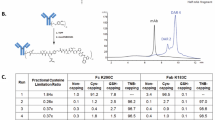
Abstract
The reactive thiol in cysteine is used for coupling maleimide linkers in the generation of antibody conjugates. To assess the impact of the conjugation site, we engineered cysteines into a therapeutic HER2/neu antibody at three sites differing in solvent accessibility and local charge. The highly solvent-accessible site rapidly lost conjugated thiol-reactive linkers in plasma owing to maleimide exchange with reactive thiols in albumin, free cysteine or glutathione. In contrast, a partially accessible site with a positively charged environment promoted hydrolysis of the succinimide ring in the linker, thereby preventing this exchange reaction. The site with partial solvent-accessibility and neutral charge displayed both properties. In a mouse mammary tumor model, the stability and therapeutic activity of the antibody conjugate were affected positively by succinimide ring hydrolysis and negatively by maleimide exchange with thiol-reactive constituents in plasma. Thus, the chemical and structural dynamics of the conjugation site can influence antibody conjugate performance by modulating the stability of the antibody-linker interface.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carter, P.J. & Senter, P.D. Antibody-drug conjugates for cancer therapy. Cancer J. 14, 154–169 (2008).
Polakis, P. Arming antibodies for cancer therapy. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 5, 382–387 (2005).
Kreitman, R.J. & Pastan, I. Immunotoxins for targeted cancer therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 31, 53–88 (1998).
Marik, J. & Junutula, J.R. Emerging role of immunoPET in receptor targeted cancer therapy. Curr. Drug Deliv. 8, 70–78 (2011).
Ryan, S.M., Mantovani, G., Wang, X., Haddleton, D.M. & Brayden, D.J. Advances in PEGylation of important biotech molecules: delivery aspects. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 5, 371–383 (2008).
McCarron, P.A. et al. Antibody conjugates and therapeutic strategies. Mol. Interv. 5, 368–380 (2005).
Medintz, I.L., Uyeda, H.T., Goldman, E.R. & Mattoussi, H. Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labelling and sensing. Nat. Mater. 4, 435–446 (2005).
Hamblett, K.J. et al. Effects of drug loading on the antitumor activity of a monoclonal antibody drug conjugate. Clin. Cancer Res. 10, 7063–7070 (2004).
Polson, A.G. et al. Antibody-drug conjugates for the treatment of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: target and linker-drug selection. Cancer Res. 69, 2358–2364 (2009).
Chapman, A.P. et al. Therapeutic antibody fragments with prolonged in vivo half-lives. Nat. Biotechnol. 17, 780–783 (1999).
Junutula, J.R. et al. Site-specific conjugation of a cytotoxic drug to an antibody improves the therapeutic index. Nat. Biotechnol. 26, 925–932 (2008).
Lewis Phillips, G.D. et al. Targeting HER2-positive breast cancer with trastuzumab-DM1, an antibody-cytotoxic drug conjugate. Cancer Res. 68, 9280–9290 (2008).
Doronina, S.O. et al. Development of potent monoclonal antibody auristatin conjugates for cancer therapy. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 778–784 (2003).
Chari, R.V.J. Targeted cancer therapy: conferring specificity to cytotoxic drugs. Acc. Chem. Res. 41, 98–107 (2008).
Wu, A.M. & Senter, P.D. Arming antibodies: prospects and challenges for immunoconjugates. Nat. Biotechnol. 23, 1137–1146 (2005).
Junutula, J.R. et al. Engineered thio-trastuzumab-DM1 conjugate with an improved therapeutic index to target human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 16, 4769–4778 (2010).
Xu, K. et al. Characterization of intact antibody-drug conjugates from plasma/serum in vivo by affinity capture capillary liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 412, 56–66 (2011).
Alley, S.C. et al. Contribution of linker stability to the activities of anticancer immunoconjugates. Bioconjug. Chem. 19, 759–765 (2008).
Lin, D., Saleh, S. & Liebler, D.C. Reversibility of covalent electrophile-protein adducts and chemical toxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 21, 2361–2369 (2008).
Knight, P. Hydrolysis of p-NN′-phenylenebismaleimide and its adducts with cysteine. Implications for cross-linking of proteins. Biochem. J. 179, 191–197 (1979).
Khan, M.N. Kinetics and mechanism of the alkaline hydrolysis of maleimide. J. Pharm. Sci. 73, 1767–1771 (1984).
Kalia, J. & Raines, R.T. Catalysis of imido group hydrolysis in a maleimide conjugate. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 17, 6286–6289 (2007).
Austin, C.D. et al. Endocytosis and sorting of ErbB2 and the site of action of cancer therapeutics trastuzumab and geldanamycin. Mol. Biol. Cell 15, 5268–5282 (2004).
Chen, Y. et al. Armed antibodies targeting the mucin repeats of the ovarian cancer antigen, MUC16, are highly efficacious in animal tumor models. Cancer Res. 67, 4924–4932 (2007).
Acknowledgements
We thank our Genentech colleagues: J. Speer and E. Wu for reagent generation and inventory; D. Bumbaca for plasma stability study; J. Lau and I. Inigo for ADC efficacy studies; P. Carter and S. Panowski for critical review of the manuscript; H.B. Lowman, S. Kenkare-Mitra and I. Mellman for their insightful discussions. Anti-MMAE mouse monoclonal antibodies were a generous gift from Seattle Genetics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.-Q.S. and K.X. designed experiments developed the methodology, performed plasma stability studies and wrote the manuscript. L.L. and M.K. performed plasma stability and LC-MS analyses. H.R. conducted ADC conjugations and S.B. generated THIOMAB constructs and performed in vitro potency studies. K.L.P.-R., J.T. and S.-F.Y. performed in vivo efficacy studies. E.M., D.L. and J.T. conducted pharmacokinetic studies. J.B. and O.M.S. quantified free MMAE levels in the plasma. S.J.S. performed internalization studies. P.J.M. and P.E.H. purified antibodies. C.E. performed antibody structural analysis. T.N., W.A.S., R.N.F. and K.M.F. designed and conducted preclinical safety studies. D.P. and S.D.S. provided project management support. L.A.K., A.E., W.L.W., R.V., S.K., M.X.S. and R.H.S. provided direction and guidance. P.P. provided direction, guidance and assisted in writing the manuscript. J.R.J. led the overall conjugation site-dependent antibody conjugate program, generated trastuzumab THIOMAB constructs, designed experiments and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
All authors were employees of Genentech/Roche at the time this work was conducted.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Tables 1 and 2 and Supplementary Figures 1–18 (PDF 1161 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, BQ., Xu, K., Liu, L. et al. Conjugation site modulates the in vivo stability and therapeutic activity of antibody-drug conjugates. Nat Biotechnol 30, 184–189 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2108
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2108