Endotoxin-Binding Peptides Derived from Casein Glycomacropeptide Inhibit Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Inflammatory Responses via Blockade of NF-κB activation in macrophages
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Preparation of GMP Hydrolysates
2.3. Cell Viability Analysis
2.4. Measurement of NO Production
2.5. RNA Isolation and Reverse Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.6. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.7. Determination of LPS-Binding Activity (TAL Assay)
2.8. Flow Cytometry Analysis of LPS-Binding Assay
2.9. Flow Cytometry Analysis of Toll-Like Receptor 4 Expression on the Surface of RAW264.7 Macrophages
2.10. Western Blot Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of GMP Hydrolysates on NO Production in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Macrophages


3.2. Effect of GHP on Inflammatory Gene Expression in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Macrophages
3.3. In Vitro LPS-Binding Activity of GHP


3.4. Effect of GHP on the Binding of FITC-LPS to the Cell Surface of RAW264.7 Macrophages
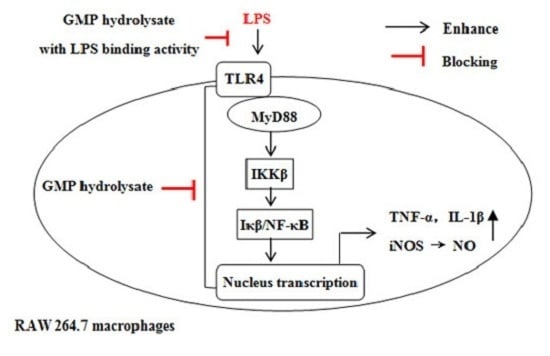
3.5. GHP Reduced LPS-Stimulated Inflammatory Response in RAW264.7 Macrophages through the TLR4/MyD88 Signaling Pathway



3.6. Effect of GHP on NF-κB Activation in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Macrophages


4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harvey, A.E.; Lashinger, L.M.; Hursting, S.D. The growing challenge of obesity and cancer: An inflammatory issue. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1229, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarantino, G.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A. Hepatic steatosis, low-grade chronic inflammation and hormone/growth factor/adipokine imbalance. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 4773–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, B.B.; Schmidt, M.I.; Pankow, J.S.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Couper, D.; Vigo, A.; Hoogeveen, R.; Folsom, A.R.; Heiss, G. Low-grade systemic inflammation and the development of type 2 diabetes the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Diabetes 2003, 52, 1799–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Indias, I.; Cardona, F.; Tinahones, F.J.; Queipo-Ortuño, M.I. Impact of the gut microbiota on the development of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D.; Bibiloni, R.; Knauf, C.; Waget, A.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Delzenne, N.M.; Burcelin, R. Changes in gut microbiota control metabolic endotoxemia-induced inflammation in high-fat diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, D.; Coudriet, G.M.; Hyun, K.D.; Lu, Y.; Perdomo, G.; Qu, S.; Slusher, S.; Tse, H.M.; Piganelli, J.; Giannoukakis, N.; et al. FoxO1 links insulin resistance to proinflammatory cytokine IL-1β production in macrophages. Diabetes 2009, 58, 2624–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.A.; Gu, W.; Lee, I.A.; Joh, E.H.; Kim, D.H. High fat diet-induced gut microbiota exacerbates inflammation and obesity in mice via the TLR4 signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskin, D.L.; Sunil, V.R.; Gardner, C.R.; Laskin, J.D. Macrophages and tissue injury: Agents of defense or destruction. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2011, 51, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisberg, S.P.; McCann, D.; Desai, M.; Rosenbaum, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Ferrante, AW. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Taeye, B.M.; Novitskaya, T.; McGuinness, O.P.; Gleaves, L.; Medda, M.; Covington, J.W.; Vaughan, D.E. Macrophage TNF-α contributes to insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in diet-induced obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, E713–E725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.S.; Jung, D.Y.; Morel, C.; Lakhani, S.A.; Kim, J.K.; Flavell, R.A.; Davis, R.J. JNK expression by macrophages promotes obesity-induced insulin resistance and inflammation. Science 2013, 339, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischman, A.; Shoelson, S.E.; Bernier, R.; Goldfine, A.B. Salsalate improves glycemia and inflammatory parameters in obese young adults. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappo, I.; Becovier, H.; Berry, E.M.; Freund, H.R. Polymyxin B reduces cecal flora, TNF production and hepatic steatosis during total parenteral nutrition in the rat. J. Surg. Res. 1991, 51, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, L.; Doan, T.L.; Smith, M.A. Neurotoxicity in patients treated with intravenous polymyxin B: Two case reports. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2009, 66, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byron Cryer, M.D.; Michael, M.D.; Kimmey, B. Gastrointestinal side effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Am. J. Med. 1998, 105, 20S–30S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.J.; Wi, H.R.; Kim, H.R.; Park, K.W.; Hwang, K.A. Pinus densiflora Sieb. et Zucc. alleviates lipogenesis and oxidative stress during oleic acid-induced steatosis in HepG2 cells. Nutrients 2014, 6, 2956–2972. [Google Scholar]
- Zemel, M.B.; Sun, X.; Sobhani, T.; Wilson, B. Effects of dairy compared with soy on oxidative and inflammatory stress in overweight and obese subjects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aihara, K.; Osaka, M.; Yoshida, M. Oral administration of the milk casein-derived tripeptide Val-Pro-Pro attenuates high-fat diet-induced adipose tissue inflammation in mice. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 28, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Brück, W.M.; Kelleher, S.L.; Gibson, G.R.; Graverholt, G.; Lönnerdal, B.L. The effects of alpha-lactalbumin and glycomacropeptide on the association of CaCo-2 cells by enteropathogenic E. coli, Salmonella typhimurium and Shigella flexneri. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 259, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Isoda, H.; Tanimoto, M.; Dosako, S.; Idota, T.; Ahiko, K. Inhibition by lactoferrin and κ-casein glycomacropeptide of binding of Cholera toxin to its receptor. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1992, 56, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.P.; Mao, X.Y.; Ren, F.Z.; Che, H.L. Attenuating effect of casein glycomacropeptide on proliferation, differentiation, and lipid accumulation of in vitro Sprague-Dawley rat preadipocytes. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Mao, X.; Cheng, X.; Chen, B. Ameliorating effects of casein glycomacropeptide on obesity induced by high-fat diet in male Sprague-Dawley rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 56, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Q.; Wang, T.T.; Tang, X.; Han, M.Z.; Leng, X.J.; Mao, X.Y. Developing a potential prebiotic of yogurt: Growth of Bifidobacterium and yogurt cultures with addition of glycomacropeptide hydrolysate. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2015, 50, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, L.C.; Wagner, D.A.; Glogowski, J.; Skipper, P.L.; Wishnok, J.S.; Tannenbaum, S.R. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal. Biochem. 1982, 126, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, A.; Takezako, N.; Tamemoto, H.; Ohto-Ozaki, H.; Ohta, S.; Tominaga, S.; Yanagisawa, K. Soluble ST2 protein inhibits LPS stimulation on monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2012, 9, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, J.M.; Lee, J.; Pilch, P.F. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes is accompanied by a loss of insulin receptor substrate-1 and GLUT4 expression without a loss of insulin receptor-mediated signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jager, J.; Gremeaux, T.; Cormont, M.; Le Marchand-Brustel, Y.; Tanti, J.F. Interleukin-1beta-induced insulin resistance in adipocytes through down-regulation of insulin receptor substrate-1 expression. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sugita, H.; Fujimoto, M.; Yasukawa, T.; Shimizu, N.; Sugita, M.; Yasuhara, S.; Martyn, J.A.; Kaneki, M. Inducible nitric-oxide synthase and NO donor induce insulin receptor substrate-1 degradation in skeletal muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 14203–14211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peake, P.W.; Shen, Y.; Campbell, L.V.; Charlesworth, J.A. Human adiponectin binds to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 341, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hsieh, C.C. Lactoferrin Dampens High-Fructose Corn Syrup-Induced Hepatic Manifestations of the Metabolic Syndrome in a Murine Model. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dankesreiter, S.; Hoess, A.; Schneider-Mergener, J.; Wagner, H.; Miethke, T. Synthetic endotoxin-binding peptides block endotoxin-triggered TNF-α production by macrophages in vitro and in vivo and prevent endotoxin-mediated toxic shock. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 4804–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasravi, F.B.; Lee, D.H.; Weisgraber, K.; Harris, H.W. Lipoprotein-bound endotoxin exerts an immunomodulatory effect on hepatocytes through the lipid a domain of LPS. J. Endotoxin Res. 2005, 11, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, J.E.; Park, Z.Y.; Kim, N.D.; Lee, J.Y. Sulforaphane inhibits the engagement of LPS with TLR4/MD2 complex by preferential binding to Cys133 in MD2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 434, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D.; Delzenne, N.M.; Amar, J.; Burcelin, R. Role of gut microflora in the development of obesity and insulin resistance following high-fat diet feeding. Pathol. Biol. 2008, 56, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; Ruan, Y.Y.; Xiong, C.N.; Xu, Q.S.; Wei, P.; Ma, P.; Bai, X.F.; Du, Y.G. Chitosan oligosaccharides suppressant LPS binding to TLR4/MD-2 receptor complex. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, M.; Woods, N.B.; de Luca, C.; Schenk, S.; Lu, J.C.; Bandyopadhyay, G.; Verma, I.M.; Olefsky, M. Hematopoietic cell-specific deletion of toll-like receptor 4 ameliorates hepatic and adipose tissue insulin resistance in high-fat-fed mice. Cell Metab. 2009, 10, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd-Leifer, C.A.; Block, E.F.; Takeda, K.; Akira, S.; Ding, A. The role of MyD88 and TLR4 in the LPS-mimetic activity of Taxol. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001, 31, 2448–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, S.H.; Bazuine, M.; Lumeng, C.N.; Geletka, L.M.; Mowers, J.; White, N.M.; Ma, J.; Zhou, J.; Qi, N.; Westcott, D.; et al. The protein kinase IKKε regulates energy balance in obese mice. Cell 2009, 138, 961–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Gaynor, R.B. Therapeutic potential of inhibition of the NF-κB pathway in the treatment of inflammation and cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Kokoeva, M.V.; Inouye, K.; Tzameli, I.; Yin, H.; Flier, J.S. TLR4 links innate immunity and fatty acid-induced insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 3015–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, X.; Gao, D.; Chen, B.; Mao, X. Endotoxin-Binding Peptides Derived from Casein Glycomacropeptide Inhibit Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Inflammatory Responses via Blockade of NF-κB activation in macrophages. Nutrients 2015, 7, 3119-3137. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7053119
Cheng X, Gao D, Chen B, Mao X. Endotoxin-Binding Peptides Derived from Casein Glycomacropeptide Inhibit Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Inflammatory Responses via Blockade of NF-κB activation in macrophages. Nutrients. 2015; 7(5):3119-3137. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7053119
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Xue, Dongxiao Gao, Bin Chen, and Xueying Mao. 2015. "Endotoxin-Binding Peptides Derived from Casein Glycomacropeptide Inhibit Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Inflammatory Responses via Blockade of NF-κB activation in macrophages" Nutrients 7, no. 5: 3119-3137. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7053119
APA StyleCheng, X., Gao, D., Chen, B., & Mao, X. (2015). Endotoxin-Binding Peptides Derived from Casein Glycomacropeptide Inhibit Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Inflammatory Responses via Blockade of NF-κB activation in macrophages. Nutrients, 7(5), 3119-3137. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7053119