Identification of an IGHV3-53-Encoded RBD-Targeting Cross-Neutralizing Antibody from an Early COVID-19 Convalescent
Abstract
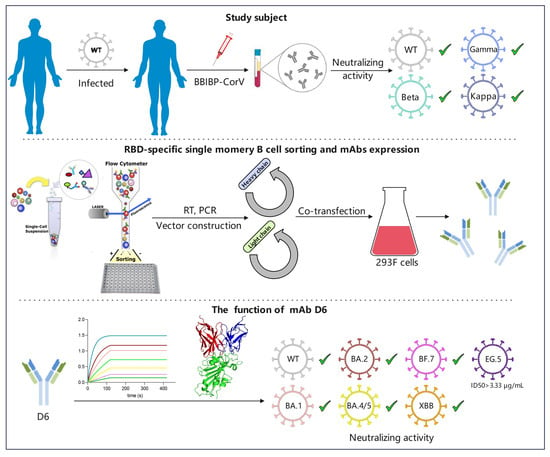
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subject
2.2. Construction of RBD Probe
2.3. Isolation of RBD-Specific Single B Cells by Flow Cytometry
2.4. MAb Gene Amplification, Vector Construction, and mAb Expression
2.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.6. SARS-CoV-2 Pseudovirus Neutralization Assays
2.7. Authentic SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization Assays
2.8. Biolayer Interferometry (BLI)
2.9. Structure Analysis of Antibody-Antigen Complex
3. Results
3.1. The Plasma of Donor YYQ Not Only Contains RBD-Targeting Antibodies but Also Contains Neutralizing Antibodies against Multiple SARS-CoV-2 Variants
3.2. RBD-Specific Memory B Cell Sorting and Antibody Cloning
3.3. The Gene Characteristics of D6
3.4. Binding Activity of D6 with RBD
3.5. The Binding Kinetics of D6 to RBD
3.6. Neutralizing Activity of D6 against SARS-CoV-2 Pseudovirus Variants
3.7. Neutralization Activity of D6 against Authentic SARS-CoV-2 Variants
3.8. Structural Basis for Neutralization
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Zhou, P.; Shi, Z.L. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreich, D.M.; Sivapalasingam, S.; Norton, T.; Ali, S.; Gao, H.; Bhore, R.; Xiao, J.; Hooper, A.T.; Hamilton, J.D.; Musser, B.J.; et al. REGEN-COV Antibody Combination and Outcomes in Outpatients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Gonzalez-Rojas, Y.; Juarez, E.; Crespo Casal, M.; Moya, J.; Falci, D.R.; Sarkis, E.; Solis, J.; Zheng, H.; Scott, N.; et al. Early Treatment for COVID-19 with SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Sotrovimab. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1941–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrabi, R.; Bhiman, J.N.; Burton, D.R. Strategies for a multi-stage neutralizing antibody-based HIV vaccine. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 53, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.C.; Zheng, X.J.; Ye, X.S. Broadly Neutralizing Antibody-Guided Carbohydrate-Based HIV Vaccine Design: Challenges and Opportunities. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cao, L.; Gao, X.S.; Zheng, B.Y.; Deng, Y.Q.; Li, J.X.; Feng, R.; Bian, Q.; Guo, X.L.; Wang, N.; et al. A proof of concept for neutralizing antibody-guided vaccine design against SARS-CoV-2. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, nwab053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altomare, C.G.; Adelsberg, D.C.; Carreno, J.M.; Sapse, I.A.; Amanat, F.; Ellebedy, A.H.; Simon, V.; Krammer, F.; Bajic, G. Structure of a Vaccine-Induced, Germline-Encoded Human Antibody Defines a Neutralizing Epitope on the SARS-CoV-2 Spike N-Terminal Domain. mBio 2022, 13, e0358021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.S. Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 cell receptor gene ACE2 in a wide variety of human tissues. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Ge, J.; Yu, J.; Shan, S.; Zhou, H.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; et al. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor. Nature 2020, 581, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Song, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, N.; Xu, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, J.; Weng, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Z.; et al. Molecular Architecture of the SARS-CoV-2 Virus. Cell 2020, 183, 730–738.e713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zost, S.J.; Gilchuk, P.; Case, J.B.; Binshtein, E.; Chen, R.E.; Nkolola, J.P.; Schafer, A.; Reidy, J.X.; Trivette, A.; Nargi, R.S.; et al. Potently neutralizing and protective human antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020, 584, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, A.T.; Gukasyan, J.; Arabian, S.; Wang, S.; Neeki, M.M. Emergent Inpatient Administration of Casirivimab and Imdevimab Antibody Cocktail for the Treatment of COVID-19 Pneumonia. Cureus 2021, 13, e15280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casirivimab and imdevimab for COVID-19. Aust. Prescr. 2022, 45, 58–59. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Group, R.C. Casirivimab and imdevimab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): A randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet 2022, 399, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, R.; Moyo, S.; Amoako, D.G.; Tegally, H.; Scheepers, C.; Althaus, C.L.; Anyaneji, U.J.; Bester, P.A.; Boni, M.F.; Chand, M.; et al. Rapid epidemic expansion of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant in southern Africa. Nature 2022, 603, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCallum, M.; De Marco, A.; Lempp, F.A.; Tortorici, M.A.; Pinto, D.; Walls, A.C.; Beltramello, M.; Chen, A.; Liu, Z.; Zatta, F.; et al. N-terminal domain antigenic mapping reveals a site of vulnerability for SARS-CoV-2. Cell 2021, 184, 2332–2347 e2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Yisimayi, A.; Jian, F.; Song, W.; Xiao, T.; Wang, L.; Du, S.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.; et al. BA.2.12.1, BA.4 and BA.5 escape antibodies elicited by Omicron infection. Nature 2022, 608, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jian, F.; Xiao, T.; Song, W.; Yisimayi, A.; Huang, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; An, R.; et al. Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies. Nature 2022, 602, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, L.; Misasi, J.; Pegu, A.; Zhang, Y.; Harris, D.R.; Olia, A.S.; Talana, C.A.; Yang, E.S.; Chen, M.; et al. Structural basis for potent antibody neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants including B.1.1.529. Science 2022, 376, eabn8897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iketani, S.; Liu, L.; Guo, Y.; Liu, L.; Chan, J.F.; Huang, Y.; Wang, M.; Luo, Y.; Yu, J.; Chu, H.; et al. Antibody evasion properties of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages. Nature 2022, 604, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Iketani, S.; Nair, M.S.; Li, Z.; Mohri, H.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Bowen, A.D.; Chang, J.Y.; et al. Antibody evasion by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants BA.2.12.1, BA.4 and BA.5. Nature 2022, 608, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, S.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, L.; Jiang, S. Origin, virological features, immune evasion and intervention of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planas, D.; Saunders, N.; Maes, P.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Planchais, C.; Buchrieser, J.; Bolland, W.H.; Porrot, F.; Staropoli, I.; Lemoine, F.; et al. Considerable escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron to antibody neutralization. Nature 2022, 602, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruel, T.; Hadjadj, J.; Maes, P.; Planas, D.; Seve, A.; Staropoli, I.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Porrot, F.; Bolland, W.H.; Nguyen, Y.; et al. Serum neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages BA.1 and BA.2 in patients receiving monoclonal antibodies. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1297–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, K.; Tzou, P.L.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Shafer, R.W. Susceptibility of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variants to Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0092622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Wu, L.; Zheng, A.; Xie, Y.; He, Q.; Rong, X.; Han, P.; Du, P.; Han, P.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Atlas of currently available human neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and escape by Omicron sub-variants BA.1/BA.1.1/BA.2/BA.3. Immunity 2022, 55, 1501–1514.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Jin, C.; Hu, C.; Feng, Y.; Su, J.; Ren, L.; Hao, Y.; et al. Characterization of RBD-specific cross-neutralizing antibodies responses against SARS-CoV-2 variants from COVID-19 convalescents. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1160283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 183, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, D.; Fu, H.; Hao, Y.; Ren, L.; Wang, S.; Hu, X.; Shao, Y.; Hong, K.; Wang, Z. Identification of a CD4-binding site-directed antibody with ADCC activity from a chronic HIV-1B’-infected Chinese donor. Virus Res. 2021, 302, 198470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Mohlenberg, M.; Thakor, J.C.; Tuli, H.S.; Wang, P.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Dhama, K.; Jiang, S. Sensitivity to Vaccines, Therapeutic Antibodies, and Viral Entry Inhibitors and Advances To Counter the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 35, e0001422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhuang, X.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Z.; Zou, Y.; Sheng, J.; Li, T.; Tai, W.; Yu, J.; et al. Inactivated vaccine-elicited potent antibodies can broadly neutralize SARS-CoV-2 circulating variants. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Kucukural, A.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER: A unified platform for automated protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; Liu, H.; Wu, N.C.; Lee, C.D.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, F.; Huang, D.; Yu, W.; Hua, Y.; Tien, H.; et al. Structural basis of a shared antibody response to SARS-CoV-2. Science 2020, 369, 1119–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, H.L.; Liang, K.H.; Lu, R.M.; Kuo, T.W.; Lin, Y.L.; Wu, H.C. Broadly neutralizing human antibodies against Omicron subvariants of SARS-CoV-2. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 30, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Jiang, L.; Zuo, T. Breakthrough infection elicits hypermutated IGHV3-53/3-66 public antibodies with broad and potent neutralizing activity against SARS-CoV-2 variants including the emerging EG.5 lineages. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wall, S.C.; Suryadevara, N.; Kim, C.; Shiakolas, A.R.; Holt, C.M.; Irbe, E.B.; Wasdin, P.T.; Suresh, Y.P.; Binshtein, E.; Chen, E.C.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 antibodies from children exhibit broad neutralization and belong to adult public clonotypes. Cell Rep. Med. 2023, 4, 101267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, T.F.; Zhao, F.; Huang, D.; Beutler, N.; Burns, A.; He, W.T.; Limbo, O.; Smith, C.; Song, G.; Woehl, J.; et al. Isolation of potent SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies and protection from disease in a small animal model. Science 2020, 369, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Thambiraja, T.S.; Karuppanan, K.; Subramaniam, G. Omicron and Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2: A comparative computational study of spike protein. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 1641–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, J.; Shen, J.; Liu, W.; Cao, G. The effects of amino acid substitution of spike protein and genomic recombination on the evolution of SARS-CoV-2. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1228128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Iketani, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Y.; Bowen, A.D.; Liu, M.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; et al. Alarming antibody evasion properties of rising SARS-CoV-2 BQ and XBB subvariants. Cell 2023, 186, 279–286.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zou, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ren, L.; Hao, Y.; Sun, S.; Hu, X.; Ruan, Y.; Ma, L.; et al. Virus Evolution and Neutralization Sensitivity in an HIV-1 Subtype B’ Infected Plasma Donor with Broadly Neutralizing Activity. Vaccines 2021, 9, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; Liu, H.; Wu, N.C.; Wilson, I.A. Recognition of the SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain by neutralizing antibodies. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 538, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagiani, F.; Catanzaro, M.; Lanni, C. Molecular features of IGHV3-53-encoded antibodies elicited by SARS-CoV-2. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, M.; Ito, M.; Kiso, M.; Yamayoshi, S.; Uraki, R.; Fukushi, S.; Watanabe, S.; Suzuki, T.; Maeda, K.; Sakai-Tagawa, Y.; et al. Efficacy of Antiviral Agents against Omicron Subvariants BQ.1.1 and XBB. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhan, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Han, L.; Ma, Y.; Lu, L.; Wen, Y.; et al. A broadly neutralizing antibody against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant infection exhibiting a novel trimer dimer conformation in spike protein binding. Cell Res. 2022, 32, 862–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenheit, R.; Galanis, I.; Sonden, K.; Sperk, M.; Movert, E.; Bacchus, P.; Efimova, T.; Petersson, L.; Rapp, M.; Sahlen, V.; et al. Rapid emergence of omicron sublineages expressing spike protein R346T. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2023, 24, 100564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, N.L.; Clark, T.; Raman, R.; Sasisekharan, R. Insights on the mutational landscape of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant receptor-binding domain. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Aw, Z.Q.; Chen, P.; Zhou, B.; Wang, R.; Ge, X.; Lv, Q.; Cheng, L.; et al. Infection with wild-type SARS-CoV-2 elicits broadly neutralizing and protective antibodies against omicron subvariants. Nat. Immunol. 2023, 24, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Donor | Age | Gender | Infection Time | Clinical Symptom | Hospitalization Length (Days) | Vaccine Type after Infection | Sampling Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YYQ | 35 | Male | 22 January 2020 | Mild | 10 | Inactivated vaccine | 16 December 2021 |
| Pseudovirus | Authentic Viruses | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prototype | Prototype | Beta (B.1.351) | Gamma (P.1) | Kappa (B.1.167.1) |
| 540 | 384 | 12 | 4 | 16 |
| Heavy Chain | Light Chain | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IGHV | IGHD | IGHJ | CDR3 (aa) | SHM (%) | IGKV | IGKJ | CDR3 (aa) | SHM (%) | |
| D6 | 3-53*01 | 2-8*01 | 6*02 | 11 | 7.37 | 1-9*01 | 3*01 | 9 | 3.94 |
| CC12.1 | 3-53*01 | 5-24*01 | 6*02 | 11 | 1.05 | 1-9*01 | 3*01 | 11 | 1.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.; Hu, C.; Wang, S.; Ren, L.; Hao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Su, J.; Zhu, B.; Li, D.; et al. Identification of an IGHV3-53-Encoded RBD-Targeting Cross-Neutralizing Antibody from an Early COVID-19 Convalescent. Pathogens 2024, 13, 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13040272
Hu Y, Hu C, Wang S, Ren L, Hao Y, Wang Z, Liu Y, Su J, Zhu B, Li D, et al. Identification of an IGHV3-53-Encoded RBD-Targeting Cross-Neutralizing Antibody from an Early COVID-19 Convalescent. Pathogens. 2024; 13(4):272. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13040272
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Yuanyuan, Caiqin Hu, Shuo Wang, Li Ren, Yanling Hao, Zheng Wang, Ying Liu, Junwei Su, Biao Zhu, Dan Li, and et al. 2024. "Identification of an IGHV3-53-Encoded RBD-Targeting Cross-Neutralizing Antibody from an Early COVID-19 Convalescent" Pathogens 13, no. 4: 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13040272
APA StyleHu, Y., Hu, C., Wang, S., Ren, L., Hao, Y., Wang, Z., Liu, Y., Su, J., Zhu, B., Li, D., Shao, Y., & Liang, H. (2024). Identification of an IGHV3-53-Encoded RBD-Targeting Cross-Neutralizing Antibody from an Early COVID-19 Convalescent. Pathogens, 13(4), 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13040272