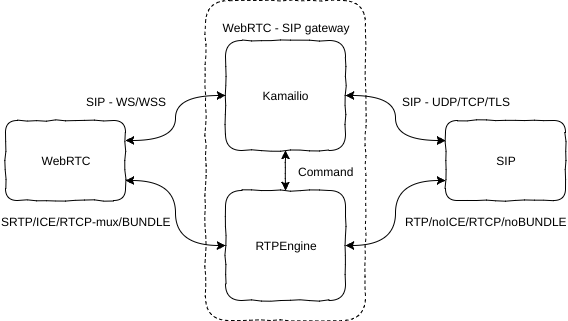
How to setup Kamailio + RTPEngine + TURN server to enable calling between WEBRTC client and legacy SIP clients. This config is IPv6 enabled by default. This setup will bridge SRTP --> RTP and ICE --> nonICE to make a WEBRTC client (SIPJs) be able to call legacy SIP clients.
This setup is for Debian 9 Stretch for all servers.
This setup is configured to run with the following servers:
- Server - Kamailio + RTPEngine + Nginx (WEBRTC client)
- Server - TURN
The configuration is setup to always bridge via RTPEngine. To change the behavior, take a look in the NATMANAGE route.
For the certificates you need a simple solution is Let's Encrypt certificates. They will work for both Kamailio TLS and Nginx TLS. On the servers you need certificates, run the following (you must stop services running on port 443 during certificate request/renewal):
apt-get install certbot
certbot certonly --standalone -d YOUR-DOMAINYou will then find the certificates under:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/YOUR-DOMAIN/privkey.pem
/etc/letsencrypt/live/YOUR-DOMAIN/fullchain.pemAll files needed to setup all components on Debian 9 Stretch.
git clone https://github.com/havfo/WEBRTC-to-SIP.git
cd WEBRTC-to-SIP
find . -type f -print0 | xargs -0 sed -i 's/XXXXXX-XXXXXX/PUT-IPV6-OF-YOUR-SIP-SERVER-HERE/g'
find . -type f -print0 | xargs -0 sed -i 's/XXXXX-XXXXX/PUT-IPV4-OF-YOUR-SIP-SERVER-HERE/g'
find . -type f -print0 | xargs -0 sed -i 's/XXXX-XXXX/PUT-DOMAIN-OF-YOUR-SIP-SERVER-HERE/g'
find . -type f -print0 | xargs -0 sed -i 's/XXX-XXX/PUT-DOMAIN-OF-YOUR-TURN-SERVER-HERE/g'This will do the SRTP-RTP bridging needed to make WEBRTC clients talk to legacy SIP server/clients. You can find the latest build instructions in their readme.
The easiest way of installing is to get it from Sipwise repository:
echo 'deb http://deb.sipwise.com/spce/mr7.1.1/ stretch main' > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/sipwise.list
echo 'deb-src http://deb.sipwise.com/spce/mr7.1.1/ stretch main' >> /etc/apt/sources.list.d/sipwise.list
apt-get update
apt-get install -y --allow-unauthenticated ngcp-keyring
apt-get update
apt-get install -y ngcp-rtpengineAfter you have successfully installed RTPEngine, copy the configuration from this repository.
cd WEBRTC-to-SIP
cp etc/default/ngcp-rtpengine-daemon /etc/default/
cp etc/rtpengine/rtpengine.conf /etc/rtpengine/
/etc/init.d/ngcp-rtpengine-daemon restartRTPEngine handles the chain for itself, but make sure to not block the RTP-ports it is using. Take a look in iptables.sh for details, and apply it by doing the following. This will persist after reboot. You can run the iptables.sh script at any time after it is set up.
cd WEBRTC-to-SIP
chmod +x iptables.sh
cp etc/network/if-up.d/iptables /etc/network/if-up.d/
chmod +x /etc/network/if-up.d/iptables
touch /etc/iptables/firewall.conf
touch /etc/iptables/firewall6.conf
./iptables.shapt-get install kamailio kamailio-websocket-modules kamailio-mysql-modules kamailio-tls-modules kamailio-presence-modules mysql-server
cd WEBRTC-to-SIP
cp etc/kamailio/* /etc/kamailio/
kamdbctl createSelect yes (Y) to all options.
kamctl add websip websip
/etc/init.d/kamailio restartapt-get install nginx
cd WEBRTC-to-SIP
cp etc/nginx/sites-available/default /etc/nginx/sites-available/
cp -r client/* /var/www/html/apt-get install coturn
cp etc/default/coturn /etc/default/
cp etc/turn* /etc/
/etc/init.d/coturn restartYou should now be able to go to https://webrtcnginxserver/ and call legacy SIP clients.