The Role of miRNAs in the Pathophysiology of Liver Diseases and Toxicity
Abstract
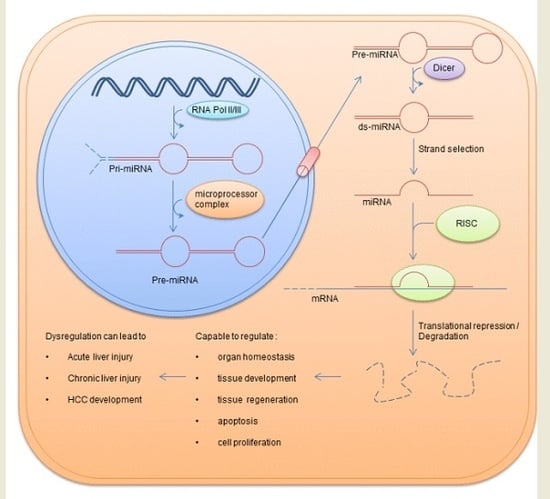
:1. miRNAs
2. miRNAs in the Physiology of the Liver
3. The Role of miRNAs in Acute Liver Toxicity
4. The Role of miRNAs in Chronic Alcoholic Liver Toxicity
5. miRNAs in Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis
6. miRNAs in HCC
7. Outlook
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADAM10 | A disintegrin and metalloprotease 10 |
| ALF | Acute liver failure |
| ALT | Alanine transaminase |
| APAP | Acetaminophen |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| ASCL1 | Acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 1 |
| CCl4 | Carbontetrachloride |
| ConA | Concanavalin A |
| d-Gal | d-Galactosamine |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| FZD7 | Frizzled type 7 receptor |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HCV | Hepatitis C Virus |
| HIF1α | Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α |
| IGF-1R | Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor |
| I/R | Ischemia and reperfusion |
| lncRNAs | Long non coding RNAs |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| LSEC | Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells |
| miR | Micro-RNA |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteases |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NASH | Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis |
| ncRNA | Noncoding RNAs |
| NFκb | Nuclear factor ‘kappa-light-chain-enhancer’ of activated B-cells |
| PAK4 | P21 (RAC1) activated kinase 4 |
| PPARγ | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma |
| PTTG1 | Pituitary tumor-transforming gene 1 |
| SRF | Serum response factor |
| TAA | Thioacetamide |
References
- Krol, J.; Loedige, I.; Filipowicz, W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchert, G.M.; Lanier, W.; Davidson, B.L. RNA polymerase iii transcribes human microRNAs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006, 13, 1097–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macfarlane, L.A.; Murphy, P.R. microRNA: Biogenesis, function and role in cancer. Curr. Genom. 2010, 11, 537–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landgraf, P.; Rusu, M.; Sheridan, R.; Sewer, A.; Iovino, N.; Aravin, A.; Pfeffer, S.; Rice, A.; Kamphorst, A.O.; Landthaler, M.; et al. A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell 2007, 129, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandiera, S.; Pfeffer, S.; Baumert, T.F.; Zeisel, M.B. MiR-122—A key factor and therapeutic target in liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benz, F.; Roy, S.; Trautwein, C.; Roderburg, C.; Luedde, T. Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for sepsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijer, H.A.; Smith, E.M.; Bushell, M. Regulation of miRNA strand selection: Follow the leader? Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2014, 42, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, M.; Kim, V.N. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, B.M.; Robles, A.I.; Harris, C.C. Genetic variation in microRNA networks: The implications for cancer research. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, G.; Bala, S. MicroRNAs in liver disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seok, J.; Warren, H.S.; Cuenca, A.G.; Mindrinos, M.N.; Baker, H.V.; Xu, W.; Richards, D.R.; McDonald-Smith, G.P.; Gao, H.; Hennessy, L.; et al. Genomic responses in mouse models poorly mimic human inflammatory diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3507–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osuchowski, M.F.; Remick, D.G.; Lederer, J.A.; Lang, C.H.; Aasen, A.O.; Aibiki, M.; Azevedo, L.C.; Bahrami, S.; Boros, M.; Cooney, R.; et al. Abandon the mouse research ship? Not just yet! Shock 2014, 41, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, S.; Marzolf, B.; Troisch, P.; Brightman, A.; Hu, Z.; Hood, L.E.; Galas, D.J. Circulating microRNAs, potential biomarkers for drug-induced liver injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4402–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roderburg, C.; Benz, F.; Vargas Cardenas, D.; Koch, A.; Janssen, J.; Vucur, M.; Gautheron, J.; Schneider, A.T.; Koppe, C.; Kreggenwinkel, K.; et al. Elevated miR-122 serum levels are an independent marker of liver injury in inflammatory diseases. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 1172–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starkey Lewis, P.J.; Dear, J.; Platt, V.; Simpson, K.J.; Craig, D.G.; Antoine, D.J.; French, N.S.; Dhaun, N.; Webb, D.J.; Costello, E.M.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as potential markers of human drug-induced liver injury. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1767–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krauskopf, J.; Caiment, F.; Claessen, S.M.; Johnson, K.J.; Warner, R.L.; Schomaker, S.J.; Burt, D.A.; Aubrecht, J.; Kleinjans, J.C. Application of high-throughput sequencing to circulating microRNAs reveals novel biomarkers for drug-induced liver injury. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 143, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.W.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Z.Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, J.; Xue, M.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A panel of serum microRNAs as specific biomarkers for diagnosis of compound- and herb-induced liver injury in rats. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qadir, X.V.; Chen, W.; Han, C.; Song, K.; Zhang, J.; Wu, T. miR-223 deficiency protects against fas-induced hepatocyte apoptosis and liver injury through targeting insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 3141–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schueller, F.; Roy, S.; Loosen, S.H.; Alder, J.; Koppe, C.; Schneider, A.T.; Wandrer, F.; Bantel, H.; Vucur, M.; Mi, Q.S.; et al. miR-223 represents a biomarker in acute and chronic liver injury. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 1971–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Han, C.; Zhang, J.; Song, K.; Wang, Y.; Wu, T. MiR-150 deficiency protects against fas-induced acute liver injury in mice through regulation of akt. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Benz, F.; Alder, J.; Bantel, H.; Janssen, J.; Vucur, M.; Gautheron, J.; Schneider, A.; Schuller, F.; Loosen, S.; et al. Down-regulation of miR-192-5p protects from oxidative stress-induced acute liver injury. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, C.; Wang, Y.L.; Xie, C.; Sang, Y.; Li, T.J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, L.; Zhuang, S.M. Identification of a novel TGF-β-miR-122-fibronectin 1/serum response factor signaling cascade and its implication in hepatic fibrogenesis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 12224–12233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Bantel, H.; Wandrer, F.; Schneider, A.T.; Gautheron, J.; Vucur, M.; Tacke, F.; Trautwein, C.; Luedde, T.; Roderburg, C. miR-1224 inhibits cell proliferation in acute liver failure by targeting the antiapoptotic gene nfib. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 966–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bala, S.; Csak, T.; Saha, B.; Zatsiorsky, J.; Kodys, K.; Catalano, D.; Satishchandran, A.; Szabo, G. The pro-inflammatory effects of miR-155 promote liver fibrosis and alcohol-induced steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1378–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roderburg, C.; Urban, G.W.; Bettermann, K.; Vucur, M.; Zimmermann, H.; Schmidt, S.; Janssen, J.; Koppe, C.; Knolle, P.; Castoldi, M.; et al. Micro-RNA profiling reveals a role for miR-29 in human and murine liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2011, 53, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Friedman, R.C.; Marquez, R.T.; Keck, K.; Kong, B.; Icardi, M.S.; Brown, K.E.; Burge, C.B.; Schmidt, W.N.; Wang, Y.; et al. Hepatitis c virus infection and hepatic stellate cell activation downregulate miR-29: miR-29 overexpression reduces hepatitis c viral abundance in culture. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 1753–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chu, E.S.; Chen, H.Y.; Man, K.; Go, M.Y.; Huang, X.R.; Lan, H.Y.; Sung, J.J.; Yu, J. MicroRNA-29b prevents liver fibrosis by attenuating hepatic stellate cell activation and inducing apoptosis through targeting PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 7325–7338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.Q.; Chen, C.; Xu, M.D.; Guo, J.; Li, Y.M.; Xia, Q.M.; Liu, H.M.; He, J.; Yu, H.Y.; Zhu, L. The rno-miR-34 family is upregulated and targets acsl1 in dimethylnitrosamine-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 1522–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, G.; Li, B.; Xin, X.; Xu, M.; Ji, G.; Yu, H. MicroRNA-34a promotes hepatic stellate cell activation via targeting acsl1. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 3008–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, S.; He, J.; Lou, L.; Ye, W.; Wang, J. MicroRNA-34a and microRNA-34c promote the activation of human hepatic stellate cells by targeting peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Glaser, S.S.; Francis, H.; Yang, F.; Han, Y.; Stokes, A.; Staloch, D.; McCarra, J.; Liu, J.; Venter, J.; et al. Epigenetic regulation of miR-34a expression in alcoholic liver injury. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 804–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trebicka, J.; Anadol, E.; Elfimova, N.; Strack, I.; Roggendorf, M.; Viazov, S.; Wedemeyer, I.; Drebber, U.; Rockstroh, J.; Sauerbruch, T.; et al. Hepatic and serum levels of miR-122 after chronic hcv-induced fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, W.C.; Hsu, S.D.; Hsu, C.S.; Lai, T.C.; Chen, S.J.; Shen, R.; Huang, Y.; Chen, H.C.; Lee, C.H.; Tsai, T.F.; et al. MicroRNA-122 plays a critical role in liver homeostasis and hepatocarcinogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2884–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyaaki, H.; Ichikawa, T.; Kamo, Y.; Taura, N.; Honda, T.; Shibata, H.; Milazzo, M.; Fornari, F.; Gramantieri, L.; Bolondi, L.; et al. Significance of serum and hepatic microRNA-122 levels in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2014, 34, e302–e307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakao, K.; Miyaaki, H.; Ichikawa, T. Antitumor function of microRNA-122 against hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakral, S.; Ghoshal, K. MiR-122 is a unique molecule with great potential in diagnosis, prognosis of liver disease, and therapy both as miRNA mimic and antimiR. Curr. Gene Ther. 2015, 15, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, S.H.; Wang, B.; Kota, J.; Yu, J.; Costinean, S.; Kutay, H.; Yu, L.; Bai, S.; La Perle, K.; Chivukula, R.R.; et al. Essential metabolic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumorigenic functions of miR-122 in liver. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2871–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.H.; Shan, H.; Li, D.; Zhou, B.; Pang, P.F. miR-199a-5p suppresses tumorigenesis by targeting clathrin heavy chain in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2017, 35, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; He, L.; Zuo, D.; He, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Yuan, Y. Mutual regulation of miR-199a-5p and HIF-1α modulates the warburg effect in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, S.; Hu, L.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, D. MiR-199a-5p suppresses human bladder cancer cell metastasis by targeting CCR7. BMC Urol. 2016, 16, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Gao, L.; Yang, G.; Tang, S.; Xie, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, J.; Gou, Y.; et al. MiR-199a regulates cell proliferation and survival by targeting FZD7. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esau, C.; Davis, S.; Murray, S.F.; Yu, X.X.; Pandey, S.K.; Pear, M.; Watts, L.; Booten, S.L.; Graham, M.; McKay, R.; et al. MiR-122 regulation of lipid metabolism revealed by in vivo antisense targeting. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castoldi, M.; Vujic Spasic, M.; Altamura, S.; Elmen, J.; Lindow, M.; Kiss, J.; Stolte, J.; Sparla, R.; D’Alessandro, L.A.; Klingmuller, U.; et al. The liver-specific microRNA miR-122 controls systemic iron homeostasis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatfield, D.; Le Martelot, G.; Vejnar, C.E.; Gerlach, D.; Schaad, O.; Fleury-Olela, F.; Ruskeepaa, A.L.; Oresic, M.; Esau, C.C.; Zdobnov, E.M.; et al. Integration of microRNA miR-122 in hepatic circadian gene expression. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, S.; Nakajima, M.; Kida, K.; Yamaura, Y.; Fukami, T.; Yokoi, T. MicroRNAs regulate human hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α, modulating the expression of metabolic enzymes and cell cycle. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 4415–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hand, N.J.; Master, Z.R.; Le Lay, J.; Friedman, J.R. Hepatic function is preserved in the absence of mature microRNAs. Hepatology 2009, 49, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Verfaillie, C.M. MicroRNAs: The fine modulators of liver development and function. Liver Int. 2014, 34, 976–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, W.M. Acute liver failure. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 33, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, K.; Hadem, J.; Krech, T.; Wahl, K.; Manns, M.P.; Dooley, S.; Batkai, S.; Thum, T.; Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Bantel, H. MicroRNAs play a role in spontaneous recovery from acute liver failure. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1346–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendizabal, M.; Silva, M.O. Liver transplantation in acute liver failure: A challenging scenario. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 1523–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teschke, R.; Schulze, J.; Eickhoff, A.; Danan, G. Drug induced liver injury: Can biomarkers assist rucam in causality assessment? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, T.M.; Hodgson, H.J. Animal models of acute hepatic failure. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2000, 81, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, T.; Hamada, Y.; Yamada, H.; Horii, I. Changes of micro-RNA expression in rat liver treated by acetaminophen or carbon tetrachloride—Regulating role of micro-RNA for RNA expression. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 32, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bala, S.; Petrasek, J.; Mundkur, S.; Catalano, D.; Levin, I.; Ward, J.; Alao, H.; Kodys, K.; Szabo, G. Circulating microRNAs in exosomes indicate hepatocyte injury and inflammation in alcoholic, drug-induced, and inflammatory liver diseases. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1946–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoine, D.J.; Dear, J.W.; Lewis, P.S.; Platt, V.; Coyle, J.; Masson, M.; Thanacoody, R.H.; Gray, A.J.; Webb, D.J.; Moggs, J.G.; et al. Mechanistic biomarkers provide early and sensitive detection of acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury at first presentation to hospital. Hepatology 2013, 58, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Russo, M.W.; Steuerwald, N.; Norton, H.J.; Anderson, W.E.; Foureau, D.; Chalasani, N.; Fontana, R.J.; Watkins, P.B.; Serrano, J.; Bonkovsky, H.L. Profiles of miRNAs in serum in severe acute drug induced liver injury and their prognostic significance. Liver Int. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannini, E.G.; Testa, R.; Savarino, V. Liver enzyme alteration: A guide for clinicians. CMAJ 2005, 172, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles-Diaz, M.; Medina-Caliz, I.; Stephens, C.; Andrade, R.J.; Lucena, M.I. Biomarkers in dili: One more step forward. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; He, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Ramirez, T.; Gao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ross, R.A.; Cao, H.; Cai, Y.; Xu, M.; et al. MicroRNA-223 ameliorates alcoholic liver injury by inhibiting the IL-6-p47phox-oxidative stress pathway in neutrophils. Gut 2017, 66, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.H.; Xu, C.F.; Li, Y.M. Association of microRNA-223 expression with hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2009, 54, 2362–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Steele, R.; Shrivastava, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Ray, R.B. Serum miR-30e and miR-223 as novel noninvasive biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taibi, F.; Metzinger-Le Meuth, V.; Massy, Z.A.; Metzinger, L. MiR-223: An inflammatory oncomir enters the cardiovascular field. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haneklaus, M.; Gerlic, M.; O’Neill, L.A.; Masters, S.L. MiR-223: Infection, inflammation and cancer. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 274, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudiger, H.A.; Clavien, P.A. Tumor necrosis factor α, but not fas, mediates hepatocellular apoptosis in the murine ischemic liver. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Yuan, Q.; Balakrishnan, A.; Bantel, H.; Klusmann, J.H.; Manns, M.P.; Ott, M.; Cantz, T.; Sharma, A.D. MicroRNA-125b-5p mimic inhibits acute liver failure. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, N.; Skoko, J.J.; Chartoumpekis, D.V.; Kimura, S.; Slocum, S.L.; Noda, K.; Palliyaguru, D.L.; Fujimuro, M.; Boley, P.A.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. Notch-Nrf2 axis: Regulation of Nrf2 gene expression and cytoprotection by notch signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 34, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, K.; Zhang, X.; Lv, L.; Zhang, J.; Liang, W.; Wang, P. Fine-tuning the expression of microRNA-155 controls acetaminophen-induced liver inflammation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 40, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, W.; Higashiyama, W.; Tohyama, C. Involvement of microRNAs in dioxin-induced liver damage in the mouse. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 122, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teschke, R.; Larrey, D.; Melchart, D.; Danan, G. Traditional chinese medicine (tcm) and herbal hepatotoxicity: Rucam and the role of novel diagnostic biomarkers such as microRNAs. Medicines 2016, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Ji, C.; Lu, X.; Tong, W.; Fan, X.; Gao, Y. Integrated expression profiles of mRNA and microRNA in the liver of fructus meliae toosendan water extract injured mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, M.; Brenner, D.A. Clinical syndromes of alcoholic liver disease. Dig. Dis. 2005, 23, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Day, C.P. Management strategies in alcoholic liver disease. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 4, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Yang, R.; Pei, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.F.; Li, Y. Ethanol exposure induces differential microRNA and target gene expression and teratogenic effects which can be suppressed by folic acid supplementation. Hum. Reprod. 2009, 24, 562–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolganiuc, A.; Petrasek, J.; Kodys, K.; Catalano, D.; Mandrekar, P.; Velayudham, A.; Szabo, G. MicroRNA expression profile in lieber-decarli diet-induced alcoholic and methionine choline deficient diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis models in mice. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 1704–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bala, S.; Marcos, M.; Kodys, K.; Csak, T.; Catalano, D.; Mandrekar, P.; Szabo, G. Up-regulation of microRNA-155 in macrophages contributes to increased tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) production via increased mRNA half-life in alcoholic liver disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 1436–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippai, D.; Bala, S.; Csak, T.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Szabo, G. Chronic alcohol-induced microRNA-155 contributes to neuroinflammation in a TLR4-dependent manner in mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avissar, M.; McClean, M.D.; Kelsey, K.T.; Marsit, C.J. MicroRNA expression in head and neck cancer associates with alcohol consumption and survival. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 2059–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dippold, R.P.; Vadigepalli, R.; Gonye, G.E.; Patra, B.; Hoek, J.B. Chronic ethanol feeding alters miRNA expression dynamics during liver regeneration. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2013, 37, E59–E69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, R.G. Cellular sources of extracellular matrix in hepatic fibrosis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2008, 12, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.J.; Pan, Q.; Li, D.G.; Sun, H.; Liu, B.W. MiR-15b and miR-16 are implicated in activation of the rat hepatic stellate cell: An essential role for apoptosis. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakner, A.M.; Steuerwald, N.M.; Walling, T.L.; Ghosh, S.; Li, T.; McKillop, I.H.; Russo, M.W.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Schrum, L.W. Inhibitory effects of microRNA 19b in hepatic stellate cell-mediated fibrogenesis. Hepatology 2012, 56, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maubach, G.; Lim, M.C.; Chen, J.; Yang, H.; Zhuo, L. MiRNA studies in in vitro and in vivo activated hepatic stellate cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 2748–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.J.; Pan, Q.; Cheng, T.; Jiang, B.; Chen, G.Y.; Li, D.G. Changes in microRNAs associated with hepatic stellate cell activation status identify signaling pathways. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 5163–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rooij, E.; Sutherland, L.B.; Thatcher, J.E.; DiMaio, J.M.; Naseem, R.H.; Marshall, W.S.; Hill, J.A.; Olson, E.N. Dysregulation of microRNAs after myocardial infarction reveals a role of miR-29 in cardiac fibrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13027–13032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwiecinski, M.; Noetel, A.; Elfimova, N.; Trebicka, J.; Schievenbusch, S.; Strack, I.; Molnar, L.; von Brandenstein, M.; Tox, U.; Nischt, R.; et al. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) inhibits collagen i and iv synthesis in hepatic stellate cells by miRNA-29 induction. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noetel, A.; Kwiecinski, M.; Elfimova, N.; Huang, J.; Odenthal, M. MicroRNA are central players in anti- and profibrotic gene regulation during liver fibrosis. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwiecinski, M.; Elfimova, N.; Noetel, A.; Tox, U.; Steffen, H.M.; Hacker, U.; Nischt, R.; Dienes, H.P.; Odenthal, M. Expression of platelet-derived growth factor-c and insulin-like growth factor i in hepatic stellate cells is inhibited by miR-29. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2012, 92, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, L.; Zhu, D.; Li, X.; Gu, H.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zen, K. Protective role of estrogen-induced miRNA-29 expression in carbon tetrachloride-induced mouse liver injury. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 14851–14862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostini, M.; Knight, R.A. MiR-34: From bench to bedside. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, Y.; Nakajima, M.; Tsuneyama, K.; Takamiya, M.; Aoki, Y.; Fukami, T.; Yokoi, T. Retinoid x receptor α in human liver is regulated by miR-34a. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 90, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutz, D.R.; Collins, P.J.; Suresh, U.; Lu, M.; Ramirez, C.M.; Fernandez-Hernando, C.; Huang, Y.; Abreu Rde, S.; Le, S.Y.; Shapiro, B.A.; et al. Two-tiered approach identifies a network of cancer and liver disease-related genes regulated by miR-122. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 18066–18078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schueller, F.; Roy, S.; Trautwein, C.; Luedde, T.; Roderburg, C. MiR-122 expression is not regulated during activation of hepatic stellate cells. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 865–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ghazwani, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, J.; Fan, J.; Gandhi, C.R.; Li, S. MiR-122 regulates collagen production via targeting hepatic stellate cells and suppressing P4HA1 expression. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, B.; Wang, G. MicroRNAs involved with hepatocellular carcinoma (review). Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 2811–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaglioni, F.; Ciccia, S.; Marino, M.; Bedogni, G.; Bellentani, S. Ash and nash. Dig. Dis. 2011, 29, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehra, M.; Chauhan, R. Long noncoding RNAs as a key player in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomark. Cancer 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramantieri, L.; Ferracin, M.; Fornari, F.; Veronese, A.; Sabbioni, S.; Liu, C.G.; Calin, G.A.; Giovannini, C.; Ferrazzi, E.; Grazi, G.L.; et al. Cyclin g1 is a target of miR-122a, a microRNA frequently down-regulated in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6092–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; Nasser, M.W.; Wang, B.; Hsu, S.H.; Datta, J.; Kutay, H.; Yadav, A.; Nuovo, G.; Kumar, P.; Ghoshal, K. MicroRNA-122 inhibits tumorigenic properties of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and sensitizes these cells to sorafenib. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 32015–32027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, C.; Wang, R.; Li, D.; Lin, X.J.; Wei, Q.K.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, W.; Zhuang, S.M. A novel GSK-3 β-C/EBP α-miR-122-insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor regulatory circuitry in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1702–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Lin, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Z.; Ding, G.; Dong, Q.; Qin, L.; Wu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. Identification of mirnomes in human liver and hepatocellular carcinoma reveals miR-199a/b-3p as therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornari, F.; Milazzo, M.; Chieco, P.; Negrini, M.; Calin, G.A.; Grazi, G.L.; Pollutri, D.; Croce, C.M.; Bolondi, L.; Gramantieri, L. miR-199a-3p regulates mtor and c-met to influence the doxorubicin sensitivity of human hepatocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 5184–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, A.; Panda, J.J.; Singh, A.K.; Yadav, N.; Bihari, C.; Biswas, S.; Sarin, S.K.; Chauhan, V.S. Targeted delivery of miR-199a-3p using self-assembled dipeptide nanoparticles efficiently reduces hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, J.C.; Park, J.K.; Jiang, J.; Kim, J.H.; Nagorney, D.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Banerjee, S.; Schmittgen, T.D. miR-199a-3p targets CD44 and reduces proliferation of CD44 positive hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 403, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.; Dasgupta, D.; Ghosh, A.; Roychoudhury, S.; Kumar, D.; Gorain, M.; Butti, R.; Datta, S.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, S.; et al. MiRNA199a-3p suppresses tumor growth, migration, invasion and angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting VEGFA, VEGFR1, VEGFR2, HGF and MMP2. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| miRNA | Model/Side of Action | Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Liver Injury | |||
| miR-122 | APAP mice model | elevated serum levels, Elevation dose and exposure dependent | [15] |
| I/R mice model | elevated miR-122 serum levels, correlation with AST, ALT and hepatic cell death | [16] | |
| APAP induced ALF patients | elevated serum levels | [17,18] | |
| Dioscorea bulbifera induced liver injury | elevated serum levels | [19] | |
| miR-223 | miR-223−/− mice in FAS induced liver injury model | protection against hepatocyte apoptosis and liver injury | [20] |
| APAP mice model | upregulation of miR-223 | [21] | |
| ConA mice model | upregulation of miR-223 | [21] | |
| acute CCl4 and I/R mice model | upregulation; KO had no effect on severity of liver damage; | [21] | |
| ALF patients | elevated liver tissue and serum levels; Impaired prognosis for patients with elevated miR-223 tissue levels; identification of miR-223 as potential biomarker for liver damage | [21] | |
| miR-150 | miR-150−/− in FAS induced liver injury model | miR-150 deficiency had protective effect; elevated AKT expression AKT1 and AKT2 are direct targets of miR-150 | [22] |
| miR-150−/− in LPS/GLN | no effect observed | [22] | |
| miR-192-5p | HepG2 cells treated with H2O2 | identification of Zeb2 as miRNA target regulating cell death | [23] |
| I/R and CCl4 mice model/ALF patients | downregulated in liver; serum levels increased after I/R and correlated with degree of liver damage | [24] | |
| miR-1224 | I/R, APAP and CCl4 mice model | upregulation was associated with impaired proliferation and elevated apoptosis In hepatocytes: miR-1224 repressed the anti-apoptotic gene Nfib | [25] |
| ALF patients | elevated serum and liver tissue levels were linked to unfavourable prognosis | [25] | |
| Chronic Liver Diseases | |||
| miR-155 | miR-155−/− in alcohol mice model | KO protected from alcohol induced steatosis, inflammation and liver fibrosis | [26] |
| miR-29 | CCl4 mice model | downregulation of miR-29a, miR-29b and miR-29c; | [27] |
| IFNα & TGFβ1 stimulated HSC, | decreased miR-29 expression; reduced ECM synthesis | [28] | |
| Ectopic expression of miR-29b in activated HSCs (LX-1, HSC-T6) | miR-29b suppressed SMAD3 and TGFβ1 and prevents liver fibrosis by regulating HSC proliferation and apoptosis through its targets PIK3R1 and AKT3 | [29] | |
| miR-34 | Dimethylnitrosamine-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats | upregulation of miR-34 family; ASCL1 is a direct target of miR-34a and miR-34c | [30] |
| activated HSC | upregulation of miR-34a was associated with regulation of ECM proteins like collagen, desmin a αSMA Identification of PPARγ as target of miR-34a and miR-34c | [31,32] | |
| alcoholic liver injury model | Caspase 2 and Sirtuin 1 are direct targets of miR-34; MMP1 and MMP2 were dysregulated after altered miR-34a expression | [33] | |
| miR-122 | chronic hepatitis C patients | decreased hepatic expression miR-122 correlated with severity of fibrosis | [34] |
| miR-122−/− | displayed inflammation and portal fibrosis due to activation of HSC; pro-fibrotic transcription factor KLF6 is a direct target of miR-122 and was activated in hepatocytes of miR-122−/− mice. | [35] | |
| Reintroduction of miR-122 in CCl4 treated mice | Inhibition of Collagen fibrils formation | ||
| NAFLD patients | high miR-122 expression was associated with more severe liver fibrosis | [36] | |
| Hepatocellular Carcinoma | |||
| miR-122 | HCC patients | downregulated miR-122 expression in HCC patients. Expression inversely correlated with presence of metastatic disease and patients´ general prognosis | [6] |
| HCC cell lines | miR-122 inhibit proliferation, migration and promotes hepatocyte death | [37,38] | |
| miR-122−/− | miR-122 deletion was associated with development of steatohepatitis, fibrosis and liver cancer | [35,39] | |
| miR-199 | HCC patients | downregulation of miR-199a-5p in HCC was associated with more advanced disease stages, higher recurrence rates and impaired overall patients’ prognosis | [40] |
| HCC cell lines | miR-199a suppressed tumour proliferation, induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest (via regulation of MMP-9, FZD7, HIF1α) | [41,42,43] | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schueller, F.; Roy, S.; Vucur, M.; Trautwein, C.; Luedde, T.; Roderburg, C. The Role of miRNAs in the Pathophysiology of Liver Diseases and Toxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010261
Schueller F, Roy S, Vucur M, Trautwein C, Luedde T, Roderburg C. The Role of miRNAs in the Pathophysiology of Liver Diseases and Toxicity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(1):261. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010261
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchueller, Florian, Sanchari Roy, Mihael Vucur, Christian Trautwein, Tom Luedde, and Christoph Roderburg. 2018. "The Role of miRNAs in the Pathophysiology of Liver Diseases and Toxicity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 1: 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010261
APA StyleSchueller, F., Roy, S., Vucur, M., Trautwein, C., Luedde, T., & Roderburg, C. (2018). The Role of miRNAs in the Pathophysiology of Liver Diseases and Toxicity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(1), 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010261