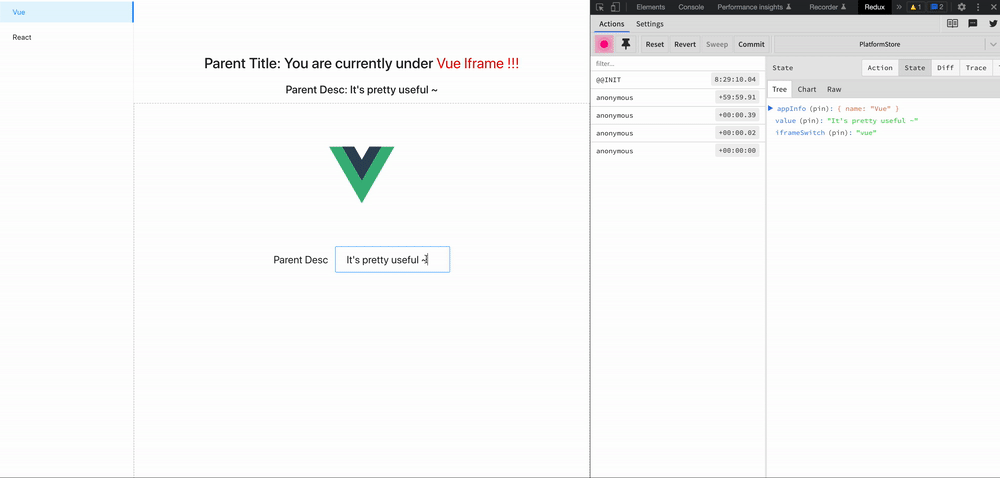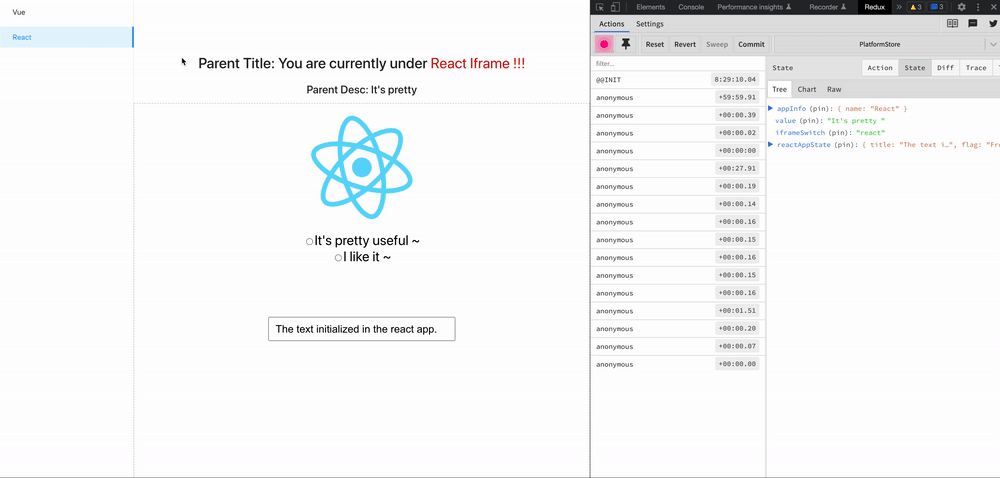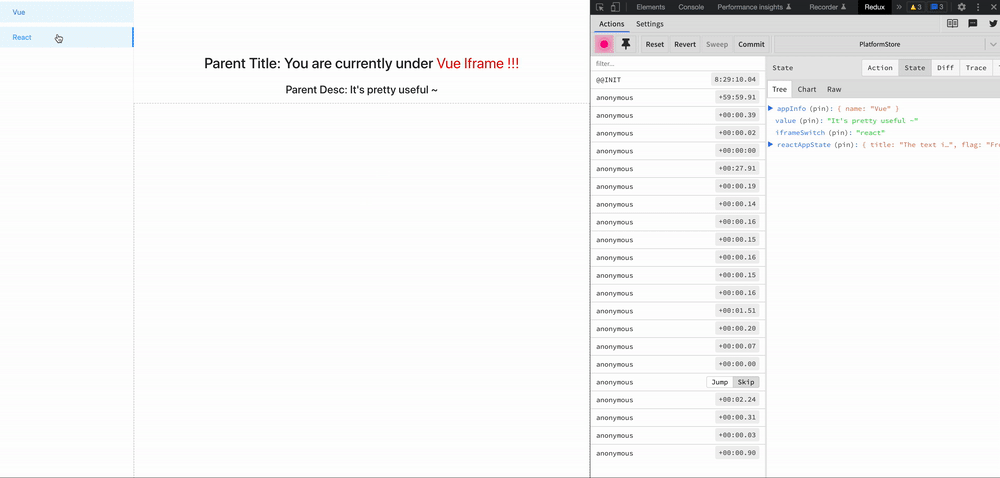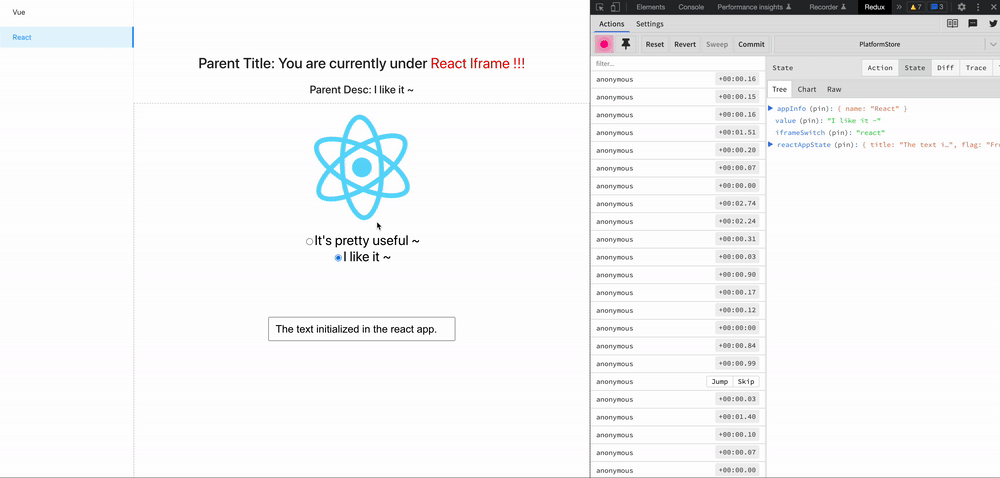
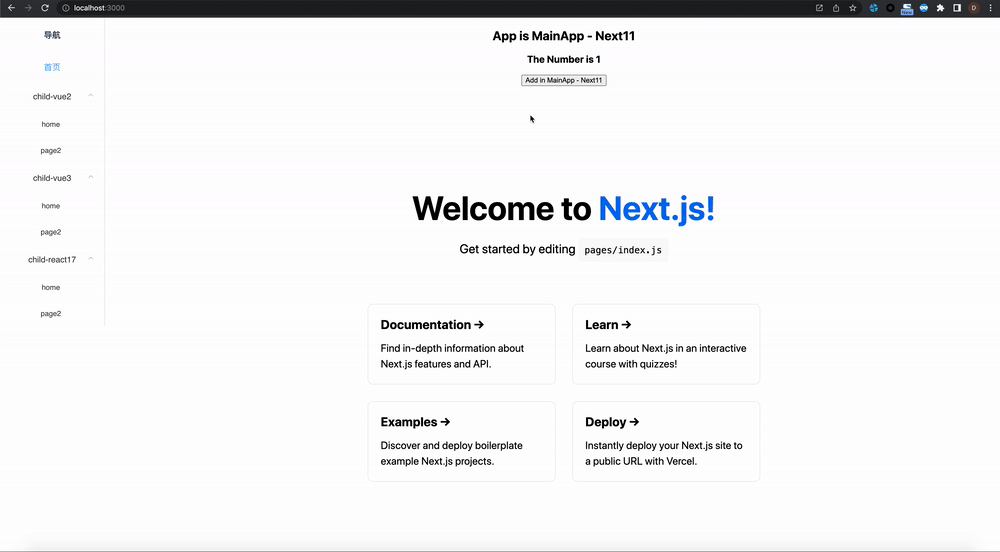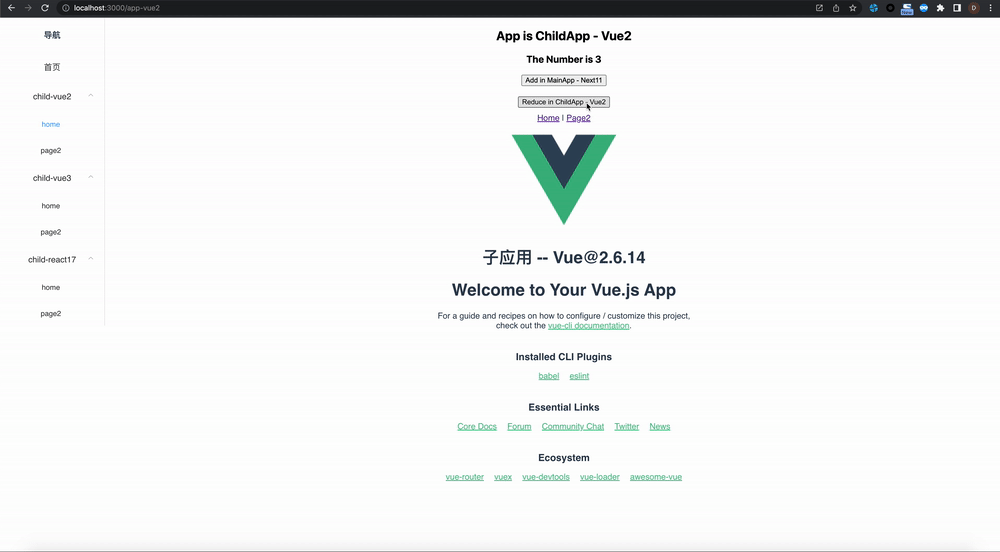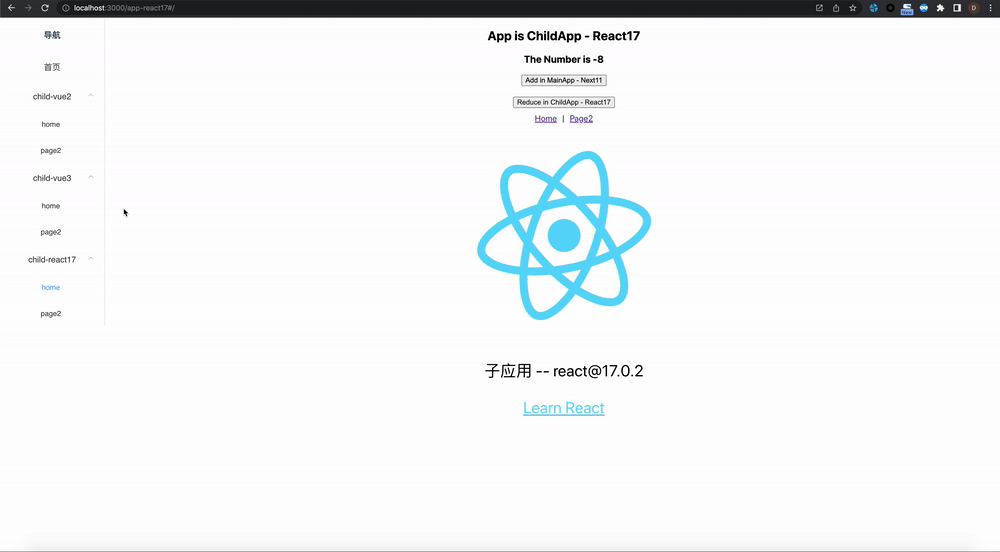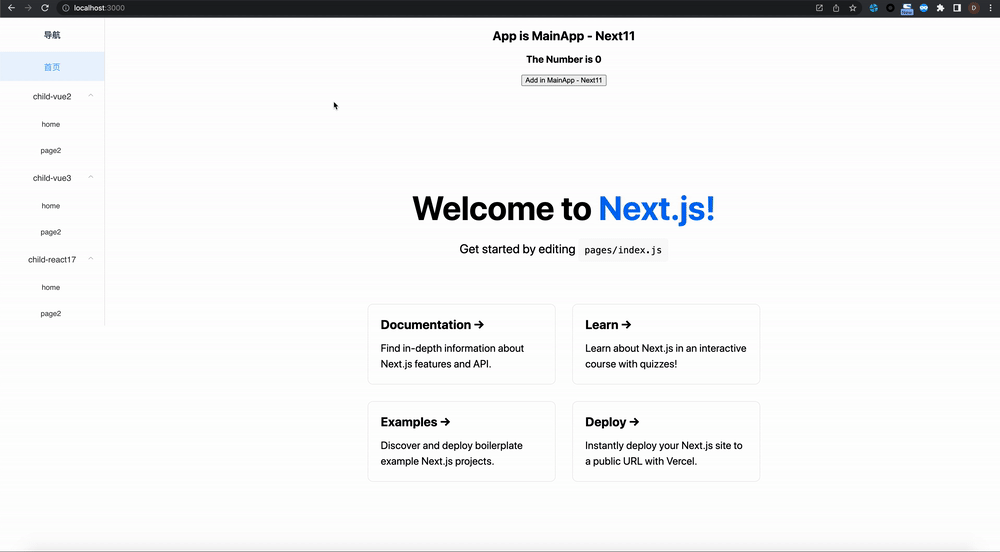
zustand-pub can provides cross-application and cross-framework(react/vue) state management and sharing capabilities for these scenarios, such as iframe, micro-frontend, modularization, componentization, multiple technology stacks exist at the same time, and gradual migration of project frameworks.
- Applications/Components can
mutually call/modify stateandtrigger component rendering- if in iframe, you can discard the hard-to-maintain
postMessage + addeventlistener + action - if in micro-frontend, you don’t need it anymore
eventCenter + action, just callactiondirectly to modify the state。
- if in iframe, you can discard the hard-to-maintain
Data Persistence Caching Schemebased on external state storage, application/component/iframe/micro-frontend,etc.state can be cached.- Usually, when we refer to the global
storein business components, it will lead to the problem that the anthor application cannot be reused, which reduces the reusability of the component. However, based onzustand-pub, such problems will no longer exist, reusability and development efficiency exist at the same time. - In the past, the store of
modular managementwas reused in different library (applications), the state could not be updated synchronously, but the state of the store based onzustand-pubmodule management could be updated synchronously, which improved the store development process. Feasibility of logic reuse and R&D efficiency. - In some iframe / micro-frontend scenarios, page rendering is slow due to
too many http requests, based on this solution,sub-application status pre-requestcan be performed to optimize user experience. - Based on devtools, you can
debug/trace stores between multiple applications at the same time, which can greatly reduce the difficulty of debugging when communicating between applications. - If you are using zustand or zustand-vue, it will be very convenient to use zustand-pub.
:::note
:::
npm install zustand-pub # or yarn add zustand-pubimport PubStore from 'zustand-pub'
const pubStore = new PubStore('key')// vue
import create from "zustand-vue";
//react
// import create from "zustand";
interface IState {
appInfo: {
name: string
}
}
interface IAction {
setAppName: (val: string) => void
}
const platformStore = pubStore.defineStore<IState & IAction>('platformStore', (set) => ({
appInfo: { name: '' },
setAppName(val: string) {
set({
appInfo: {
name: val
}
})
}
}))
const usePlatformStore = create(platformStore)return value usePlatformStore is hook,in scenario A, you can get the corresponding state through state selector
// vue3
<template>
<div>{name}</div>
</template>
<script>
const name = usePlatformStore((state) => state.appInfo.name);
const setAppName = usePlatformStore((state) => state.setAppName);
export default {
name: "AppA",
data(){
return {
name
}
},
methods:{
setAppName
}
}
</script>
// react
// function AppA() {
// const name = usePlatformStore((state) => state.appInfo.name);
// const setAppName = usePlatformStore((state) => state.setAppName);
// return <div>{name}</div>
// }Step 3: Get the platformStore under the isolated container pubStore and bind the Component (Scene B)
// vue3
<template>
<div>{name}</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
interface IState {
appInfo: {
name: string
}
}
interface IAction {
setAppName: (val: string) => void
}
import PubStore from "zustand-pub";
import create from "zustand-vue";
const pubStore = new PubStore('key')
const store = pubStore.getStore<IState & IAction>("platformStore");
const usePlatformStore = create(store || {});
const name = usePlatformStore((state) => state.appInfo.name);
const setAppName = usePlatformStore((state) => state.setAppName);
</script>
// react
// import PubStore from "zustand-pub";
// import create from "zustand";
// const pubStore = new PubStore('key')
// const store = pubStore.getStore<IState & IAction>("platformStore");
// const usePlatformStore = create(store || {});
// function AppB() {
// const name = usePlatformStore((state) => state.appInfo.name);
// const setAppName = usePlatformStore((state) => state.setAppName);
// return <div>{name}</div>
// }:::info The Usage of React to bind Component
The Usage of Vue to bind Component :::
Used to create state isolation containers, the data key inside different isolation containers can have the same name and do not affect each other
:::info
In the same application, key is unchanged and the pubStore is returned unchanged
:::
const pubStore = new PubStore() Used to fill data into isolated containers
:::info
In the same application, key is unchanged and the defined store will be merged in the order of loading
that is defineStore(key,()=>({a:1,c:1})) defineStore(key,()=>({b:2,c:2})) works like defineStore(key,()=>({a:1,b:2,c:1}))
:::
| Parameter | Desc | Type |
|---|---|---|
| key | data unique identifier | string |
| fn | callback | (set, get) => Object |
interface IStore {
...
}
// usePlatformStore is `hook`, and the corresponding state can be obtained through state `selector`
const usePlatformStore = pubStore.defineStore<IStore>('platformStore', (set, get) => ({}))Used to fetch data from isolated containers
| Parameter | Desc | Type |
|---|---|---|
| key | data unique identifier | string |
const platformStore = pubStore.getStore("platformStore");Return value platformStore can be used to create hook
import create from "zustand";
//vue
// import create from "zustand-vue";
const usePlatformStore = create(platformStore || {});