Colossal-AI: Making large AI models cheaper, faster, and more accessible test
Paper | Documentation | Examples | Forum | Blog
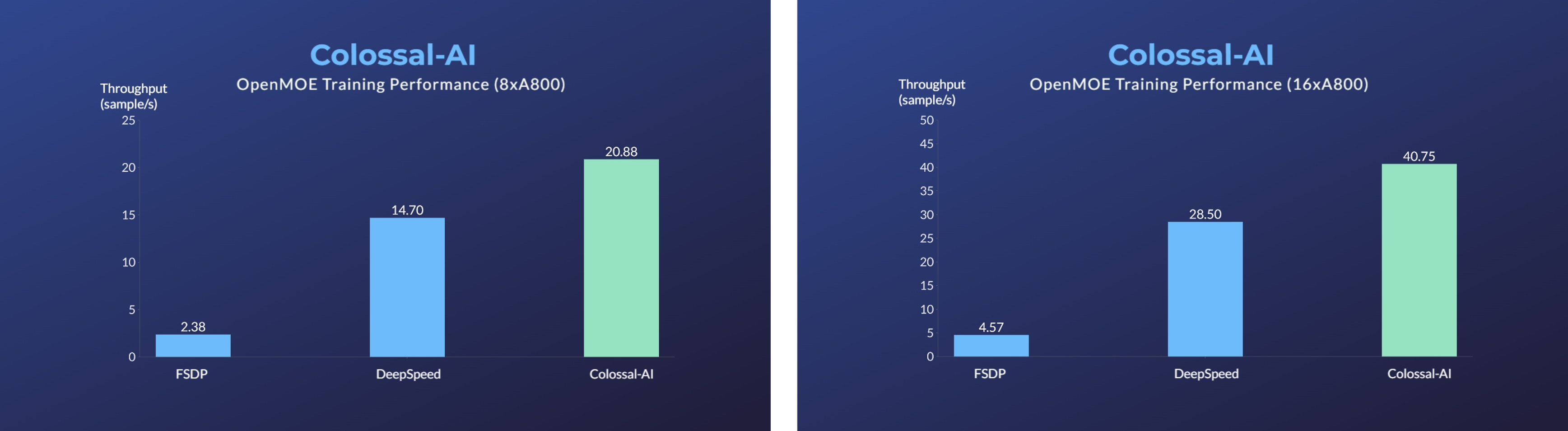
- [2023/11] Enhanced MoE Parallelism, Open-source MoE Model Training Can Be 9 Times More Efficient
- [2023/09] One Half-Day of Training Using a Few Hundred Dollars Yields Similar Results to Mainstream Large Models, Open-Source and Commercial-Free Domain-Specific LLM Solution
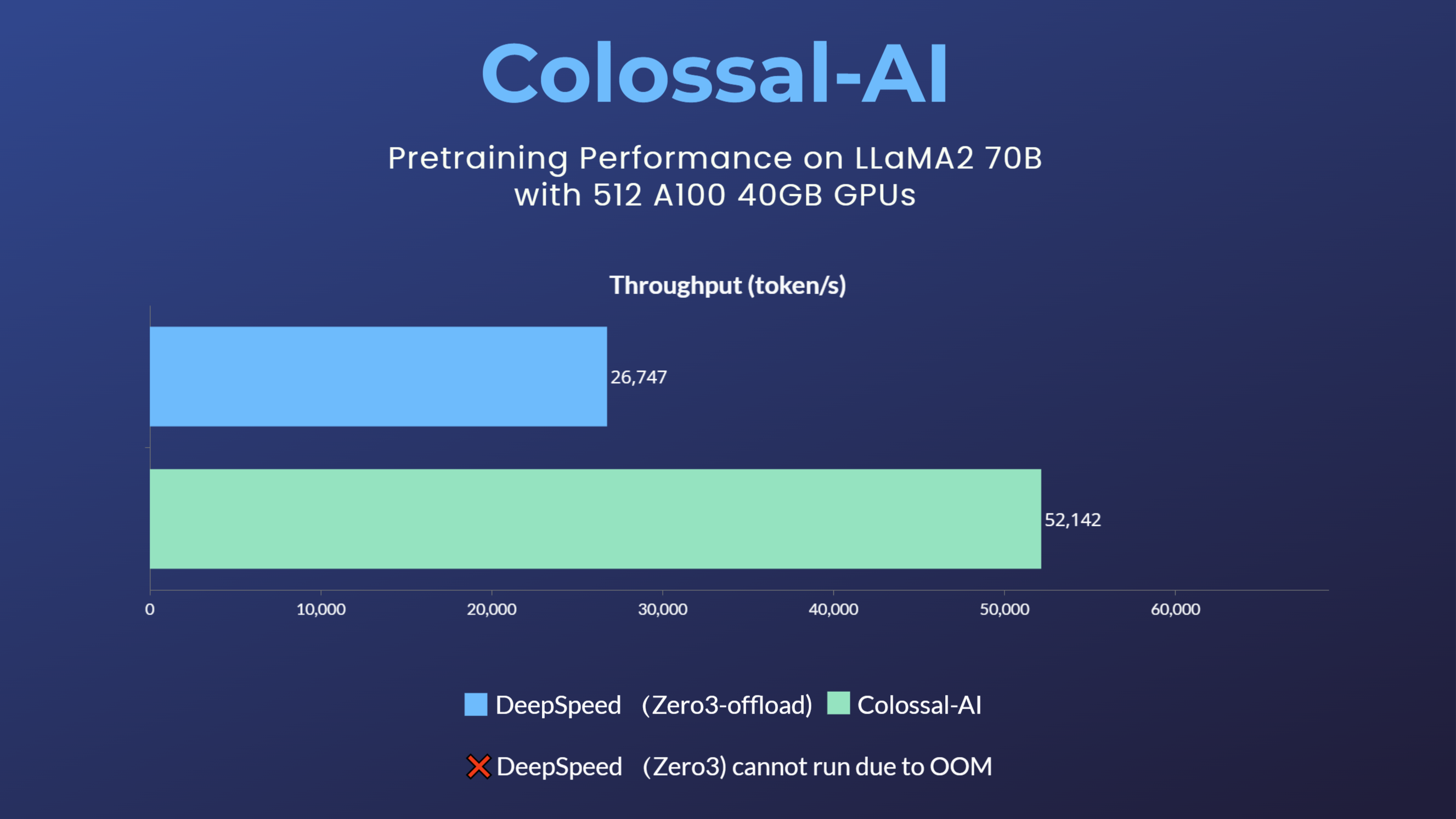
- [2023/09] 70 Billion Parameter LLaMA2 Model Training Accelerated by 195%
- [2023/07] HPC-AI Tech Raises 22 Million USD in Series A Funding
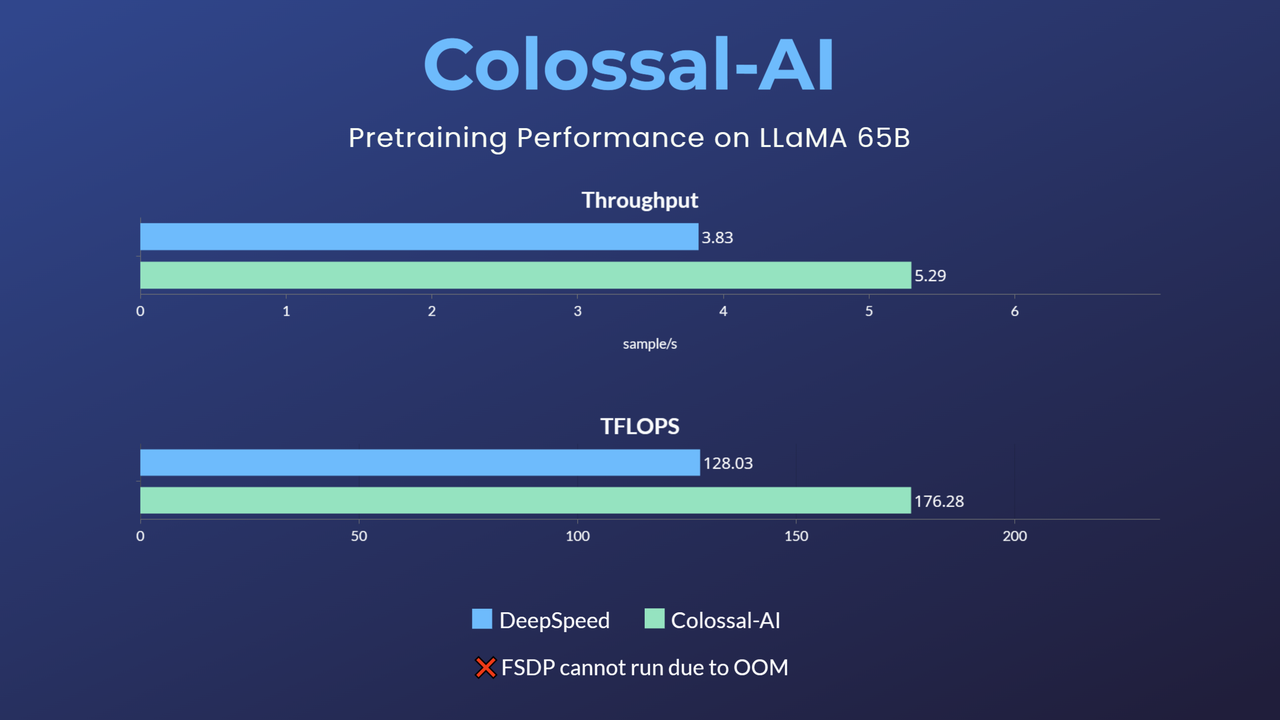
- [2023/07] 65B Model Pretraining Accelerated by 38%, Best Practices for Building LLaMA-Like Base Models Open-Source
- [2023/03] ColossalChat: An Open-Source Solution for Cloning ChatGPT With a Complete RLHF Pipeline
- [2023/03] Intel and Colossal-AI Partner to Deliver Cost-Efficient Open-Source Solution for Protein Folding Structure Prediction
- [2023/03] AWS and Google Fund Colossal-AI with Startup Cloud Programs
- [2023/02] Open Source Solution Replicates ChatGPT Training Process! Ready to go with only 1.6GB GPU Memory
- [2023/01] Hardware Savings Up to 46 Times for AIGC and Automatic Parallelism
- Why Colossal-AI
- Features
-
Colossal-AI for Real World Applications
- Colossal-LLaMA-2: One Half-Day of Training Using a Few Hundred Dollars Yields Similar Results to Mainstream Large Models, Open-Source and Commercial-Free Domain-Specific Llm Solution
- ColossalChat: An Open-Source Solution for Cloning ChatGPT With a Complete RLHF Pipeline
- AIGC: Acceleration of Stable Diffusion
- Biomedicine: Acceleration of AlphaFold Protein Structure
- Parallel Training Demo
- Single GPU Training Demo
- Inference (Energon-AI) Demo
- Installation
- Use Docker
- Community
- Contributing
- Cite Us

Prof. James Demmel (UC Berkeley): Colossal-AI makes training AI models efficient, easy, and scalable.
Colossal-AI provides a collection of parallel components for you. We aim to support you to write your distributed deep learning models just like how you write your model on your laptop. We provide user-friendly tools to kickstart distributed training and inference in a few lines.
-
Parallelism strategies
- Data Parallelism
- Pipeline Parallelism
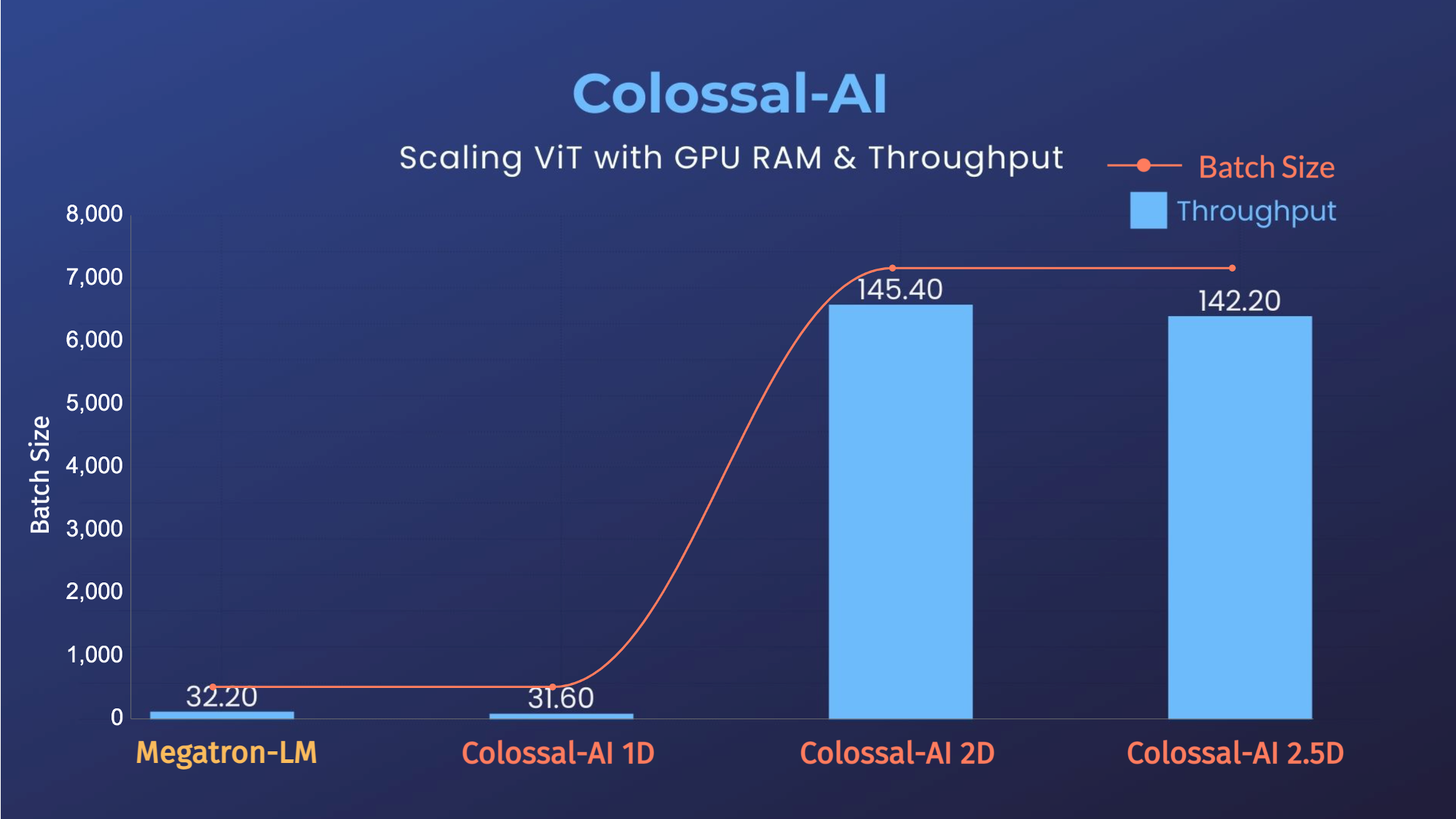
- 1D, 2D, 2.5D, 3D Tensor Parallelism
- Sequence Parallelism
- Zero Redundancy Optimizer (ZeRO)
- Auto-Parallelism
-
Heterogeneous Memory Management
-
Friendly Usage
- Parallelism based on the configuration file
-
Inference
- One half-day of training using a few hundred dollars yields similar results to mainstream large models, open-source and commercial-free domain-specific LLM solution. [code] [blog] [HuggingFace model weights] [Modelscope model weights]
| Backbone | Tokens Consumed | MMLU | CMMLU | AGIEval | GAOKAO | CEval | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | 5-shot | 5-shot | 5-shot | 0-shot | 5-shot | |||
| Baichuan-7B | - | 1.2T | 42.32 (42.30) | 44.53 (44.02) | 38.72 | 36.74 | 42.80 | |
| Baichuan-13B-Base | - | 1.4T | 50.51 (51.60) | 55.73 (55.30) | 47.20 | 51.41 | 53.60 | |
| Baichuan2-7B-Base | - | 2.6T | 46.97 (54.16) | 57.67 (57.07) | 45.76 | 52.60 | 54.00 | |
| Baichuan2-13B-Base | - | 2.6T | 54.84 (59.17) | 62.62 (61.97) | 52.08 | 58.25 | 58.10 | |
| ChatGLM-6B | - | 1.0T | 39.67 (40.63) | 41.17 (-) | 40.10 | 36.53 | 38.90 | |
| ChatGLM2-6B | - | 1.4T | 44.74 (45.46) | 49.40 (-) | 46.36 | 45.49 | 51.70 | |
| InternLM-7B | - | 1.6T | 46.70 (51.00) | 52.00 (-) | 44.77 | 61.64 | 52.80 | |
| Qwen-7B | - | 2.2T | 54.29 (56.70) | 56.03 (58.80) | 52.47 | 56.42 | 59.60 | |
| Llama-2-7B | - | 2.0T | 44.47 (45.30) | 32.97 (-) | 32.60 | 25.46 | - | |
| Linly-AI/Chinese-LLaMA-2-7B-hf | Llama-2-7B | 1.0T | 37.43 | 29.92 | 32.00 | 27.57 | - | |
| wenge-research/yayi-7b-llama2 | Llama-2-7B | - | 38.56 | 31.52 | 30.99 | 25.95 | - | |
| ziqingyang/chinese-llama-2-7b | Llama-2-7B | - | 33.86 | 34.69 | 34.52 | 25.18 | 34.2 | |
| TigerResearch/tigerbot-7b-base | Llama-2-7B | 0.3T | 43.73 | 42.04 | 37.64 | 30.61 | - | |
| LinkSoul/Chinese-Llama-2-7b | Llama-2-7B | - | 48.41 | 38.31 | 38.45 | 27.72 | - | |
| FlagAlpha/Atom-7B | Llama-2-7B | 0.1T | 49.96 | 41.10 | 39.83 | 33.00 | - | |
| IDEA-CCNL/Ziya-LLaMA-13B-v1.1 | Llama-13B | 0.11T | 50.25 | 40.99 | 40.04 | 30.54 | - | |
| Colossal-LLaMA-2-7b-base | Llama-2-7B | 0.0085T | 53.06 | 49.89 | 51.48 | 58.82 | 50.2 |
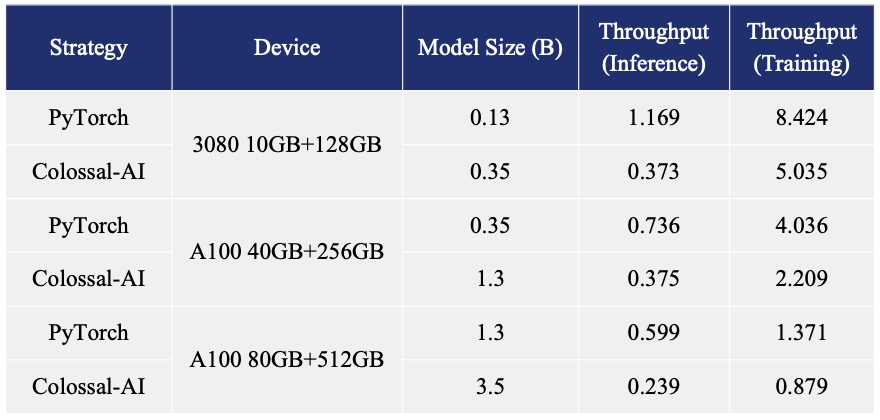
ColossalChat: An open-source solution for cloning ChatGPT with a complete RLHF pipeline. [code] [blog] [demo] [tutorial]
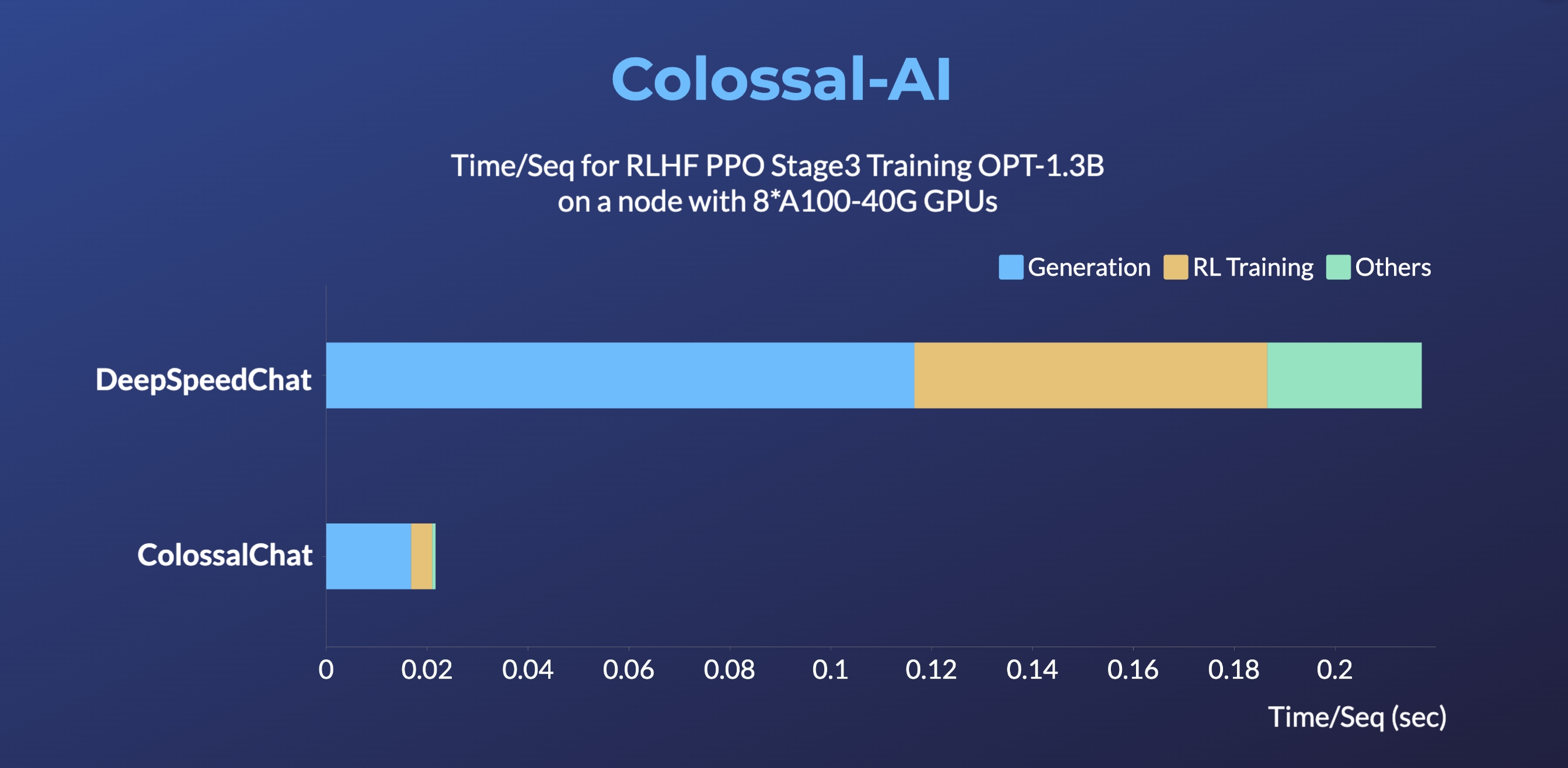
- Up to 10 times faster for RLHF PPO Stage3 Training
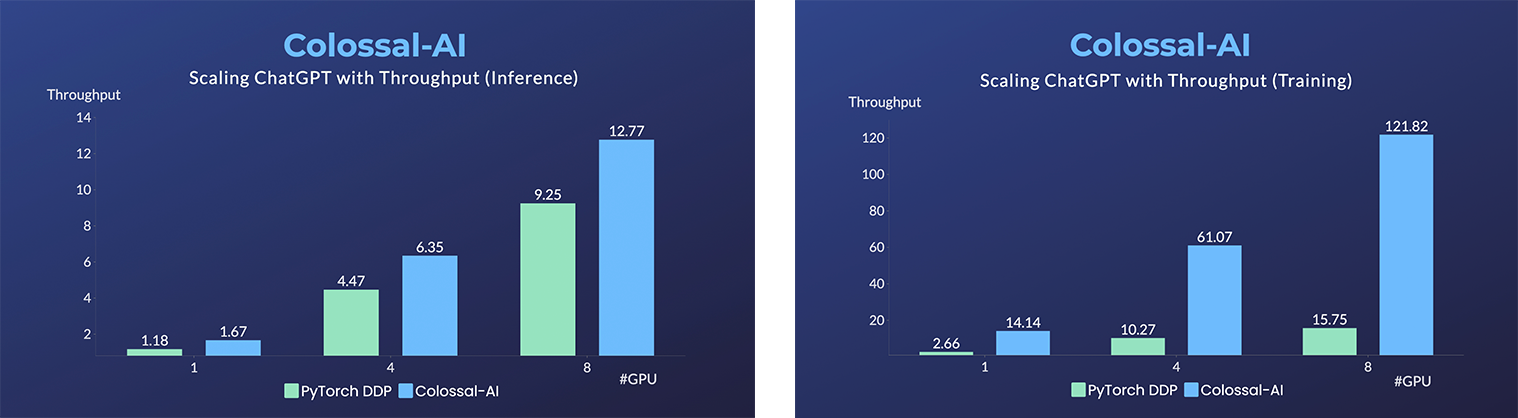
- Up to 7.73 times faster for single server training and 1.42 times faster for single-GPU inference
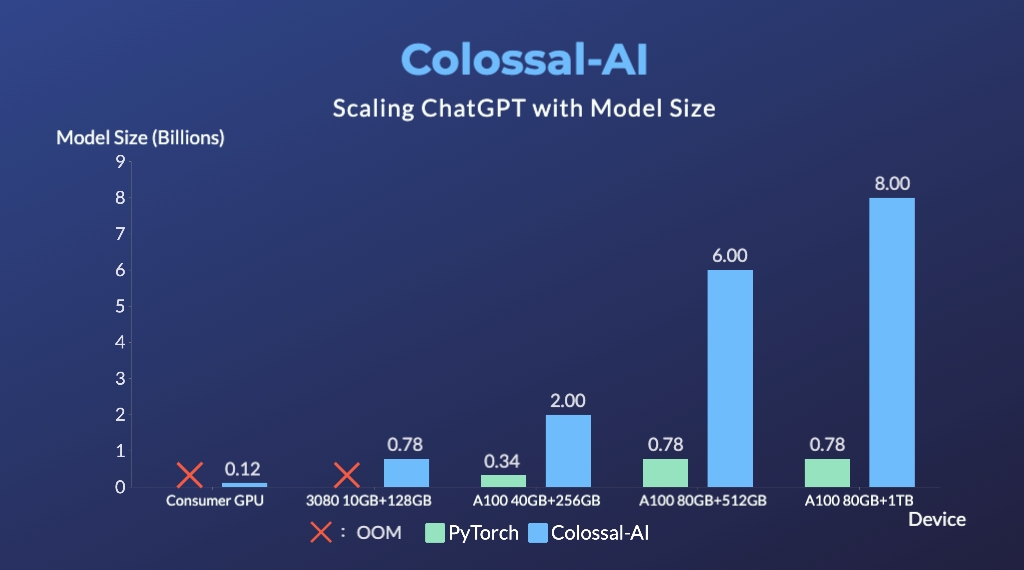
- Up to 10.3x growth in model capacity on one GPU
- A mini demo training process requires only 1.62GB of GPU memory (any consumer-grade GPU)
- Increase the capacity of the fine-tuning model by up to 3.7 times on a single GPU
- Keep at a sufficiently high running speed
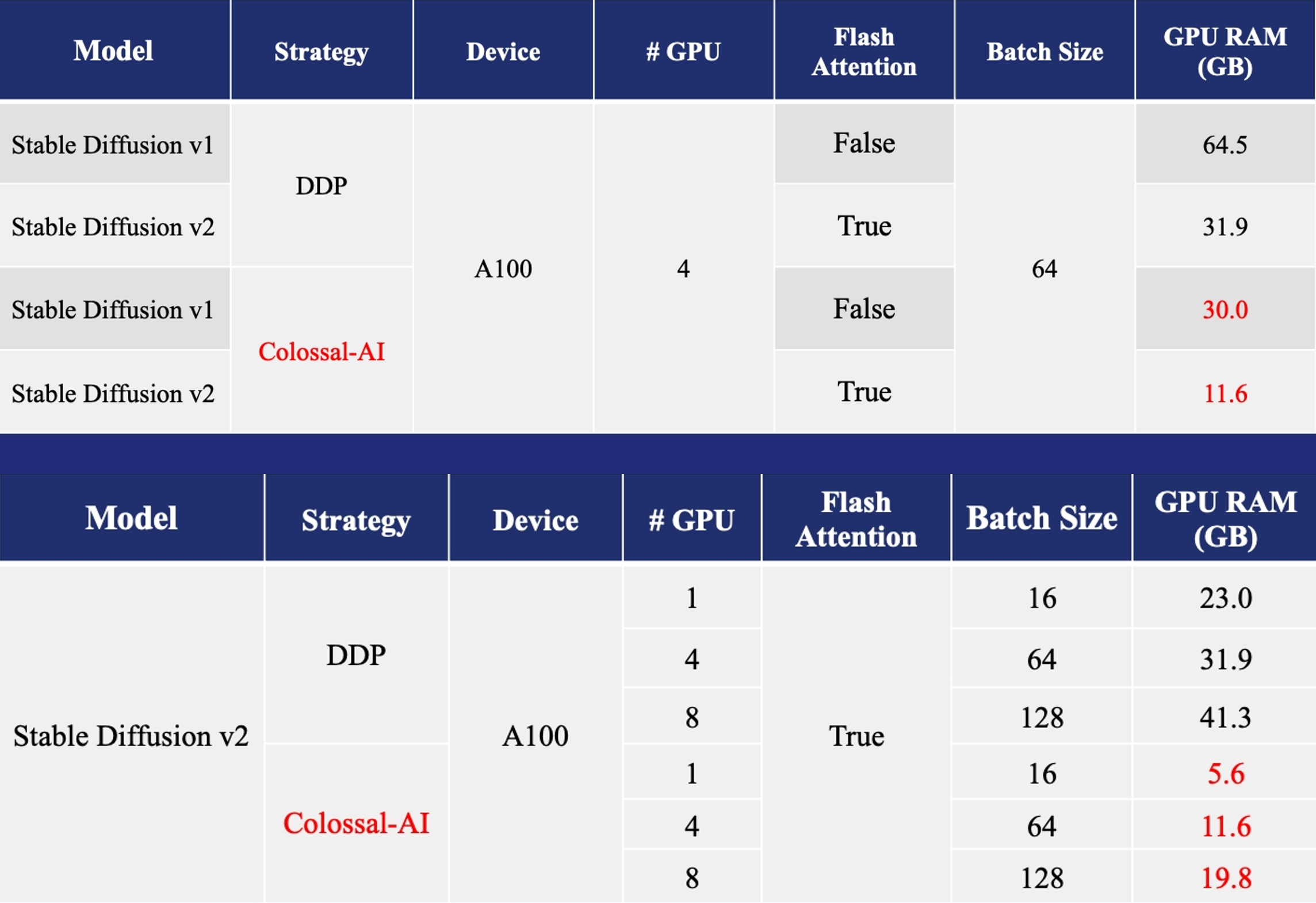
Acceleration of AIGC (AI-Generated Content) models such as Stable Diffusion v1 and Stable Diffusion v2.
- Training: Reduce Stable Diffusion memory consumption by up to 5.6x and hardware cost by up to 46x (from A100 to RTX3060).
- DreamBooth Fine-tuning: Personalize your model using just 3-5 images of the desired subject.
- Inference: Reduce inference GPU memory consumption by 2.5x.
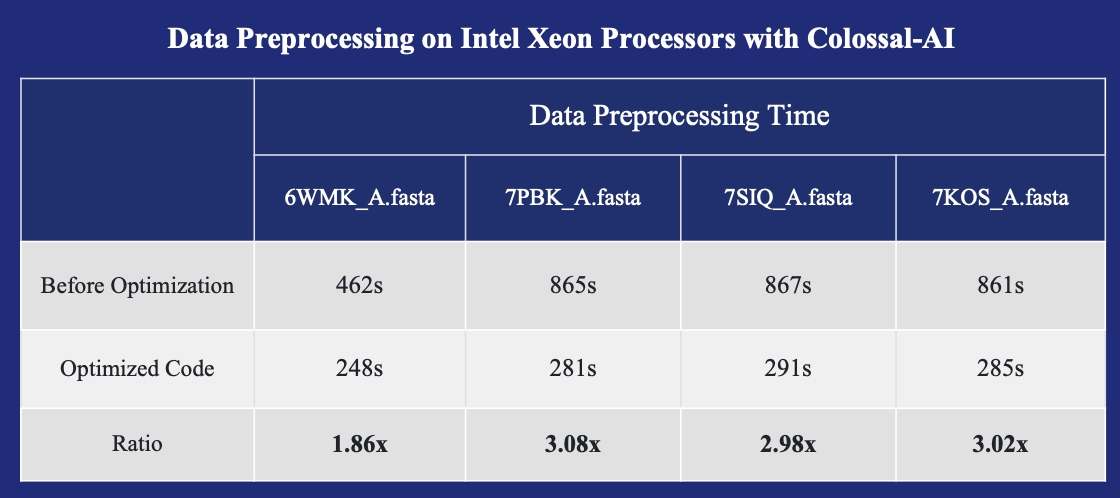
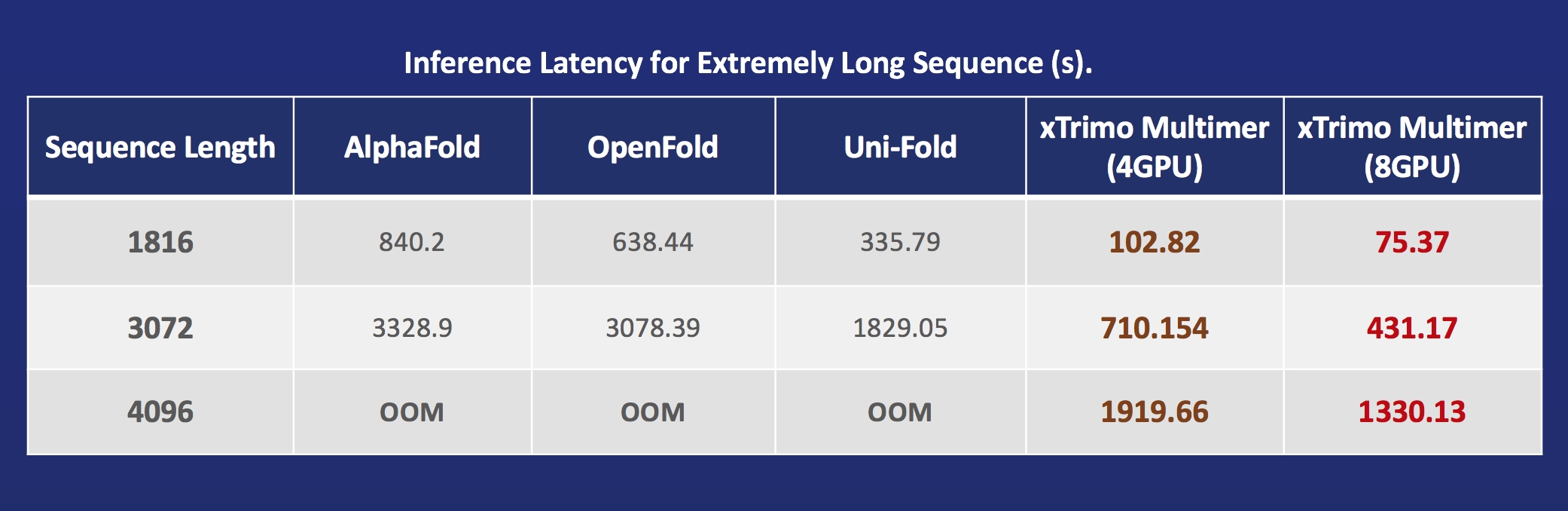
Acceleration of AlphaFold Protein Structure
- FastFold: Accelerating training and inference on GPU Clusters, faster data processing, inference sequence containing more than 10000 residues.
- FastFold with Intel: 3x inference acceleration and 39% cost reduce.
- xTrimoMultimer: accelerating structure prediction of protein monomers and multimer by 11x.
- Enhanced MoE parallelism, Open-source MoE model training can be 9 times more efficient [code] [blog]
- Save 50% GPU resources and 10.7% acceleration
- 11x lower GPU memory consumption, and superlinear scaling efficiency with Tensor Parallelism
- 24x larger model size on the same hardware
- over 3x acceleration
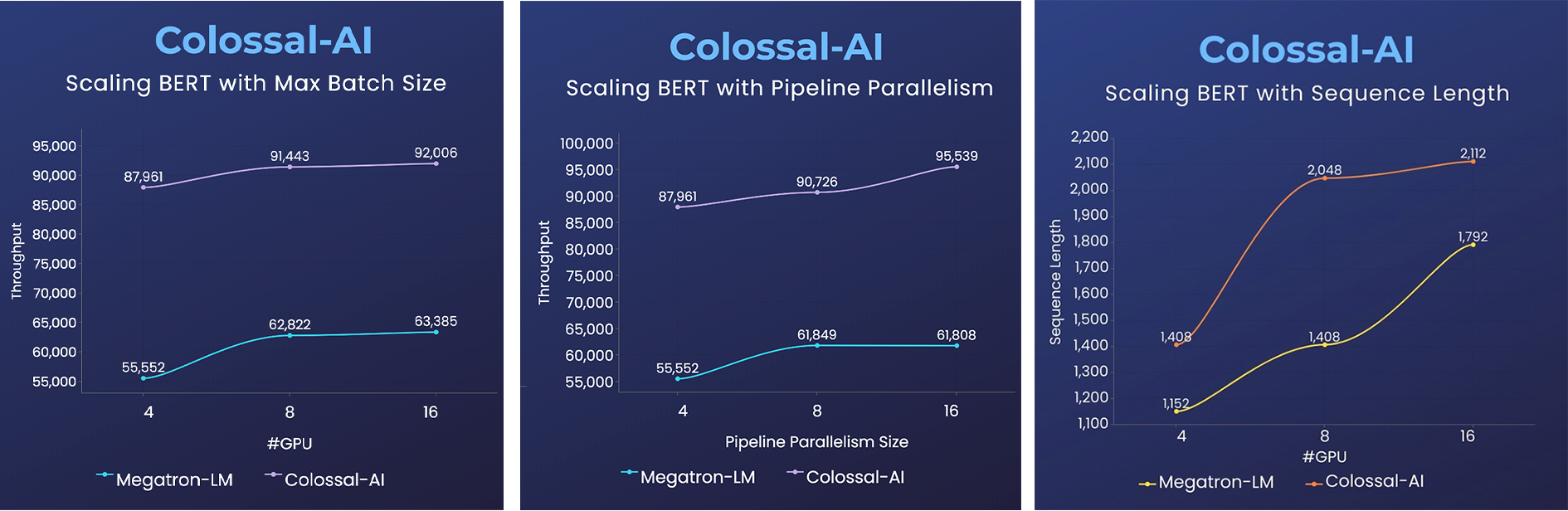
- 2x faster training, or 50% longer sequence length
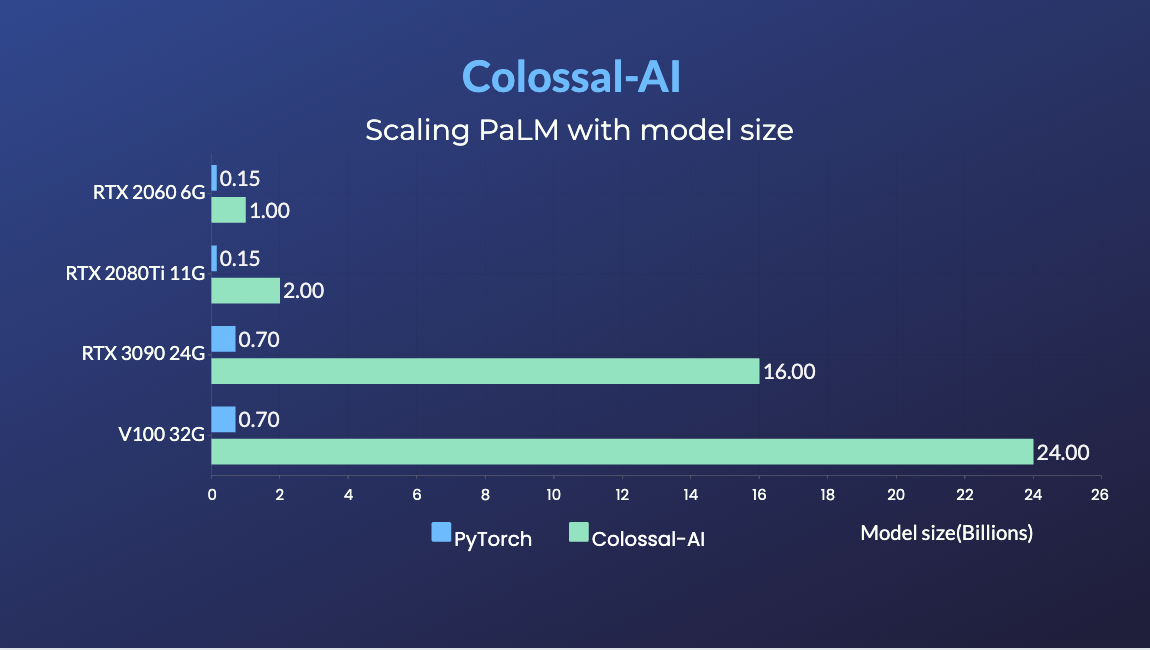
- PaLM-colossalai: Scalable implementation of Google's Pathways Language Model (PaLM).
- Open Pretrained Transformer (OPT), a 175-Billion parameter AI language model released by Meta, which stimulates AI programmers to perform various downstream tasks and application deployments because of public pre-trained model weights.
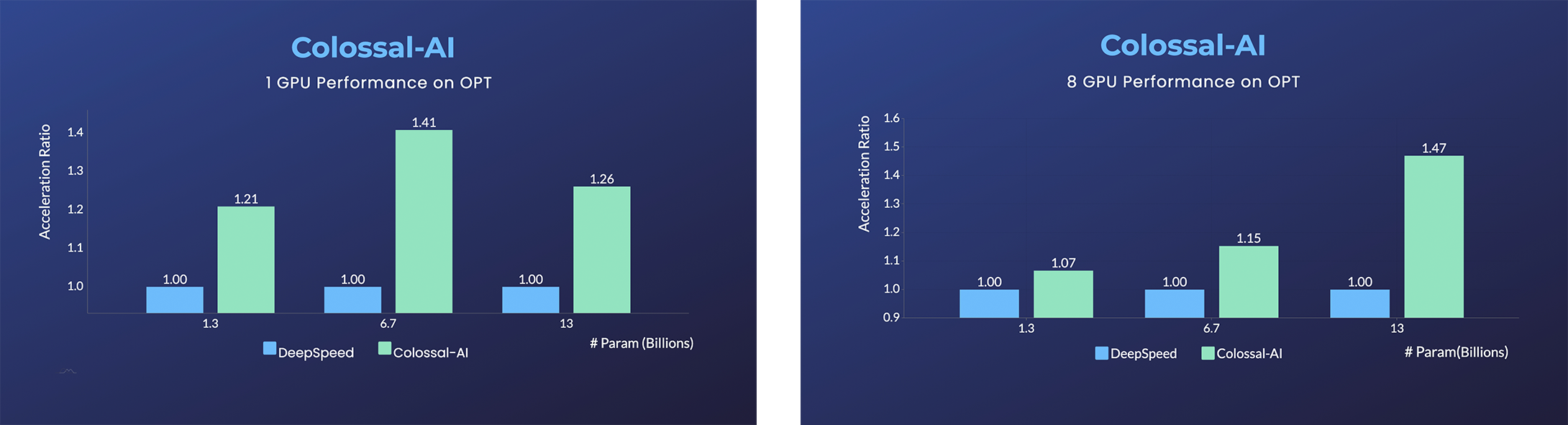
- 45% speedup fine-tuning OPT at low cost in lines. [Example] [Online Serving]
Please visit our documentation and examples for more details.
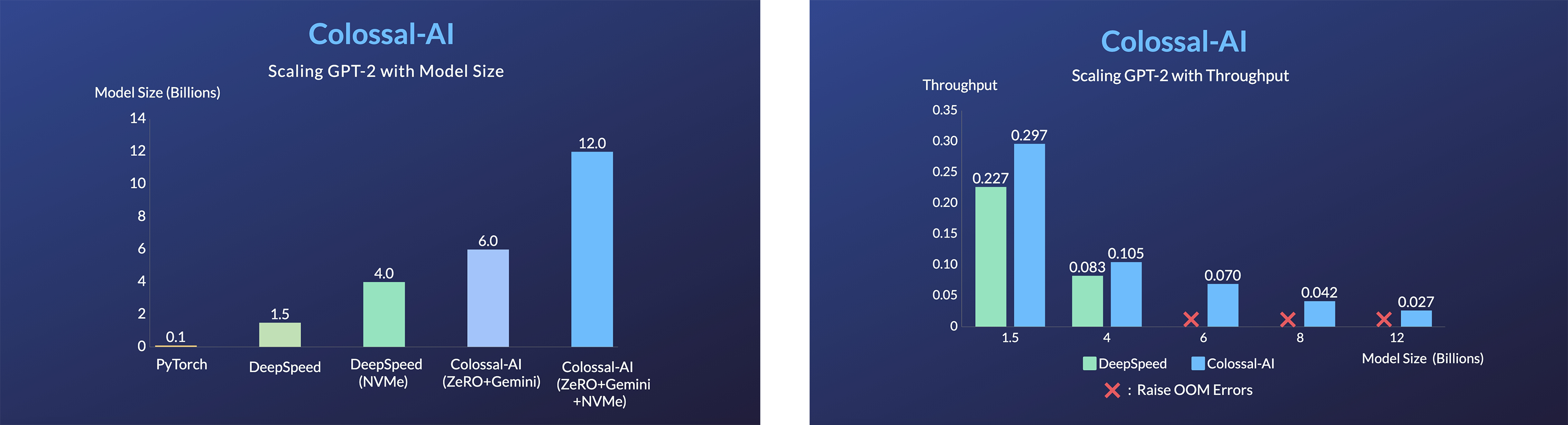
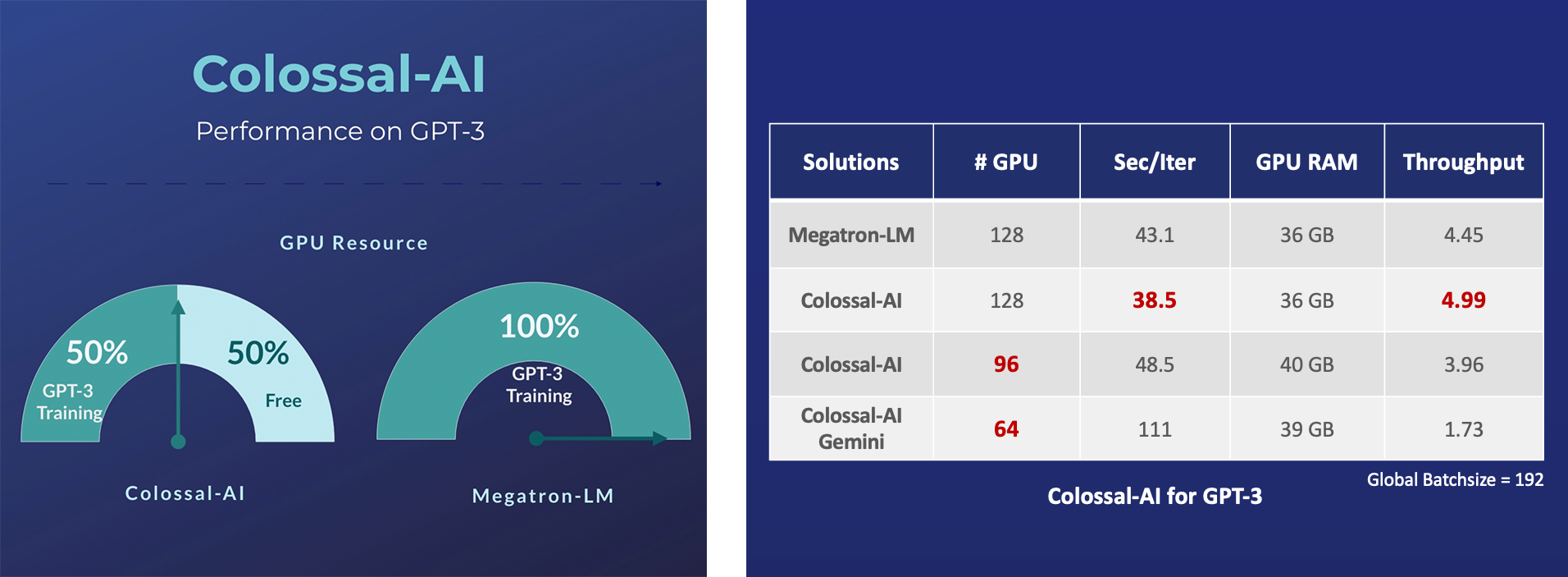
- 14x larger batch size, and 5x faster training for Tensor Parallelism = 64
- Cached Embedding, utilize software cache to train larger embedding tables with a smaller GPU memory budget.
- 20x larger model size on the same hardware
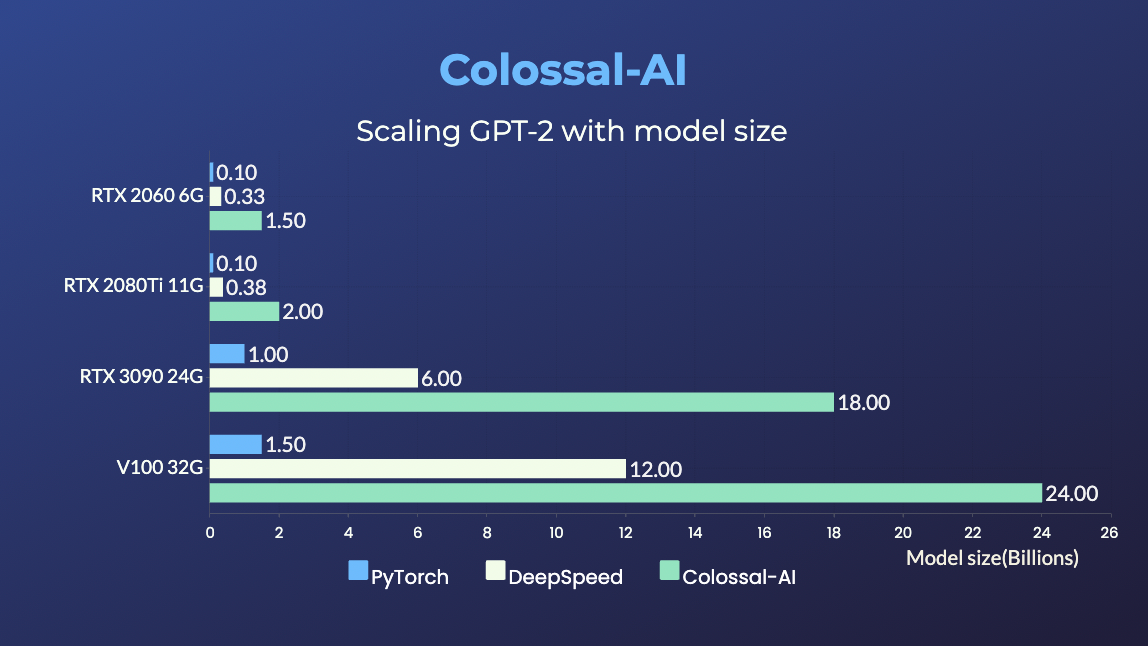
- 120x larger model size on the same hardware (RTX 3080)
- 34x larger model size on the same hardware
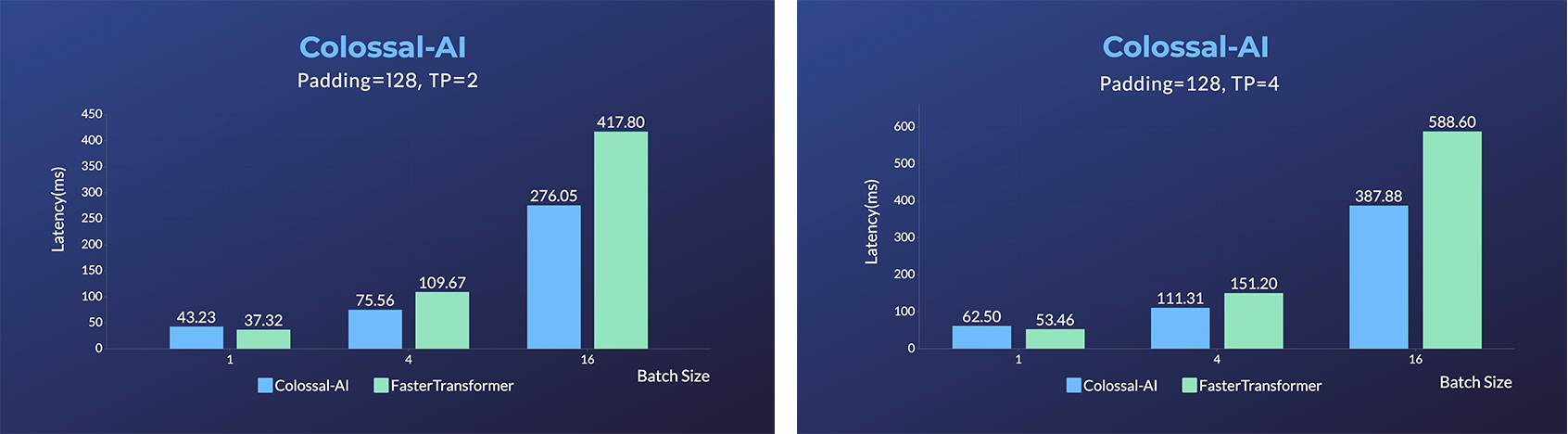
- Energon-AI: 50% inference acceleration on the same hardware
- OPT Serving: Try 175-billion-parameter OPT online services
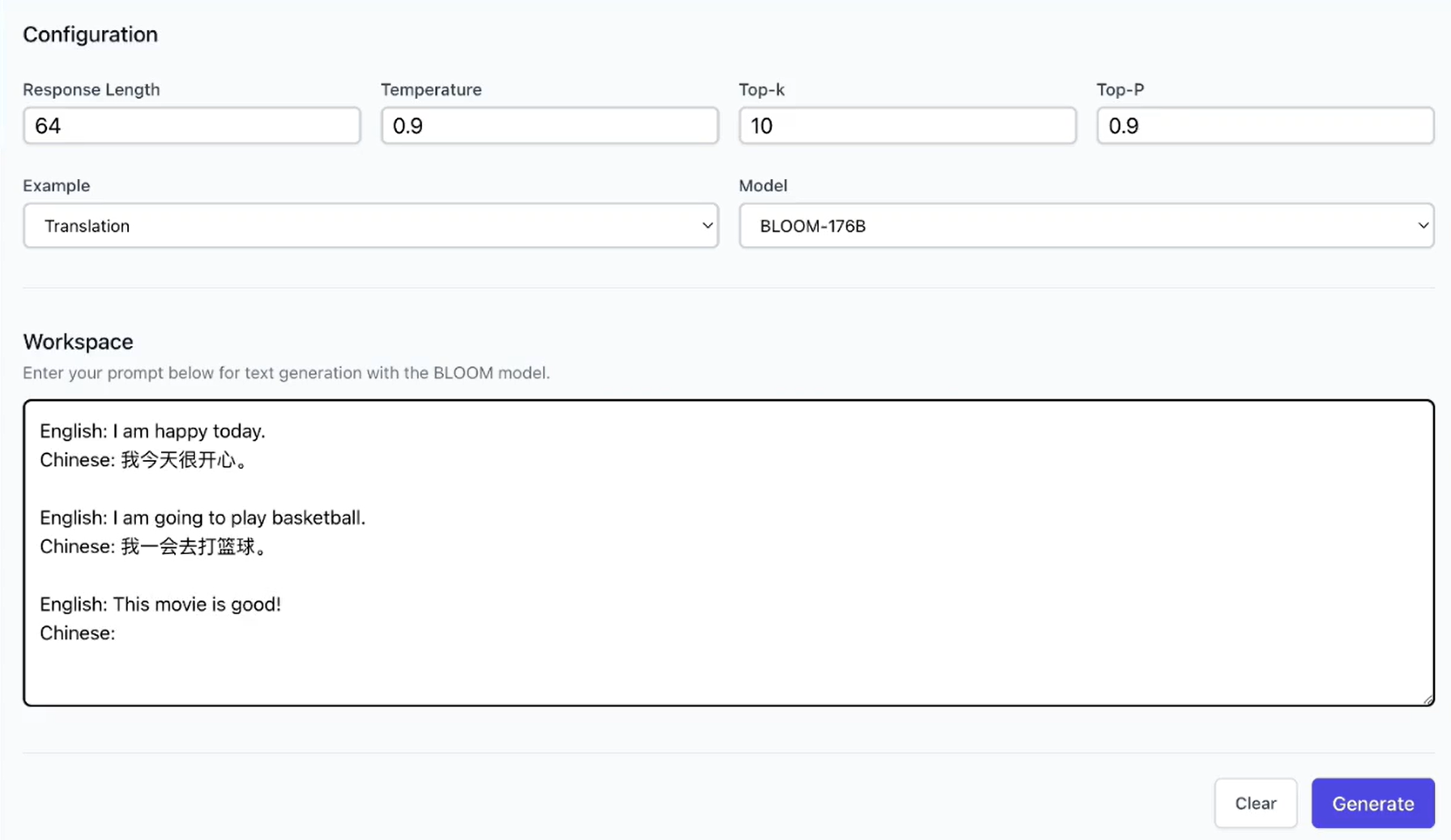
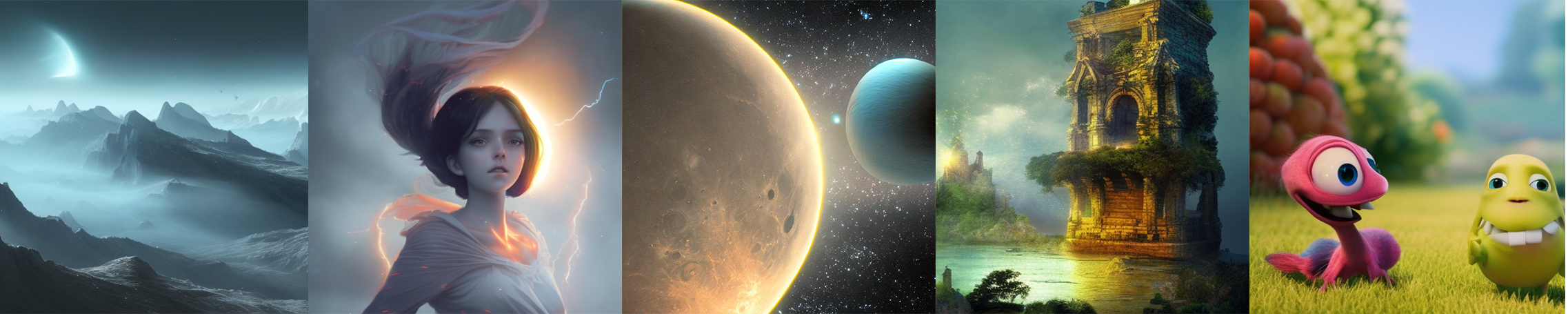
- BLOOM: Reduce hardware deployment costs of 176-billion-parameter BLOOM by more than 10 times.
Requirements:
- PyTorch >= 1.11 (PyTorch 2.x in progress)
- Python >= 3.7
- CUDA >= 11.0
- NVIDIA GPU Compute Capability >= 7.0 (V100/RTX20 and higher)
- Linux OS
If you encounter any problem with installation, you may want to raise an issue in this repository.
You can easily install Colossal-AI with the following command. By default, we do not build PyTorch extensions during installation.
pip install colossalaiNote: only Linux is supported for now.
However, if you want to build the PyTorch extensions during installation, you can set CUDA_EXT=1.
CUDA_EXT=1 pip install colossalaiOtherwise, CUDA kernels will be built during runtime when you actually need them.
We also keep releasing the nightly version to PyPI every week. This allows you to access the unreleased features and bug fixes in the main branch. Installation can be made via
pip install colossalai-nightlyThe version of Colossal-AI will be in line with the main branch of the repository. Feel free to raise an issue if you encounter any problems. :)
git clone https://github.com/hpcaitech/ColossalAI.git
cd ColossalAI
# install colossalai
pip install .By default, we do not compile CUDA/C++ kernels. ColossalAI will build them during runtime. If you want to install and enable CUDA kernel fusion (compulsory installation when using fused optimizer):
CUDA_EXT=1 pip install .For Users with CUDA 10.2, you can still build ColossalAI from source. However, you need to manually download the cub library and copy it to the corresponding directory.
# clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/hpcaitech/ColossalAI.git
cd ColossalAI
# download the cub library
wget https://github.com/NVIDIA/cub/archive/refs/tags/1.8.0.zip
unzip 1.8.0.zip
cp -r cub-1.8.0/cub/ colossalai/kernel/cuda_native/csrc/kernels/include/
# install
CUDA_EXT=1 pip install .You can directly pull the docker image from our DockerHub page. The image is automatically uploaded upon release.
Run the following command to build a docker image from Dockerfile provided.
Building Colossal-AI from scratch requires GPU support, you need to use Nvidia Docker Runtime as the default when doing
docker build. More details can be found here. We recommend you install Colossal-AI from our project page directly.
cd ColossalAI
docker build -t colossalai ./dockerRun the following command to start the docker container in interactive mode.
docker run -ti --gpus all --rm --ipc=host colossalai bashJoin the Colossal-AI community on Forum, Slack, and WeChat(微信) to share your suggestions, feedback, and questions with our engineering team.
Referring to the successful attempts of BLOOM and Stable Diffusion, any and all developers and partners with computing powers, datasets, models are welcome to join and build the Colossal-AI community, making efforts towards the era of big AI models!
You may contact us or participate in the following ways:
- Leaving a Star ⭐ to show your like and support. Thanks!
- Posting an issue, or submitting a PR on GitHub follow the guideline in Contributing
- Send your official proposal to email contact@hpcaitech.com
Thanks so much to all of our amazing contributors!
We leverage the power of GitHub Actions to automate our development, release and deployment workflows. Please check out this documentation on how the automated workflows are operated.
This project is inspired by some related projects (some by our team and some by other organizations). We would like to credit these amazing projects as listed in the Reference List.
To cite this project, you can use the following BibTeX citation.
@inproceedings{10.1145/3605573.3605613,
author = {Li, Shenggui and Liu, Hongxin and Bian, Zhengda and Fang, Jiarui and Huang, Haichen and Liu, Yuliang and Wang, Boxiang and You, Yang},
title = {Colossal-AI: A Unified Deep Learning System For Large-Scale Parallel Training},
year = {2023},
isbn = {9798400708435},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3605573.3605613},
doi = {10.1145/3605573.3605613},
abstract = {The success of Transformer models has pushed the deep learning model scale to billions of parameters, but the memory limitation of a single GPU has led to an urgent need for training on multi-GPU clusters. However, the best practice for choosing the optimal parallel strategy is still lacking, as it requires domain expertise in both deep learning and parallel computing. The Colossal-AI system addressed the above challenge by introducing a unified interface to scale your sequential code of model training to distributed environments. It supports parallel training methods such as data, pipeline, tensor, and sequence parallelism and is integrated with heterogeneous training and zero redundancy optimizer. Compared to the baseline system, Colossal-AI can achieve up to 2.76 times training speedup on large-scale models.},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 52nd International Conference on Parallel Processing},
pages = {766–775},
numpages = {10},
keywords = {datasets, gaze detection, text tagging, neural networks},
location = {Salt Lake City, UT, USA},
series = {ICPP '23}
}
Colossal-AI has been accepted as official tutorial by top conferences NeurIPS, SC, AAAI, PPoPP, CVPR, ISC, NVIDIA GTC ,etc.




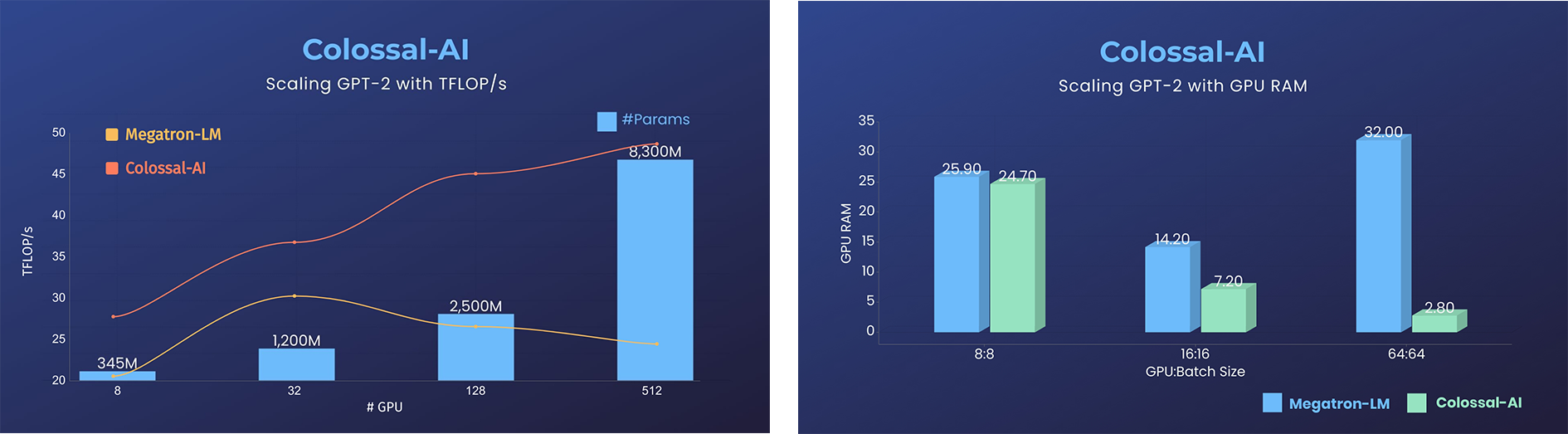
GPT-2.png)