-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 5
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
Added Basic level Interview Questions
- Loading branch information
1 parent
6fbff56
commit a3d4a83
Showing
1 changed file
with
103 additions
and
0 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,103 @@ | ||
| # Git Interview Questions | ||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| ###Q. What is Git and why do we use it? | ||
| Answer: Git is a version control system that allows multiple developers to work on the same codebase without interfering with each other's work. It keeps track of changes to the codebase over time and makes it easy to revert to previous versions if necessary. We use Git to collaborate on code, track changes, and ensure that everyone on the team is working on the same version of the code. | ||
| 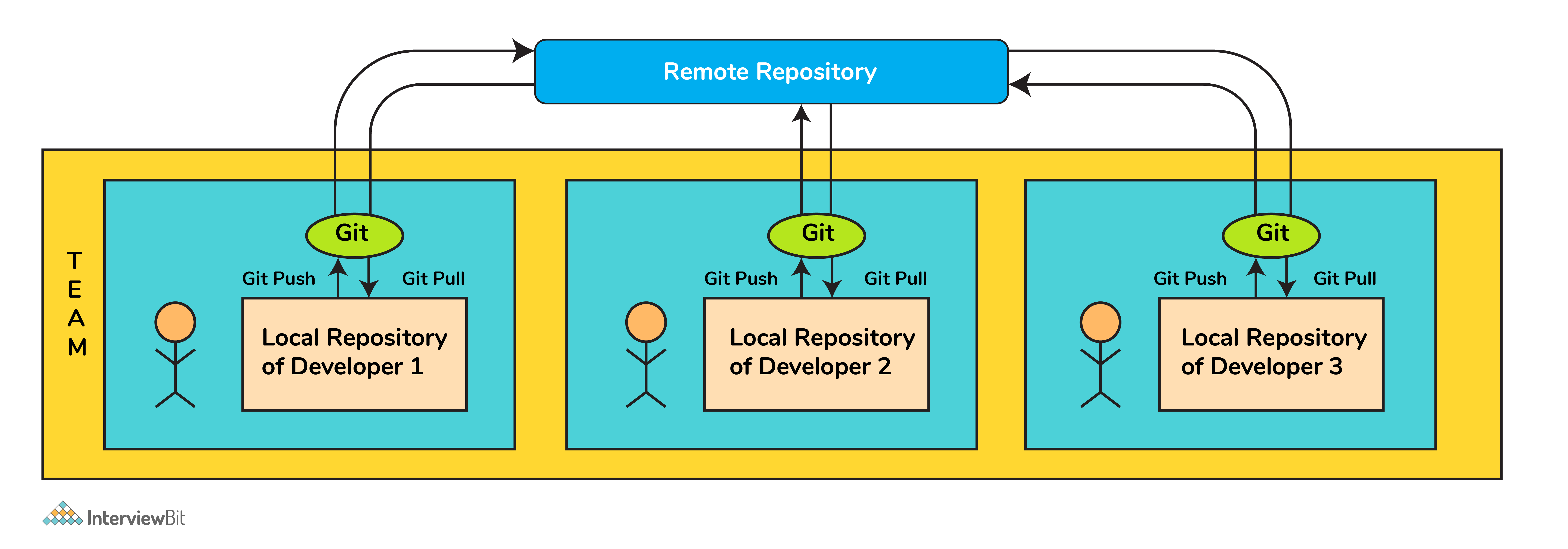 | ||
| OR you can also describe it as: | ||
|
|
||
| - Git is the most popular, open-source, widely used, and an example of distributed version control system (DVCS) used for handling the development of small and large projects in a more efficient and neat manner. | ||
| - It is most suitable when there are multiple people working on projects as a team and is used for tracking the project changes and efficiently supports the collaboration of the development process. | ||
| - With the help of the versioning system, the developer can identify who has made what changes and then run tests and fix bugs if any and then do necessary feature implementation. In case of any unforeseen circumstances, the code can be reverted to any of the previously working versions thereby saving huge efforts. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Q. What are the advantages of using Git over other version control systems? | ||
| Answer: Some of the advantages of using Git over other version control systems include its distributed nature, its ability to handle large projects, its branching and merging capabilities, and its fast performance. Git allows developers to work on their own local copies of a codebase and then easily merge their changes back into the main codebase. It also allows for multiple branches of a codebase to be developed simultaneously, which can speed up development and reduce the risk of conflicts. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Q. What is a branch in Git? | ||
| Answer: A branch in Git is a separate line of development that allows developers to work on a specific feature or bug fix without affecting the main codebase. Each branch is a separate copy of the codebase that can be modified independently, and changes made to one branch do not affect the other branches until they are merged together. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Q. What is a commit in Git? | ||
| Answer: A commit in Git is a snapshot of changes made to the codebase at a specific point in time. Each commit includes a unique identifier, a commit message that describes the changes made, and a reference to the previous commit. Commits are used to track changes to the codebase over time and to revert to previous versions if necessary. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Q. What is a merge conflict in Git? | ||
| Answer: A merge conflict in Git occurs when two or more developers make conflicting changes to the same file or lines of code. Git is unable to automatically merge the changes, and the developers must manually resolve the conflict by editing the affected files and deciding which changes to keep and which to discard. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Q. What is a version control system (VCS)? | ||
| Answer: A VCS keeps track of the contributions of the developers working as a team on the projects. They maintain the history of code changes done and with project evolution, it gives an upper hand to the developers to introduce new code, fixes bugs, and run tests with confidence that their previously working copy could be restored at any moment in case things go wrong. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Q. What is a git repository? | ||
| Answer: A repository is a file structure where git stores all the project-based files. Git can either stores the files on the local or the remote repository | ||
|
|
||
| ### Q. What does git clone do? | ||
| Answer: The command creates a copy (or clone) of an existing git repository. Generally, it is used to get a copy of the remote repository to the local repository. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Q. What does the command git config do? | ||
| Answer: The git config command is a convenient way to set configuration options for defining the behavior of the repository, user information and preferences, git installation-based configurations, and many such things. | ||
|
|
||
| For example: | ||
|
|
||
| To set up your name and email address before using git commands, we can run the below commands: | ||
|
|
||
| ``` | ||
| git config --global user.name “<<your_name>>” | ||
| git config --global user.email “<<your_email>>” | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ### Q. Can you explain head in terms of git and also tell the number of heads that can be present in a repository? | ||
| Answer: A head is nothing but a reference to the last commit object of a branch. | ||
| For every repository, there will always be a default head referred to as “master” or now “main” (as per GitHub) but there is no restriction to the count of heads available. In other words, it can have any number of heads. | ||
| Usages: | ||
|
|
||
| - To go or checkout to 1 commit before the latest commit, we use ```git checkout HEAD~1``` | ||
|
|
||
| - To uncommit the last 3 commits without losing the changes, we first run ```git reset HEAD~3```. Then we can see the changes made in the last 3 commits and then update it manually and commit it finally. | ||
|
|
||
| - In order to uncommit the last 3 commits and also remove the changes, we can run the command: ```git reset --hard HEAD~3```. This command will completely remove all the changes. | ||
|
|
||
| - To look into the changes made in the last 3 commits, we can run ```git diff HEAD~3``` | ||
|
|
||
| - To make a new commit by reverting the last 3 commits, we can run the command: ```git revert --no-commit HEAD~3...HEAD``` | ||
|
|
||
| ### Q. What is a conflict? | ||
| Answer: Git usually handles feature merges automatically but sometimes while working in a team environment, there might be cases of conflicts such as: | ||
|
|
||
| 1. When two separate branches have changes to the same line in a file | ||
| 2. A file is deleted in one branch but has been modified in the other. | ||
|
|
||
| These conflicts have to be solved manually after discussion with the team as git will not be able to predict what and whose changes have to be given precedence. | ||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| ### Q. What is the functionality of git ls-tree? | ||
| Answer: This command returns a tree object representation of the current repository along with the mode and the name of each item and the SHA-1 value of the blob. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Q. What does git status command do? | ||
| Answer: ```git status``` command is used for showing the difference between the working directory and the index which is helpful for understanding git in-depth and also keep track of the tracked and non-tracked changes. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Q. Define “Index” | ||
| Answer: Before making commits to the changes done, the developer is given provision to format and review the files and make innovations to them. All these are done in the common area which is known as ‘Index’ or ‘Staging Area’. | ||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| In the above image, the staging area where files will be staged and provides an opportunity for the people to evaluate changes before committing them. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Q. What does git add command do? | ||
| Answer: | ||
| - This command adds files and changes to the index of the existing directory. | ||
| - You can add all changes at once using git add . command. | ||
| - You can add files one by one specifically using git add <file_name> command. | ||
| - You can add contents of a particular folder by using git add /<folder_name>/ command | ||
|
|
||
| ### Q. You are working on a project with multiple developers and you need to merge your changes into the main codebase. However, there are conflicts that need to be resolved. How would you resolve the conflicts? | ||
| Answer: To resolve conflicts, I would first use the Git command git status to identify the files with conflicts. Then, I would open the files in a text editor and manually resolve the conflicts by selecting which changes to keep and which to discard. Once I have resolved all conflicts, I would use the git add command to stage the changes and then use the git commit command to commit the changes. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Q. You accidentally deleted a file in your local Git repository. How would you retrieve the file? | ||
| Answer: To retrieve the deleted file, I would use the Git command git checkout <file> followed by the name of the file that was deleted. This would retrieve the file from the most recent commit in the Git repository. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Q. You need to revert to a previous version of your codebase because of a bug introduced in the latest commit. How would you revert to the previous version? | ||
| Answer: To revert to a previous version of the codebase, I would use the Git command git log to identify the commit that introduced the bug. Then, I would use the git checkout <commit> command followed by the commit ID to revert to the previous version of the codebase. If I need to make changes to this version, I would create a new branch and make the necessary changes there. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Q. You need to create a new branch to work on a specific feature. How would you create a new branch and switch to it? | ||
| Answer: To create a new branch, I would use the Git command git branch <branch-name> followed by the name of the new branch. To switch to the new branch, I would use the git checkout <branch-name> command followed by the name of the branch. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Q. You need to update your local repository with the latest changes from the remote repository. How would you update your local repository? | ||
| Answer: To update my local repository with the latest changes from the remote repository, I would use the Git command git pull. This command would fetch the latest changes from the remote repository and merge them into my local repository. |