FOOOF is a fast, efficient, and physiologically-informed tool to parameterize neural power spectra.
Note: FOOOF is currently on a pre-release. Please check the install instructions for updating to the pre-release version, and check the changelog for how to get started with the new version.
FOOOF conceives of a model of the power spectrum as a combination of two distinct functional processes:
- An aperiodic component, reflecting 1/f like characteristics, with
- A variable number of periodic components (putative oscillations), as peaks rising above the aperiodic component
This model driven approach can be used to measure periodic and aperiodic properties of electrophysiological data, including EEG, MEG, ECoG and LFP data.
The benefit of using FOOOF for measuring putative oscillations, is that peaks in the power spectrum are characterized in terms of their specific center frequency, power and bandwidth without requiring predefining specific bands of interest and controlling for the aperiodic component. FOOOF also gives you a measure of this aperiodic components of the signal, allowing for measuring and comparison of 1/f-like components of the signal within and between subjects.
Documentation for FOOOF is available on the documentation site.
This documentation includes:
- Motivations: with motivating examples of why we recommend parameterizing neural power spectra
- Tutorials: with a step-by-step guide through the model and how to apply it
- Examples: demonstrating example analyses and use cases, and other functionality
- API list: which lists and describes all the code and functionality available in the module
- FAQ: answering frequency asked questions
- Glossary: which defines all the key terms used in the module
- Reference: with information for reporting on using and reference the module
FOOOF is written in Python, and requires Python >= 3.5 to run.
It has the following required dependencies:
There are also optional dependencies, which are not required for model fitting itself, but offer extra functionality:
- matplotlib is needed to visualize data and model fits
- tqdm is needed to print progress bars when fitting many models
- pytest is needed to run the test suite locally
We recommend using the Anaconda distribution to manage these requirements.
Pre-Release Version
To install the current pre-release version, use pip:
$ pip install fooof --pre
If you already have a version of FOOOF installed, you will need to remove it first:
$pip uninstall fooof
Stable Version
To install the latest stable release, use pip:
$ pip install fooof
Note that this will install only the core (non-optional) FOOOF requirements.
Development Version
To get the current development version, first clone this repository:
$ git clone https://github.com/fooof-tools/fooof
To install this cloned copy, move into the directory you just cloned, and run:
$ pip install .
Editable Version
To install an editable version, download the development version as above, and run:
$ pip install -e .
FOOOF is implemented in Python, but there is also Matlab wrapper that allows you to use FOOOF from Matlab. The wrapper is available in the fooof_mat repository.
If you would like to use FOOOF, from Python, within a pipeline that is mostly in Matlab, the mat_py_mat repository also has some examples and utilities for doing so.
Please use the Github issue tracker to file bug reports and/or ask questions about this project.
If you use this code in your project, please cite:
Haller M, Donoghue T, Peterson E, Varma P, Sebastian P, Gao R, Noto T, Knight RT, Shestyuk A,
Voytek B (2018) Parameterizing Neural Power Spectra. bioRxiv, 299859.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/299859
More information for how to cite this method can be found on the reference page.
Direct Link: https://doi.org/10.1101/299859
Code and analyses from the paper are also available in the paper repository.
This project welcomes and encourages contributions from the community!
If you have an idea of something to add to FOOOF, please start by opening an issue. Note that this issue tracker is used for code specific questions and suggestions. If you have a question or suggestion related to the model or conceptual ideas, check out the development page.
When writing code to add to FOOOF, please follow the Contribution Guidelines , and also make sure to follow our Code of Conduct.
FOOOF is object oriented, and uses a similar approach as used in scikit-learn.
The algorithm works on frequency representations, that is power spectra in linear space.
Fitting a Single Power Spectrum
With a power spectrum loaded (with 'freqs' storing frequency values, and 'spectrum' storing the power spectrum, both as 1D arrays in linear space) FOOOF can be used as follows:
from fooof import FOOOF
# Initialize FOOOF object
fm = FOOOF()
# Define frequency range across which to model the spectrum
freq_range = [3, 40]
# Model the power spectrum with FOOOF, and print out a report
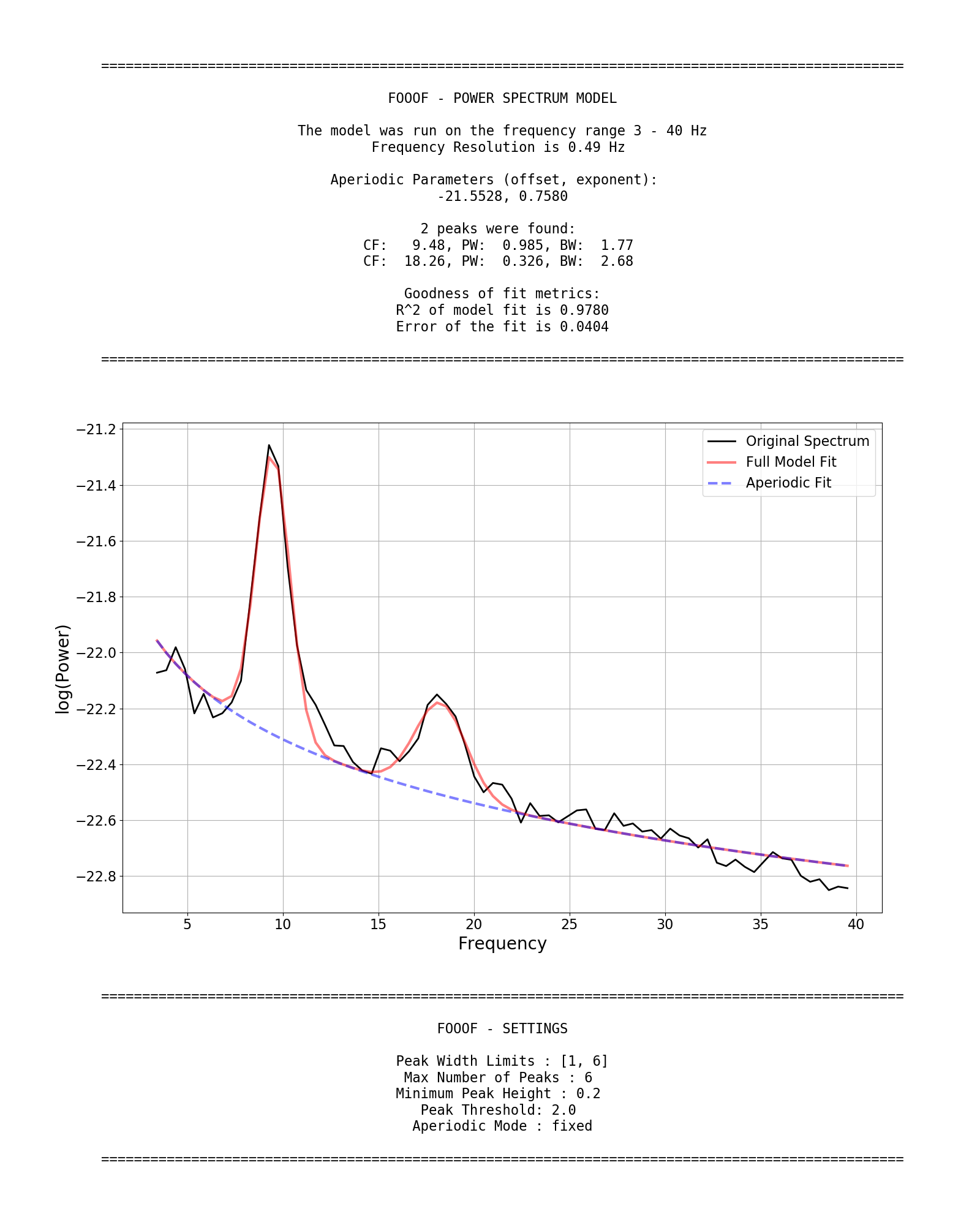
fm.report(freqs, spectrum, freq_range)FOOOF.report() fits the model, plots the original power spectrum with the associated FOOOF model fit, and prints out the parameters of the model fit for both the aperiodic component, and parameters for any identified peaks, reflecting periodic components.
Example output for the report of a FOOOF fit on an individual power spectrum:
Defining the model Settings
FOOOF also has some settings for the algorithm.
These settings are:
peak_width_limitssets the possible lower- and upper-bounds for the fitted peak widths.max_n_peakssets the maximum number of peaks to fit.min_peak_heightsets an absolute limit on the minimum height (above aperiodic) for any extracted peak.peak_thresholdsets a relative threshold above which a peak height must cross to be included in the model.aperiodic_modedefines the approach to use to parameterize the aperiodic component.
These settings can be defined when initializing the model, for example:
fm = FOOOF(peak_width_limits=[1.0, 8.0], max_n_peaks=6, min_peak_height=0.1,
peak_threshold=2.0, aperiodic_mode='fixed')Fitting a Group of Power Spectra
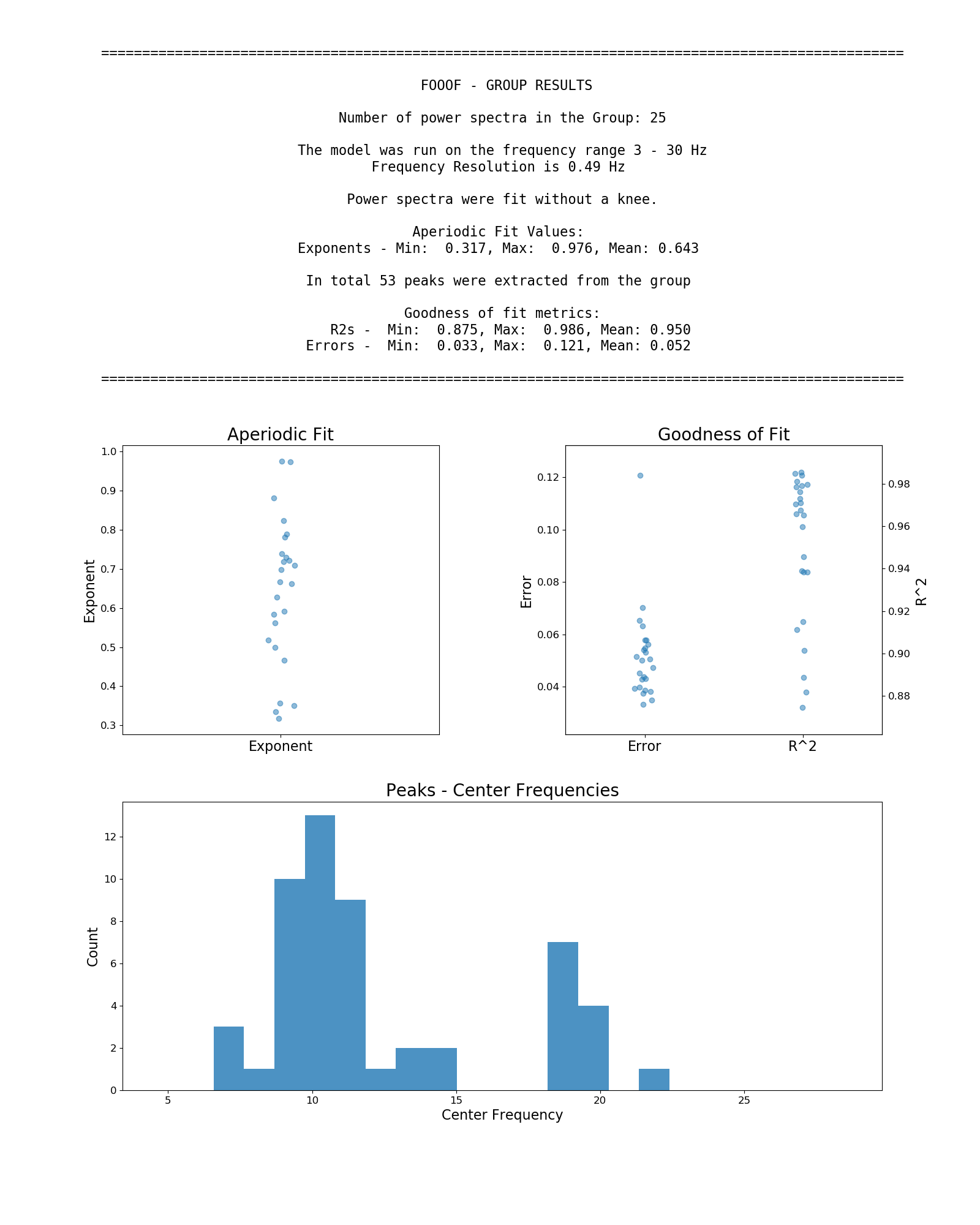
Next is an example workflow for fitting a group of neural power spectra. In this case, 'freqs' is again a 1D array of frequency values, and 'spectra' as a 2D array of power spectra. We can fit this which can be fit as:
# Initialize a FOOOFGroup object, specifying some parameters
fg = FOOOFGroup(peak_width_limits=[1.0, 8.0], max_n_peaks=8)
# Fit FOOOF model across the matrix of power spectra
fg.fit(freqs, spectra)
# Create and save out a report summarizing the results across the group of power spectra
fg.save_report()
# Save out FOOOF results for further analysis later
fg.save(file_name='fooof_group_results', save_results=True)Example output from using FOOOFGroup across a group of power spectra:
Other Functionality
FOOOF also has functionality for running the FOOOF model across matrices of multiple power spectra, saving and loading results, creating reports from FOOOF outputs, analyzing model outputs, plotting models and parameters, and simulating power spectra, all of which is described in the documentation.