Abstract
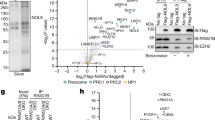
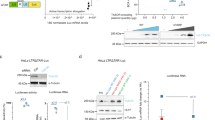
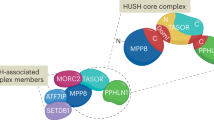
Argonaute proteins are the core components of effector complexes that facilitate RNA interference (RNAi). Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) targeted to promoter regions mediate transcriptional gene silencing (TGS) in human cells through heterochromatin formation. RNAi effector complexes have yet to be implicated in the mechanism of mammalian TGS. Here we describe the role of the human Argonaute-1 homolog (AGO1) in directing TGS at the promoters for human immunodeficiency virus-1 coreceptor CCR5 and tumor suppressor RASSF1A. AGO1 associates with RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) and is required for histone H3 Lys9 dimethylation and TGS. AGO1, TAR RNA-binding protein-2 (7TRBP2) and Polycomb protein EZH2 colocalize to the siRNA-targeted RASSF1A promoter, implicating Polycomb silencing in the mechanism of mammalian TGS. These results establish a connection between RNAi components AGO1 and TRBP2, RNAPII transcription and Polycomb-regulated control of gene expression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zamore, P.D. & Haley, B. Ribo-gnome: the big world of small RNAs. Science 309, 1519–1524 (2005).
Zilberman, D., Cao, X. & Jacobsen, S.E. ARGONAUTE4 control of locus-specific siRNA accumulation and DNA and histone methylation. Science 299, 716–719 (2003).
Volpe, T.A. et al. Regulation of heterchromatic silencing and histone H3 lysine-9 methylation by RNAi. Science 297, 1833–1837 (2002).
Verdel, A. et al. RNAi-mediated targeting of heterochromatin by the RITS complex. Science 303, 672–676 (2004).
Morris, K.V., Chan, S.W., Jacobsen, S.E. & Looney, D.J. Small interfering RNA-induced transcriptional gene silencing in human cells. Science 305, 1289–1292 (2004).
Weinberg, M.S. et al. The antisense strand of small interfering RNAs directs histone methylation and transcriptional gene silencing in human cells. RNA 12, 256–262 (2006).
Chow, J.C., Yen, Z., Ziesche, S.M. & Brown, C.J. Silencing of the mammalian X chromosome. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 6, 69–92 (2005).
Moriuchi, H., Moriuchi, M. & Fauci, A.S. Cloning and analysis of the promoter region of CCR5, a coreceptor for HIV-1 entry. J. Immunol. 159, 5441–5449 (1997).
Dammann, R. et al. Epigenetic inactivation of a RAS association domain family protein from the lung tumour suppressor locus 3p21.3. Nat. Genet. 25, 315–319 (2000).
Ting, A.H., Schuebel, K.E., Herman, J.G. & Baylin, S.B. Short double-stranded RNA induces transcriptional gene silencing in human cancer cells in the absence of DNA methylation. Nat. Genet. 37, 906–910 (2005).
Castanotto, D. et al. Short hairpin RNA-directed cytosine (CpG) methylation of the RASSF1A gene promoter in HeLa cells. Mol. Ther. 12, 179–183 (2005).
Meister, G. et al. Human Argonaute2 mediates RNA cleavage targeted by miRNAs and siRNAs. Mol. Cell 15, 185–197 (2004).
Gatignol, A., Buckler-White, A., Berkhout, B. & Jeang, K.T. Characterization of a human TAR RNA-binding protein that activates the HIV-1 LTR. Science 251, 1597–1600 (1991).
Chendrimada, T.P. et al. TRBP recruits the Dicer complex to Ago2 for microRNA processing and gene silencing. Nature 436, 740–744 (2005).
Kato, H. et al. RNA polymerase II is required for RNAi-dependent heterochromatin assembly. Science 309, 467–469 (2005).
Pirrotta, V. Polycombing the genome: PcG, trxG, and chromatin silencing. Cell 93, 333–336 (1998).
Cao, R. et al. Role of histone H3 lysine 27 methylation in Polycomb-group silencing. Science 298, 1039–1043 (2002).
Kuzmichev, A., Nishioka, K., Erdjument-Bromage, H., Tempst, P. & Reinberg, D. Histone methyltransferase activity associated with a human multiprotein complex containing the Enhancer of Zeste protein. Genes Dev. 16, 2893–2905 (2002).
Kirmizis, A. et al. Silencing of human polycomb target genes is associated with methylation of histone H3 Lys 27. Genes Dev. 18, 1592–1605 (2004).
Bracken, A.P., Dietrich, N., Pasini, D., Hansen, K.H. & Helin, K. Genome-wide mapping of Polycomb target genes unravels their roles in cell fate transitions. Genes Dev. 20, 1123–1136 (2006).
Dellino, G.I. et al. Polycomb silencing blocks transcription initiation. Mol. Cell 13, 887–893 (2004).
Buhler, M., Verdel, A. & Moazed, D. Tethering RITS to a nascent transcript initiates RNAi- and heterochromatin-dependent gene silencing. Cell 125, 873–886 (2006).
Daviet, L. et al. Analysis of a binding difference between the two dsRNA-binding domains in TRBP reveals the modular function of a KR-helix motif. Eur. J. Biochem. 267, 2419–2431 (2000).
Grimaud, C. et al. RNAi components are required for nuclear clustering of Polycomb group response elements. Cell 124, 957–971 (2006).
Acknowledgements
We thank S. Jacobsen, S. Grewal and R. Martienssen for discussions on TGS, J. Zhang, T. Hong, L. Aagaard and K. Sakurai for technical assistance, D. Castanotto and M. Kalkum for reagents, A. Gatignol (McGill University) for anti-TRBP, G. Pavlakis (National Cancer Institute) for pR5-GFPsg143, members of the Rossi laboratory for technical advice and support and H. Soifer, R. Lin, R. Natarajan and G. Pfeifer for helpful discussions. This work was supported by grants from the US National Institutes of Health to J.J.R. (HL07470 and AI42552) and K.V.M. (HL83473) and from the National Cancer Institute to J.J.R. and K.V.M. (CA33572).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.H.K., K.V.M. and J.J.R. designed the study, D.H.K. carried out most of the experiments, K.V.M. and L.M.V. generated 293T CCR5-GFP cells and performed siRNA screening and D.H.K, K.V.M. and J.J.R. interpreted data and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, D., Villeneuve, L., Morris, K. et al. Argonaute-1 directs siRNA-mediated transcriptional gene silencing in human cells. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13, 793–797 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1142
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1142
This article is cited by
-
The current state and future directions of RNAi-based therapeutics
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2019)
-
Photostable and Biocompatible Fluorescent Silicon Nanoparticles for Imaging-Guided Co-Delivery of siRNA and Doxorubicin to Drug-Resistant Cancer Cells
Nano-Micro Letters (2019)
-
Thymic Epithelial Tumors phenotype relies on miR-145-5p epigenetic regulation
Molecular Cancer (2017)
-
Demystifying the mechanistic and functional aspects of p21 gene activation with double-stranded RNAs in human cancer cells
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2016)
-
saRNA-guided Ago2 targets the RITA complex to promoters to stimulate transcription
Cell Research (2016)