therefore not recommended for open-source projects.
When installing Frogbot using GitHub Actions and GitLab however, Frogbot will initiate the scan only after it is approved by a maintainer of the project. The goal of this review is to ensure that external code contributors don't introduce malicious code as part of the pull request. Since this review step is enforced by Frogbot when used with GitHub Actions and GitLab, it is safe to be used for open-source projects.
Scan results
Frogbot adds the scan results to the pull request in the following format:
👍 No issues
If no new vulnerabilities are found, Frogbot automatically adds the following comment to the pull request:
👎 Issues were found
Software Composition Analysis (SCA)
If new vulnerabilities are found, Frogbot adds them as a comment on the pull request. For example:
VULNERABLE DEPENDENCIES
Vulnerability Contextual Analysis
Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
Infrastructure as Code scans (IaC)
Validate Dependency Licenses
When Frogbot scans newly opened pull requests, it checks the licenses of any new direct project dependencies introduced by the pull request. If Frogbot identifies licenses that are not listed in a predefined set of approved licenses, it appends a comment to the pull request providing this information.
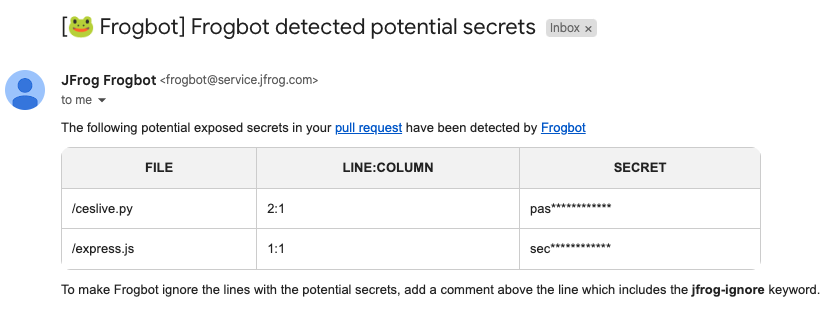
Secrets Detection
When Frogbot detects secrets that have been inadvertently exposed within the code of a pull request, it promptly triggers an email notification to the user who pushed the corresponding commit. The email address utilized for this notification is sourced from the committer's Git profile configuration. Moreover, Frogbot offers the flexibility to direct the email notification to an extra email address if desired. To activate email notifications, it is necessary to configure your SMTP server details as variables within your Frogbot workflows.
Scanning repositories
Frogbot scans your Git repositories periodically and automatically creates pull requests for upgrading vulnerable dependencies to a version with a fix.
For GitHub repositories, issues that are found during Frogbot's periodic scans are also added to the Security Alerts view in the UI. The following alert types are supported:
You can show people that your repository is scanned by Frogbot by adding a badge to the README of your Git repository.
You can add this badge by copying the following markdown snippet and pasting it into your repository's README.md file.
[](https://github.com/jfrog/frogbot#readme)
Please help us improve Frogbot by reporting issues you encounter.
We welcome pull requests from the community. To help us improve this project, please read our Contribution guide.