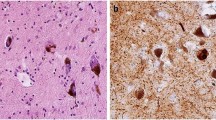
Abstract
Lewy bodies, the characteristic pathological lesion of substantia nigra neurons in Parkinson’s disease (PD), are frequently observed to accompany the amyloid plaque and neurofibrillary tangle pathology of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However the typical anatomic distribution of Lewy bodies in AD is distinct from PD. The most common site of occurrence is the amygdala, where Lewy bodies are observed in approximately 60% of both sporadic and familial AD. Other common sites of occurrence include the periamygdaloid and entorhinal cortex, while neocortical and brainstem areas develop Lewy bodies in a lower percentage of cases. In contrast, dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), defined by widespread neocortical and brainstem Lewy bodies but frequently accompanied by variable levels of AD-type pathology, represents the other end of a spectrum of pathology associated with dementia. The observation of Lewy bodies in familial AD cases suggests that like neurofibrillary tangles, the formation of Lewy bodies can be induced by the pathological state caused by Aβ-amyloid over-production. The role of Lewy body formation in the dysfunction and degeneration of neurons remains unclear. The protein α-synuclein appears to be an important structural component of Lewy bodies, an observation spurred by the discovery of point mutations in the α-synuclein gene linked to rare cases of autosomal dominant PD. Further investigation of α-synuclein and its relationship to pathological conditions promoting Lewy body formation in AD, PD, and DLB may yield further insight into pathogenesis of these diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeliovich A., Schmitz Y., Farinas I., Choi-Lundberg D., Ho W. H., Castillo P. E., et al. (2000) Mice lacking alpha-synuclein display functional deficits in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuron 25(1), 239–52.
Arai K., Kato N., Kashiwado K., and Hattori T. (2000) Pure autonomic failure in association with human alpha-synucleinopathy. Neurosci. Lett. 296(2–3), 171–173.
Arawaka S., Saito Y., Murayama S., and Mori H. (1998) Lewy body in neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation type 1 is immunoreactive for alpha-synuclein. Neurology 51(3), 887–889.
Baba M., Nakajo S., Tu P. H., et al. (1998) Aggregation of alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies of sporadic Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Am. J. Pathol. 152(4), 879–884.
Bayer T. A., Jakala P., Hartmann T., Egensperger R., Buslei R., Falkai P., and Beyreuther K. (1999) Neural expression profile of alpha-synuclein in developing human cortex. Neuroreport 10(13), 2799–2803.
Bayer T. A., Jakala P., Hartmann T., Havas L., McLean C., Culvenor J. G., et al. (1999) Alpha-synuclein accumulates in Lewy bodies in Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies but not in Alzheimer’s disease beta-amyloid plaque cores. Neurosci. Lett. 266(3), 213–216.
Betarbet R., Sherer T. B., Mackenzie G., Garcia-Osuna M., Panov A. V., and Greenamyre J. T. (2000) Chronic systemic pesticide exposure reproduces features of Parkinson’s disease. Nature Neurosci. 3(12), 1301–1306.
Clayton D. F. and George J. M. (1998) The synucleins: a family of proteins involved in synaptic function, plasticity, neurodegeneration and disease. Trends Neurosci. 21(6), 249–254.
Conway K. A., Harper J. D., and Lansbury P. T. (1998) Accelerated in vitro fibril formation by a mutant alpha-synuclein linked to early-onset Parkinson disease. Nat. Med. 4(11), 1318–1320.
Culvenor J. G., McLean C. A., Cutt S., Campbell B. C., Maher F., Jakala P., et al. (1999) Non-Abeta component of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid (NAC) revisited. NAC and alpha-synuclein are not associated with Abeta amyloid. Am. J. Pathol. 155(4), 1173–1181.
da Costa C. A., Ancolio K., and Checler F. (2000) Wildtype but not Parkinson’s disease-related ala-53 → Thr mutant alpha -synuclein protects neuronal cells from apoptotic stimuli. J. Biol. Chem. 275(31), 24,065–24,069.
El-Agnaf O. M., Jakes R., Curran M. D., and Wallace A. (1998) Effects of the mutations Ala30 to Pro and Ala53 to Thr on the physical and morphological properties of alpha-synuclein protein implicated in Parkinson’s disease. FEBS Lett. 440(1–2), 67–70.
Feany M. B. and Bender W. W. (2000) A Drosophila model of Parkinson’s disease. Nature 404(6776), 394–398.
Forno L. S. (1996) Neuropathology of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 55(3), 259–272.
Forstl H., Burns A., Luthert P., Cairns N., and Levy R. (1993) The Lewy-body variant of Alzheimer’s disease. Clinical and pathological findings. Br. J. Psychiatry 162, 385–392.
Galasko D., Hansen L. A., Katzman R., Wiederholt W., Masliah E., Terry R., et al. (1994) Clinical-neuropathological correlations in Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias. Arch. Neurol. 51(9), 888–895.
Giasson B. I., Duda J. E., Murray I. V., Chen Q., Souza J. M., Hurtig H. I., et al. (2000) Oxidative damage linked to neurodegeneration by selective alpha-synuclein nitration in synucleinopathy lesions [In Process Citation]. Science 290(5493), 985–989.
Giasson B. I., Uryu K., Trojanowski J. Q., and Lee V. M. (1999) Mutant and wild type human alpha-synucleins assemble into elongated filaments with distinct morphologies in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 274(12), 7619–7622.
Goedert M., Jakes R., Crowther R. A., Hasegawa M., Smith M. J., and Spillantini M. G. (1998) Intraneuronal filamentous tau protein and alpha-synuclein deposits in neurodegenerative diseases. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 26(3), 463–471.
Goldman J. E., Yen S. H., Chiu F. C., and Peress N. S. (1983) Lewy bodies of Parkinson’s disease contain neurofilament antigens. Science 221, 1082–1804.
Gomez-Tortosa E., Ingraham A. O., Irizarry M. C., and Hyman B. T. (1998) Dementia with Lewy bodies. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 46(11), 1449–1458.
Gomez-Tortosa E., Irizarry M. C., Gomez-Isla T., and Hyman B. T. (2000) Clinical and neuropathological correlates of dementia with Lewy bodies. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 920, 9–15.
Hamilton R. L. (2000) Lewy bodies in Alzheimer’s disease: a neuropathological review of 145 cases using alpha-synuclein immunohistochemistry. Brain Pathol. 10(3), 378–384.
Hansen L., Salmon D., Galasko D., Masliah E., Katzman R., DeTeresa R., et al. (1990) The Lewy body variant of Alzheimer’s disease: a clinical and pathologic entity. Neurology 40(1), 1–8.
Hansen L. A., Masliah E., Galasko D., and Terry R. D. (1993) Plaque-only Alzheimer disease is usually the lewy body variant, and vice versa. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 52(6), 648–654.
Hartley D. M., Walsh D. M., Ye C. P., Diehl T., Vasquez S., Vassilev P. M., et al. (1999) Protofibrillar intermediates of amyloid beta-protein induce acute electrophysiological changes and progressive neurotoxicity in cortical neurons. J. Neurosci. 19(20), 8876–8884.
Heyman A., Fillenbaum G. G., Gearing M., Mirra S. S., Welsh-Bohmer K. A., Peterson B., and Pieper C. (1999) Comparison of Lewy body variant of Alzheimer’s disease with pure Alzheimer’s disease: Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer’s Disease, Part XIX. Neurology 52(9), 1839–1844.
Hsu L. J., Mallory M., Xia Y., Veinbergs I., Hashimoto M., Yoshimoto M., et al. (1998) Expression pattern of synucleins (non-Abeta component of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid precursor protein/alpha-synuclein) during murine brain development. J. Neurochem. 71(1), 338–344.
Hsu L. J., Sagara Y., Arroyo A., Rockenstein E., Sisk A., Mallory M., et al. (2000) Alpha-synuclein promotes mitochondrial deficit and oxidative stress. Am. J. Pathol. 157(2), 401–410.
Hughes T. A., Ross H. F., Musa S., Bhattacherjee S., Nathan R. N., Mindham R. H., and Spokes E. G. (2000) A 10-year study of the incidence of and factors predicting dementia in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 54(8), 1596–1602.
Hurtig H. I., Trojanowski J. Q., Galvin J., Ewbank D., Schmidt M. L., Lee V. M., et al. (2000) Alpha-synuclein cortical Lewy bodies correlate with dementia in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 54(10), 1916–1921.
Ii K., Ito H., Tanaka K., and Hirano A. (1997) Immunocytochemical co-localization of the proteasome in ubiquitinated structures in neurodegenerative diseases and the elderly. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 56(2), 125–131.
Ince P., Irving D., MacArthur F., and Perry R. H. (1991) Quantitative neuropathological study of Alzheimer-type pathology in the hippocampus: comparison of senile dementia of Alzheimer type, senile dementia of Lewy body type, Parkinson’s diseas and non-demented elderly control patients. J. Neurol. Sci. 106(2), 142–152.
Ince P. G., McArthur F. K., Bjertness E., Torvik A., Candy J. M., and Edwardson J. A. (1995) Neuropathological diagnoses in elderly patients in Oslo: Alzheimer’s disease, Lewy body disease, vascular lesions. Dementia 6(3), 162–168.
Iwatsubo T., Yamaguchi H., Fujimuro M., et al. (1996) Purification and characterization of Lewy bodies from the brains of patients with diffuse Lewy body disease. Am. J. Pathol. 148(5), 1517–1529.
Jenco J. M., Rawlingson A., Daniels B., and Morris A. J. (1998) Regulation of phospholipase D2: selective inhibition of mammalian phospholipase D isoenzymes by alpha- and beta-synucleins. Biochemistry 37(14), 4901–4909.
Kanda S., Bishop J. F., Eglitis M. A., Yang Y., and Mouradian M. M. (2000) Enhanced vulnerability to oxidative stress by alpha-synuclein mutations and C-terminal truncation. Neuroscience 97(2), 279–284.
Kaufmann H., Hague K., and Perl D. (2001) Accumulation of alpha-synuclein in autonomic nerves in pure autonomic failure. Neurology 56(7), 980–981.
Ko L., Mehta N. D., Farrer M., Easson C., Hussey J., Yen S., Hardy J., and Yen S. H. (2000) Sensitization of neuronal cells to oxidative stress with mutated human alpha-synuclein. J. Neurochem. 75(6), 2546–2554.
Kruger R., Kuhn W., Muller T., Woitalla D., Graeber M., Kosel S., et al. (1998) Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease [letter]. Nat. Genet. 18(2), 106–108.
Lambert M. P., Barlow A. K., Chromy B. A., Edwards C., Freed R., Liosatos M., et al. (1998) Diffusible, nonfibrillar ligands derived from Abeta1–42 are potent central nervous system neurotoxins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95(11), 6448–6453.
Langston J. W., Ballard P., Tetrud J. W., and Irwin I. (1983) Chronic Parkinsonism in humans due to a product of meperidine-analog synthesis. Science 219(4587), 979–980.
Lavedan C. (1998) The synuclein family. Genome Res. 8(9), 871–880.
Lee M., Hyun D., Halliwell B., and Jenner P. (2001) Effect of the overexpression of wild-type or mutant alpha-synuclein on cell susceptibility to insult. J. Neurochem. 76(4), 998–1009.
Liberatore G. T., Jackson-Lewis V., Vukosavic S., Mandir A. S., Vila M., McAuliffe W. G., et al. (1999) Inducible nitric oxide synthase stimulates dopaminergic neurodegeneration in the MPTP model of Parkinson disease [see comments]. Nat. Med. 5(12), 1403–1409.
Lindboe C. F. and Hansen H. B. (1998) The frequency of Lewy bodies in a consecutive autopsy series. Clin. Neuropathol. 17(4), 204–209.
Lippa C. F., Fujiwara H., Mann D. M., Giasson B., Baba M., Schmidt M. L., et al. (1998) Lewy bodies contain altered alpha-synuclein in brains of many familial Alzheimer’s disease patients with mutations in presenilin and amyloid precursor protein genes. Am. J. Pathol. 153(5), 1365–1370.
Lippa C. F., Schmidt M. L., Lee V. M., and Trojanowski J. Q. (1999) Antibodies to alpha-synuclein detect Lewy bodies in many Down’s syndrome brains with Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 45(3), 353–357.
Lopez O. L., Wisniewski S., Hamilton R. L., Becker J. T., Kaufer D. I., and DeKosky S. T. (2000) Predictors of progression in patients with AD and Lewy bodies. Neurology 54(9), 1774–1779.
Lowe J., McDermott H., Landon M., et al. (1990) Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase (PGP9.5) is selectively present in ubiquitinated inclusion bodies characteristic of human neurodegenerative diseases. J. Pathol. 161(2), 153–160.
Masliah E., Rockenstein E., Veinbergs I., Mallory M., Hashimoto M., Takeda A., et al. (2000) Dopaminergic loss and inclusion body formation in alpha-synuclein mice: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Science 287(5456), 1265–1269.
Mattson M. P., Barger S. W., Cheng B., Lieberburg I., Smith-Swintosky V. L., and Rydel R. E. (1993) beta-Amyloid precursor protein metabolites and loss of neuronal Ca2+ homeostasis in Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Neurosci. 16(10), 409–414.
McGeer P. L. and McGeer E. G. (1995) The inflammatory response system of brain: implications for therapy of Alzheimer and other neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 21(2), 195–218.
McLean P. J., Kawamata H., Ribich S., and Hyman B. T. (2000) Membrane association and protein conformation of alpha-synuclein in intact neurons. Effect of Parkinson’s disease-linked mutations. J. Biol. Chem. 275(12), 8812–8816.
Murphy D. D., Rueter S. M., Trojanowski J. Q., and Lee V. M. (2000) Synucleins are developmentally expressed, and alpha-synuclein regulates the size of the presynaptic vesicular pool in primary hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. 20(9), 3214–3220.
Narhi L., Wood S. J., Steavenson S., Jiang Y., Wu G. M., Anafi D., et al. (1999) Both familial Parkinson’s disease mutations accelerate alpha-synuclein aggregation. J. Biol. Chem. 274(14), 9843–9846.
Newell K. L., Boyer P., Gomez-Tortosa E., Hobbs W., Hedley-Whyte E. T., Vonsattel J. P., and Hyman B. T. (1999) Alpha-synuclein immunoreactivity is present in axonal swellings in neuroaxonal dystrophy and acute traumatic brain injury. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 58(12), 1263–1268.
Ostrerova N., Petrucelli L., Farrer M., Mehta N., Choi P., Hardy J., and Wolozin B. (1999) alpha-Synuclein shares physical and functional homology with 14-3-3 proteins. J. Neurosci. 19(14), 5782–5791.
Ostrerova-Golts N., Petrucelli L., Hardy J., Lee J. M., Farer M., and Wolozin B. (2000) The A53T alpha-synuclein mutation increases iron-dependent aggregation and toxicity. J. Neurosci. 20(16), 6048–6054.
Parker W. D. Jr., Boyson S. J., and Parks J. K. (1989) Abnormalities of the electron transport chain in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 26(6), 719–723.
Polymeropoulos M. H., Lavedan C., Leroy E., Ide S. E., Dehejia A., Dutra A., et al. (1997) Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease [see comments]. Science 276(5321), 2045–2047.
Przedborski S. and Jackson-Lewis V. (1998) Mechanisms of MPTP toxicity. Mov. Disord. 13(Suppl 1), 35–38.
Rogers J., Webster S., Lue L. F., Brachova L., Civin W. H., Emmerling M., et al. (1996) Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Neurobiol. Aging 17(5), 681–686.
Saha A. R., Ninkina N. N., Hanger D. P., Anderton B. H., Davies A. M., and Buchman V. L. (2000) Induction of neuronal death by alpha-synuclein. Eur. J. Neurosci. 12(8), 3073–3077.
Schapira A. H., Cooper J. M., Dexter D., Clark J. B., Jenner P., and Marsden C. D. (1990) Mitochondrial complex I deficiency in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 54(3), 823–827.
Schmidt M. L., Martin J. A., Lee V. M., and Trojanowski J. Q. (1996) Convergence of Lewy bodies and neurofibrillary tangles in amygdala neurons of Alzheimer’s disease and Lewy body disorders. Acta. Neuropathol. 91(5), 475–481.
Schulz J. B., Matthews R. T., Klockgether T., Dichgans J., and Beal M. F. (1997) The role of mitochondrial dysfunction and neuronal nitric oxide in animal models of neurodegenerative diseases. Mol. Cell Biochem. 174(1–2), 193–197.
Selkoe D. J. (2001) Alzhemier’s disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol. Rev. 81(2), 741–766.
Souza J. M., Giasson B. I., Chen Q., Lee V. M., and Ischiropoulos H. (2000) Dityrosine cross-linking promotes formation of stable alpha -synuclein polymers. Implication of nitrative and oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative synucleinopathies. J. Biol. Chem. 275(24), 18,344–18,349.
Spillantini M. G., Crowther R. A., Jakes R., Cairns N. J., Lantos P. L., and Goedert M. (1998a) Filamentous alphasynuclein inclusions link multiple system atrophy with Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurosci. Lett. 251(3), 205–208.
Spillantini M. G., Crowther R. A., Jakes R., Hasegawa M., and Goedert M. (1998b) alpha-Synuclein in filamentous inclusions of Lewy bodies from Parkinson’s disease and dementia with lewy bodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95(11), 6469–6473.
Spillantini M. G., Schmidt M. L., Lee V. M., Trojanowski J. Q., Jakes R., and Goedert M. (1997) Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies [letter]. Nature 388(6645), 839–840.
Swerdlow R. H., Parks J. K., Miller S. W., Tuttle J. B., Trimmer P. A., Sheehan J. P., et al. (1996) Origin and functional consequences of the complex I defect in Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 40(4), 663–671.
Tu P. H., Galvin J. E., Baba M., Giasson B., Tomita T., Leight S., et al. (1998) Glial cytoplasmic inclusions in white matter oligodendrocytes of multiple system atrophy brains contain insoluble alpha-synuclein. Ann. Neurol. 44(3), 415–422.
Ueda K., Fukushima H., Masliah E., Xia Y., Iwai A., Yoshimoto M., et al. (1993) Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding an unrecognized component of amyloid in Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90(23), 11,282–11,286.
Varadarajan S., Yatin S., Aksenova M., and Butterfield D. A. (2000) Review: Alzheimer’s amyloid beta-peptide-associated free radical oxidative stress and neurotoxicity. J. Struct. Biol. 130(2–3), 184–208.
Wakabayashi K., Yoshimoto M., Fukushima T., Koide R., Horikawa Y., Morita T., and Takahashi H. (1999) Widespread occurrence of alpha-synuclein/NACP-immunoreactive neuronal inclusions in juvenile and adult-onset Hallervorden-Spatz disease with Lewy bodies. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 25(5), 363–368.
Weinreb P. H., Zhen W., Poon A. W., Conway K. A., and Lansbury P. T. Jr. (1996) NACP, a protein implicated in Alzheimer’s disease and learning, is natively unfolded. Biochemistry 35(43), 13,709–13,715.
Withers G. S., George J. M., Banker G. A., and Clayton D. F. (1997) Delayed localization of synelfin (synuclein, NACP) to presynaptic terminals in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 99(1), 87–94.
Zhou W., Hurlbert M. S., Schaack J., Prasad K. N., and Freed C. R. (2000) Overexpression of human alpha-synuclein causes dopamine neuron death in rat primary culture and immortalized mesencephalon-derived cells. Brain Res. 866(1–2), 33–43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kotzbauer, P.T., Trojanowski, J.Q. & Lee, V.MY. Lewy body pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. J Mol Neurosci 17, 225–232 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:17:2:225
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:17:2:225