Abstract
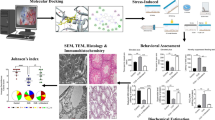
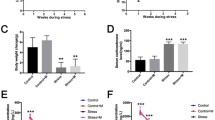
Stress affects the male reproductive system and can cause sub-fertility or infertility. Although Phyllanthus emblica L. (PE) extract has been shown to have high antioxidant capacity and protective properties in damaged tissue, the preventive effects of PE extract on testicular function from stress-related impairment have never been demonstrated. This study aimed to investigate the effects of PE aqueous leaf extract on testicular impairment and protein marker changes in rats suffering from chronic stress. Adult male rats were divided into four groups: a control group, a chronic stress (CS) group, and two groups with CS that received different doses of PE extract (50 or 100 mg/kg body weight (BW)). In the treatment groups, the animals were given PE extract daily before stress induction for 42 consecutive days. Stress was induced through immobilization (4 h/d) followed by forced cold swimming (15 min/d). Sperm quality and the histology of the testes and caudal epididymis were examined, as were levels of serum corticosterone, testosterone, and malondialdehyde (MDA). The expressions of testicular steroidogenic acute regulatory (StAR) and tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins were investigated using immuno-Western blot analysis, as these proteins are assumed to play important roles in spermatogenesis and androgen synthesis. The results showed that PE (50 mg/kg BW) significantly increased sperm concentration and testosterone levels, while decreasing corticosterone levels, MDA levels, sperm head abnormalities, and acrosome-reacted sperm in CS rats. In addition, PE at both doses was found to diminish testicular histopathology in the CS rats. We also found that 50 mg/kg BW of PE significantly improved StAR protein expression and altered the intensities of some tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins in testis. We conclude that PE leaf extract at 50 mg/kg BW can prevent testicular damage in rats with CS.
摘要
目的
探讨Phyllanthus emblica L.(PE)叶提取物对慢性应激大鼠睾丸损伤和相关蛋白标志物变化的影响。
方法
将成年雄性大鼠分成四组:对照组、慢性应激(CS)组和两组PE 提取物治疗组(50 或100 mg/kg 体重(BW))。对各组的精子质量、睾丸和尾附睾的组织学特征、以及血清皮质酮、睾酮和丙二醛 (MDA)的水平进行分析比较。并使用免疫印迹 分析研究睾丸类固醇合成快速调节蛋白(StAR)和酪氨酸磷酸化蛋白的表达。
结论
结果显示,50 mg/kg BW 的PE 能显着增加精子浓度和睾酮水平,同时降低CS 大鼠中皮质酮水平、MDA 水平、以及精子头异常和顶体反应精子的比例。此外,两种剂量的PE 都能缓解CS 大 鼠的睾丸组织病理学特征。同时我们还发现, 50 mg/kg BW 的PE 可以显著提高StAR 蛋白的表达,并改变睾丸中部分酪氨酸磷酸化蛋白的强 度。总之,50 mg/kg BW 的PE 叶提取物可以预防CS大鼠的睾丸损伤。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akinpelu BA, Oyedapo OO, Iwalewa EO, et al., 2012. Biochemical and histopathological profile of toxicity induced by saponin fraction of Erythrophleum suaveolens (Guill. & Perri.) bark extract. Phytopharmacology, 3(1):38–53.
Al-Shafi SM, 2002. Toxic effect of tannic and related compounds on human plasma proteins. Saudi Med J, 23(2): 221–225.
Arad-Dann H, Beller U, Haimovitch R, et al., 1993. Immunohistochemistry of phosphotyrosine residues: identification of distinct intracellular patterns in epithelial and steroidogenic tissues. J Histochem Cytochem, 41(4):513–519. https://doi.org/10.1177/41.4.7680679
Arun S, Burawat J, Sukhorum W, et al., 2016a. Changes of testicular phosphorylated proteins in response to restraint stress in male rats. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 17(1):21–29. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1500174
Arun S, Burawat J, Sukhorum W, et al., 2016b. Chronic restraint stress induces sperm acrosome reaction and changes in testicular tyrosine phosphorylated proteins in rats. Int J Reprod Biomed (Yazd), 14(7):443–452.
Aziz NM, Ragy MM, Gayyed MF, 2013. Effect of acute immobilization stress with or without a heme oxygenase inducer on testicular structure and function in male albino rats. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol, 24(4):255–462. https://doi.org/10.1515/jbcpp-2012-0066
Bandyopadhyay SK, Pakrashi SC, Pakrashi A, 2000. The role of antioxidant activity of Phyllanthus emblica fruits on prevention from indomethacin induced gastric ulcer. J Ethnopharmacol, 70(2):171–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-8741(99)00146-4
Bhatia N, Jaggi AS, Singh N, et al., 2011. Adaptogenic potential of curcumin in experimental chronic stress and chronic unpredictable stress-induced memory deficits and alterations in functional homeostasis. J Nat Med, 65(3-4): 532–543. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-011-0535-9
Bitgul G, Tekmen I, Keles D, et al., 2013. Protective effects of resveratrol against chronic immobilization stress on testis. ISRN Urol, 2013:278720. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/278720
Calixto JB, Santos ARS, Filho CV, et al., 1998. A review of the plants of the genus Phyllanthus: their chemistry, pharmacology, and therapeutic potential. Med Res Rev, 18(4):225–258. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1098-1128(199807)18:4<225::AID-MED2>3.0.CO;2-X
Chaichun A, Arun S, Burawat J, et al., 2017. Localization and identification of tyrosine phosphorylated proteins in adult sprague-dawley rat testis. Int J Morphol, 35(4):1322–1327. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-95022017000401322
Chaphalkar R, Apte KG, Talekar Y, et al., 2017. Antioxidants of Phyllanthus emblica L. Bark extract provide hepatoprotection against ethanol-induced hepatic damage: a comparison with silymarin. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2017: 3876040. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3876040
Dhanabalan S, Jubendradass R, Latha P, et al., 2010. Effect of restraint stress on 2,3,7,8 tetrachloro dibenzo-p-dioxin induced testicular and epididymal toxicity in rats. Hum Exp Toxicol, 30(7):567–578. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327110376548
Everds NE, Snyder PW, Bailey KL, et al., 2013. Interpreting stress responses during routine toxicity studies: a review of the biology, impact, and assessment. Toxicol Pathol, 41(4):560–614. https://doi.org/10.1177/0192623312466452
Hanks SK, Quinn AM, Hunter T, 1988. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science, 241(4861):42–52. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.3291115
Huang CZ, Tung YT, Hsia SM, et al., 2017. The hepatoprotective effect of Phyllanthus emblica L. fruit on high fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in SD rats. Food Funct, 8(2):842–850. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6FO01585A
Hunter T, Cooper JA, 1985. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem, 54(1):897–930. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341
Iamsaard S, Prabsattroo T, Sukhorum W, et al., 2013. Anethum graveolens Linn. (dill) extract enhances the mounting frequency and level of testicular tyrosine protein phosphorylation in rats. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 14(3):247–252. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1200287
Iamsaard S, Arun S, Burawat J, et al., 2014. Phenolic contents and antioxidant capacities of Thai-Makham Pom (Phyllanthus emblica L.) aqueous extracts. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 15(4):405–408. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1300284
Iamsaard S, Arun S, Burawat J, et al., 2015. Phyllanthus emblica L. branch extract ameliorates testicular damage in valproic acid-Induced rats. Int J Morphol, 33(3):1016–1022. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-95022015000300033
Iamsaard S, Welbat JU, Sukhorum W, et al., 2018. Methotrexate changes the testicular tyrosine phosphorylated protein expression and seminal vesicle epithelia of adult rats. Int J Morphol, 36(2):737–742. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-95022018000200737
Izgüt-Uysal VN, Gemici B, Birsen I, et al., 2014. The protective effect of apelin against water-immersion and restraint stress-induced gastric damage. J Physiol Sci, 64(4):279–289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12576-014-0317-8
Khandelwal S, Shukla LJ, Shanker R, 2002. Modulation of acute cadmium toxicity by emblica officinalis fruit in rat. Indian J Exp Biol, 40(5):564–570.
Krishnaveni M, Mirunalini S, 2012. Chemopreventive efficacy of Phyllanthus emblica L. (amla) fruit extract on 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene induced oral carcinogenesis—a dose-response study. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol, 34(3): 801–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2012.09.006
Kumnerdkhonkaen P, Saenglee S, Asgar MA, et al., 2018. Antiproliferative activities and phenolic acid content of water and ethanolic extracts of the powdered formula of Houttuynia cordata Thunb. Fermented broth and Phyllanthus emblica Linn. Fruit. BMC Complement Altern Med, 18:130. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-018-2185-x
Lee SH, Choi KH, Cha KM, et al., 2017. Protective effects of Korean Red Ginseng against sub-acute immobilization stress-induced testicular damage in experimental rats. J Ginseng Res, in press. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2017.09.002
Lin H, Yuan KM, Zhou HY, et al., 2014. Time-course changes of steroidogenic gene expression and steroidogenesis of rat Leydig cells after acute immobilization stress. Int J Mol Sci, 15(11):21028–21044. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151121028
Liu XL, Cui C, Zhao MM, et al., 2008. Identification of phenolics in the fruit of emblica (Phyllanthus emblica L.) and their antioxidant activities. Food Chem, 109(4):909–915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.01.071
Lu CC, Yang SH, Hsia SM, et al., 2016. Inhibitory effects of Phyllanthus emblica L. on hepatic steatosis and liver fibrosis in vitro. J Funct Foods, 20:20–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2015.10.012
Luo W, Zhao MM, Yang B, et al., 2011. Antioxidant and antiproliferative capacities of phenolics purified from Phyllanthus emblica L. fruit. Food Chem, 126(1):277–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.11.018
Maneenin C, Burawat J, Maneenin N, et al., 2018. Antioxidant capacity of Momordica charantia extract and its protective effect on testicular damage in valproic acid-induced rats. Int J Morphol, 36(2):447–453. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-95022018000200447
Matsuura N, Nagasawa K, Minagawa Y, et al., 2015. Restraint stress exacerbates cardiac and adipose tissue pathology via β-adrenergic signaling in rats with metabolic syndrome. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 308(10):H1275–H1286.
Naninck EFG, Hoeijmakers L, Kakava-Georgiadou N, et al., 2015. Chronic early life stress alters developmental and adult neurogenesis and impairs cognitive function in mice. Hippocampus, 25(3):309–328. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.22374
Pertsov SS, Koplik EV, Kalinichenko LS, 2015. Effect of interleukin-4 on peripheral blood leukocytes in rats with various behavioral characteristics during acute stress. Bull Exp Biol Med, 158(5):595–599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-015-2814-z
Podolak I, Galanty A, Sobolewska D, 2010. Saponins as cytotoxic agents: a review. Phytochem Rev, 9(3):425–474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-010-9183-z
Popovic N, Pajovic SB, 2010. Lithium modulates the chronic stress-induced effect on blood glucose level of male rats. Arch Biol Sci, 62(2):289–295. https://doi.org/10.2298/ABS1002289P
Prabsattroo T, Wattanathorn J, Iamsaard S, et al., 2015. Moringa oleifera extract enhances sexual performance in stressed rats. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 16(3):179–190. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1400197
Pramyothin P, Samosorn P, Poungshompoo S, et al., 2006. The protective effects of Phyllanthus emblica Linn. extract on ethanol induced rat hepatic injury. J Ethnopharmacol, 107(3):361–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2006.03.035
Priya PH, Reddy PS, 2012. Effect of restraint stress on leadinduced male reproductive toxicity in rats. J Exp Zool A Ecol Genet Physiol, 317(7):455–465. https://doi.org/10.1002/jez.1738
Rai J, Pandey SN, Srivastava RK, 2003. Effect of immobilization stress on spermatogenesis of albino rats. J Anat Soc India, 52(1):55–57.
Rai J, Pandey SN, Srivastava RK, 2004. Testosterone hormone level in albino rats following restraint stress of long duration. J Anat Soc India, 53(1):17–19.
Rao M, Zhao XL, Yang J, et al., 2015. Effect of transient scrotal hyperthermia on sperm parameters, seminal plasma biochemical markers, and oxidative stress in men. Asian J Androl, 17(4):668–675. https://doi.org/10.4103/1008-682X.146967
Reis DG, Scopinho AA, Guimarães FS, 2011. Behavioral and autonomic responses to acute restraint stress are segregated within the lateral septal area of rats. PLoS ONE, 6(8):e23171. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0023171
Retana-Márquez S, Bonilla-Jaime H, Vázquez-Palacios G, et al., 2003. Changes in masculine sexual behavior, corticosterone and testosterone in response to acute and chronic stress in male rats. Horm Behav, 44(4):327–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2003.04.001
Richburg JH, 2000. The relevance of spontaneous-and chemically-induced alterations in testicular germ cell apoptosis to toxicology. Toxicol Lett, 112-113:79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4274(99)00253-2
Saha S, Verma RJ, 2015. Antioxidant activity of polyphenolic extract of Phyllanthus emblica against lead acetate induced oxidative stress. Toxicol Environ Health Sci, 7(1): 82–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-015-0224-2
Sakr SA, Zowail ME, Marzouk AM, 2014. Effect of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) on sodium valporate induced cytogenetic and testicular alterations in albino rats. Anat Cell Biol, 47(3):171–179. https://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2014.47.3.171
Sampannang A, Arun S, Sukhorum W, et al., 2017. Antioxidant and hypoglycemic effects of Momordica cochinchinensis Spreng. (Gac) aril extract on reproductive damages in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced hyperglycemia mice. Int J Morphol, 35(2):667–675. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-95022017000200046
Sawant L, Pandita N, Prabhakar B, 2010. Determination of gallic acid in Phyllanthus emblica Linn. Dried fruit powder by HPTLC. J Pharm Bioallied Sci, 2(2):105–108. https://doi.org/10.4103/0975-7406.67012
She GM, Cheng RY, Sha L, et al., 2013. A novel phenolic compound from Phyllanthus emblica. Nat Prod Commun, 8(4):461–462.
Srinivasan P, Vijayakumar S, Kothandaraman S, et al., 2018. Anti-diabetic activity of quercetin extracted from Phyllanthus emblica L. fruit: in silico and in vivo approaches. J Pharm Anal, 8(2):109–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2017.10.005
Sripanidkulchai B, Junlatat J, 2014. Bioactivities of alcohol based extracts of Phyllanthus emblica branches: antioxidation, antimelanogenesis and anti-inflammation. J Nat Med, 68(3):615–622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-014-0824-1
Sukhorum W, Iamsaard S, 2017. Changes in testicular function proteins and sperm acrosome status in rats treated with valproic acid. Reprod Fertil Dev, 29(8):1585–1592. https://doi.org/10.1071/RD16205
Tahir I, Khan MR, Shah NA, et al., 2016. Evaluation of phytochemicals, antioxidant activity and amelioration of pulmonary fibrosis with Phyllanthus emblica leaves. BMC Complement Altern Med, 16:406. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-016-1387-3
Tasanarong A, Kongkham S, Itharat A, 2014. Antioxidant effect of Phyllanthus emblica extract prevents contrastinduced acute kidney injury. BMC Complement Altern Med, 14:138. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6882-14-138
Toyang NJ, Ateh EN, Keiser J, et al., 2012. Toxicity, antimicrobial and anthelmintic activities of Vernonia guineensis Benth. (Asteraceae) crude extracts. J Ethnopharmacol, 144(3):700–704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2012.10.016
Ullrich A, Schlessinger J, 1990. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell, 61(2):203–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-K
Verma R, Chakraborty D, 2008. Emblica officinalis aqueous extract ameliorates ochratoxin-induced lipid peroxidation in the testis of mice. Acta Pol Pharm, 65(2):187–194.
Visconti PE, Kopf GS, 1998. Regulation of protein phosphorylation during sperm capacitation. Biol Reprod, 59(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod59.1.1
Xu ML, Wei QW, Zheng KZ, et al., 2014. Protective effects of Big-leaf mulberry and physiological roles of nitric oxide synthases in the testis of mice following water immersion and restraint stress. Acta Histochem, 116(8):1323–1330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acthis.2014.08.003
Yanagimachi R, 1994. Mammalian fertilization. In: Knobil E (Ed.), The Physiology of Reproduction. Raven Press, New York, p.189–317.
Zhang MH, Shi ZD, Yu JC, et al., 2015. Scrotal heat stress causes sperm chromatin damage and cysteinyl aspartatespicific proteinases 3 changes in fertile men. J Assist Reprod Genet, 32(5):747–755. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-015-0451-0
Zhao TJ, Sun Q, Marques M, et al., 2015. Anticancer properties of Phyllanthus emblica (Indian Gooseberry). Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2015:950890. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/950890
Zhong ZG, Wu DP, Huang JL, et al., 2011. Progallin A isolated from the acetic ether part of the leaves of Phyllanthus emblica L. induces apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma BEL-7404 cells by up-regulation of Bax expression and down-regulation of Bcl-2 expression. J Ethnopharmacol, 133(2):765–772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2010.11.001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, Thailand (No. IN61105)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arun, S., Burawat, J., Yannasithinon, S. et al. Phyllanthus emblica leaf extract ameliorates testicular damage in rats with chronic stress. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 19, 948–959 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1800362
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1800362