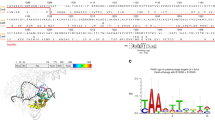
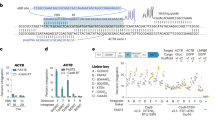
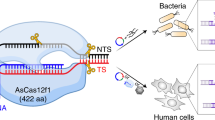
Abstract
We employ the CRISPR-Cas system of Streptococcus pyogenes as programmable RNA-guided endonucleases (RGENs) to cleave DNA in a targeted manner for genome editing in human cells. We show that complexes of the Cas9 protein and artificial chimeric RNAs efficiently cleave two genomic sites and induce indels with frequencies of up to 33%.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wiedenheft, B., Sternberg, S.H. & Doudna, J.A. Nature 482, 331–338 (2012).
Jinek, M. et al. Science 337, 816–821 (2012).
Cohen, J. Science 332, 784–789 (2011).
Kim, H., Um, E., Cho, S.R., Jung, C. & Kim, J.S. Nat. Methods 8, 941–943 (2011).
Kim, H.J., Lee, H.J., Kim, H., Cho, S.W. & Kim, J.S. Genome Res. 19, 1279–1288 (2009).
Miller, J.C. et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 29, 143–148 (2011).
Mussolino, C. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 39, 9283–9293 (2011).
Perez, E.E. et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 26, 808–816 (2008).
Kim, E. et al. Genome Res. 22, 1327–1333 (2012).
Lee, H.J., Kweon, J., Kim, E., Kim, S. & Kim, J.S. Genome Res. 22, 539–548 (2012).
Lee, H.J., Kim, E. & Kim, J.S. Genome Res. 20, 81–89 (2010).
Kim, J.S., Lee, H.J. & Carroll, D. Nat. Methods 7, 91, author reply 91–92 (2010).
Reyon, D. et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 30, 460–465 (2012).
Cong, L. et al. Science doi:10.1126/science.1231143 (3 January 2013).
Mali, P. et al. Science doi:10.1126/science.1232033 (3 January 2013).
Jiang, W., Bikard, D., Cox, D., Zhang, F. & Marraffini, L.A. RNA-guided editing of bacterial genomes using CRISPR-Cas systems. Nat. Biotechnol. advance online publication, doi:10.1038/nbt.2508 (29 January 2013).
Hwang, W.Y. et al. Efficient genome editing in zebrafish using a CRISPR-Cas system. Nat. Biotechnol. advance online publication, doi:10.1038/nbt.2501 (29 January 2013).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (2012-0001225) and ToolGen, Inc. We thank Jae Kyung Chon for bioinformatic analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.W.C., S.K. and J.M.K. performed the experiments. J.-S.K. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
S.W.C., S.K. and J.-S.K. have filed a patent based on this work.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–6, Supplementary Methods and Supplementary Table 1 (PDF 550 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, S., Kim, S., Kim, J. et al. Targeted genome engineering in human cells with the Cas9 RNA-guided endonuclease. Nat Biotechnol 31, 230–232 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2507
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2507
This article is cited by
-
Bacterial genome engineering using CRISPR-associated transposases
Nature Protocols (2024)
-
A robust CRISPR interference gene repression system in Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Archives of Microbiology (2024)
-
Extru-seq: a method for predicting genome-wide Cas9 off-target sites with advantages of both cell-based and in vitro approaches
Genome Biology (2023)
-
Elongation roadblocks mediated by dCas9 across human genes modulate transcription and nascent RNA processing
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2023)
-
Dual intron-targeted CRISPR-Cas9-mediated disruption of the AML RUNX1-RUNX1T1 fusion gene effectively inhibits proliferation and decreases tumor volume in vitro and in vivo
Leukemia (2023)