Abstract
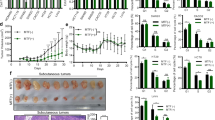
Metformin is a widely used antidiabetic agent, which regulates glucose homeostasis through inhibition of liver glucose production and an increase in muscle glucose uptake. Recent studies suggest that metformin may reduce the risk of cancer, but its mode of action in cancer remains not elucidated. We investigated the effect of metformin on human prostate cancer cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Metformin inhibited the proliferation of DU145, PC-3 and LNCaP cancer cells with a 50% decrease of cell viability and had a modest effect on normal prostate epithelial cell line P69. Metformin did not induce apoptosis but blocked cell cycle in G0/G1. This blockade was accompanied by a strong decrease of cyclin D1 protein level, pRb phosphorylation and an increase in p27kip protein expression. Metformin activated the AMP kinase pathway, a fuel sensor signaling pathway. However, inhibition of the AMPK pathway using siRNA against the two catalytic subunits of AMPK did not prevent the antiproliferative effect of metformin in prostate cancer cells. Importantly, oral and intraperitoneal treatment with metformin led to a 50 and 35% reduction of tumor growth, respectively, in mice bearing xenografts of LNCaP. Similar, to the in vitro study, metformin led to a strong reduction of cyclin D1 protein level in tumors providing evidence for a mechanism that may contribute to the antineoplastic effects of metformin suggested by recent epidemiological studies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AICAR:
-
5 amino-imidazol-4-carboxamide-1-β-4-ribofuranoside
- ACC:
-
Acetyl Coenzyme-A Carboxylase
- AMPK:
-
AMP-activated protein kinase
- pRb:
-
retinoblastoma protein
References
Alao JP . (2007). The regulation of cyclin D1 degradation: roles in cancer development and the potential for therapeutic invention. Mol Cancer 6: 24.
An D, Kewalramani G, Chan JK, Qi D, Ghosh S, Pulinilkunnil T et al. (2006). Metformin influences cardiomyocyte cell death by pathways that are dependent and independent of caspase-3. Diabetologia 49: 2174–2184. Epub 2006 Jul 26.
Aouadi M, Laurent K, Prot M, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Binetruy B, Bost F . (2006). Inhibition of p38MAPK increases adipogenesis from embryonic to adult stages. Diabetes 55: 281–289.
Bost F, McKay R, Bost M, Potapova O, Dean NM, Mercola D . (1999). The Jun kinase 2 isoform is preferentially required for epidermal growth factor-induced transformation of human A549 lung carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol 19: 1938–1949.
Bost F, McKay R, Dean NM, Potapova O, Mercola D . (2000). Antisense methods for discrimination of phenotypic properties of closely related gene products: Jun kinase family. Methods Enzymol 314: 342–362.
Campbell IW . (1985). Metformin and the sulphonylureas: the comparative risk. Horm Metab Res Suppl 15: 105–111.
Chen Y, Martinez LA, LaCava M, Coghlan L, Conti CJ . (1998). Increased cell growth and tumorigenicity in human prostate LNCaP cells by overexpression to cyclin D1. Oncogene 16: 1913–1920.
Collins SP, Reoma JL, Gamm DM, Uhler MD . (2000). LKB1, a novel serine/threonine protein kinase and potential tumour suppressor, is phosphorylated by cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) and prenylated in vivo. Biochem J 345: 673–680.
Dagon Y, Avraham Y, Berry EM . (2006). AMPK activation regulates apoptosis, adipogenesis, and lipolysis by eIF2alpha in adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 340: 43–47.
Davis JN, Wojno KJ, Daignault S, Hofer MD, Kuefer R, Rubin MA et al. (2006). Elevated E2F1 inhibits transcription of the androgen receptor in metastatic hormone-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Res 66: 11897–11906.
Denmeade SR, Isaacs JT . (2004). Development of prostate cancer treatment: the good news. Prostate 58: 211–224.
Detaille D, Guigas B, Chauvin C, Batandier C, Fontaine E, Wiernsperger N et al. (2005). Metformin prevents high-glucose-induced endothelial cell death through a mitochondrial permeability transition-dependent process. Diabetes 54: 2179–2187.
Diehl JA, Cheng M, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ . (1998). Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta regulates cyclin D1 proteolysis and subcellular localization. Genes Dev 12: 3499–3511.
Drobnjak M, Osman I, Scher HI, Fazzari M, Cordon-Cardo C . (2000). Overexpression of cyclin D1 is associated with metastatic prostate cancer to bone. Clin Cancer Res 6: 1891–1895.
El-Mir MY, Nogueira V, Fontaine E, Averet N, Rigoulet M, Leverve X . (2000). Dimethylbiguanide inhibits cell respiration via an indirect effect targeted on the respiratory chain complex I. J Biol Chem 275: 223–228.
Erlich S, Tal-Or P, Liebling R, Blum R, Karunagaran D, Kloog Y et al. (2006). Ras inhibition results in growth arrest and death of androgen-dependent and androgen-independent prostate cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol 72: 427–436.
Evans JM, Donnelly LA, Emslie-Smith AM, Alessi DR, Morris AD . (2005). Metformin and reduced risk of cancer in diabetic patients. BMJ 330: 1304–1305.
Guigas B, Bertrand L, Taleux N, Foretz M, Wiernsperger N, Vertommen D et al. (2006). 5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-D-ribofuranoside and metformin inhibit hepatic glucose phosphorylation by an AMP-activated protein kinase-independent effect on glucokinase translocation. Diabetes 55: 865–874.
Han EK, Lim JT, Arber N, Rubin MA, Xing WQ, Weinstein IB . (1998). Cyclin D1 expression in human prostate carcinoma cell lines and primary tumors. Prostate 35: 95–101.
Hardie DG . (2003). Minireview: the AMP-activated protein kinase cascade: the key sensor of cellular energy status. Endocrinology 144: 5179–5183.
Hawley SA, Gadalla AE, Olsen GS, Hardie DG . (2002). The antidiabetic drug metformin activates the AMP-activated protein kinase cascade via an adenine nucleotide-independent mechanism. Diabetes 51: 2420–2425.
Herrant M, Jacquel A, Marchetti S, Belhacene N, Colosetti P, Luciano F et al. (2004). Cleavage of Mcl-1 by caspases impaired its ability to counteract Bim-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 23: 7863–7873.
Hunter T . (1997). Oncoprotein networks. Cell 88: 333–346.
Ibanez L, Ong K, Valls C, Marcos MV, Dunger DB, de Zegher F . (2006). Metformin treatment to prevent early puberty in girls with precocious pubarche. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91: 2888–2891.
Kahn BB, Alquier T, Carling D, Hardie DG . (2005). AMP-activated protein kinase: ancient energy gauge provides clues to modern understanding of metabolism. Cell Metab 1: 15–25.
Kim WH, Lee JW, Suh YH, Lee HJ, Lee SH, Oh YK et al. (2007). AICAR potentiates ROS production induced by chronic high glucose: roles of AMPK in pancreatic beta-cell apoptosis. Cell Signal 19: 791–805.
Libertini SJ, Tepper CG, Guadalupe M, Lu Y, Asmuth DM, Mudryj M . (2006). E2F1 expression in LNCaP prostate cancer cells deregulates androgen dependent growth, suppresses differentiation, and enhances apoptosis. Prostate 66: 70–81.
Lord JM, Flight IH, Norman RJ . (2003). Metformin in polycystic ovary syndrome: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 327: 951–953.
Loubat A, Rochet N, Turchi L, Rezzonico R, Far DF, Auberger P et al. (1999). Evidence for a p23 caspase-cleaved form of p27[KIP1] involved in G1 growth arrest. Oncogene 18: 3324–3333.
Marchesini G, Brizi M, Bianchi G, Tomassetti S, Zoli M, Melchionda N . (2001). Metformin in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Lancet 358: 893–894.
Matsushime H, Quelle DE, Shurtleff SA, Shibuya M, Sherr CJ, Kato JY . (1994). D-type cyclin-dependent kinase activity in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol 14: 2066–2076.
Park C, Lee I, Kang WK . (2006). Influence of small interfering RNA corresponding to ets homologous factor on senescence-associated modulation of prostate carcinogenesis. Mol Cancer Ther 5: 3191–3196.
Perry JE, Grossmann ME, Tindall DJ . (1998). Epidermal growth factor induces cyclin D1 in a human prostate cancer cell line. Prostate 35: 117–124.
Plymate SR, Tennant M, Birnbaum RS, Thrasher JB, Chatta G, Ware JL . (1996). The effect on the insulin-like growth factor system in human prostate epithelial cells of immortalization and transformation by simian virus-40 T antigen. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81: 3709–3716.
Ruderman NB, Park H, Kaushik VK, Dean D, Constant S, Prentki M et al. (2003). AMPK as a metabolic switch in rat muscle, liver and adipose tissue after exercise. Acta Physiol Scand 178: 435–442.
Schneider MB, Matsuzaki H, Haorah J, Ulrich A, Standop J, Ding XZ et al. (2001). Prevention of pancreatic cancer induction in hamsters by metformin. Gastroenterology 120: 1263–1270.
Sharan SK, Morimatsu M, Albrecht U, Lim DS, Regel E, Dinh C et al. (1997). Embryonic lethality and radiation hypersensitivity mediated by Rad51 in mice lacking Brca2. Nature 386: 804–810.
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM . (1995). Inhibitors of mammalian G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev 9: 1149–1163.
Weinberg RA . (1995). The retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle control. Cell 81: 323–330.
Zakikhani M, Dowling R, Fantus IG, Sonenberg N, Pollak M . (2006). Metformin is an AMP kinase-dependent growth inhibitor for breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 66: 10269–10273.
Zhang Y, Howell RD, Alfonso DT, Yu J, Kong L, Wittig JC et al. (2007). IFI16 inhibits tumorigenicity and cell proliferation of bone and cartilage tumor cells. Front Biosci 12: 4855–4863.
Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, Chen Y, Shen X, Fenyk-Melody J et al. (2001). Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J Clin Invest 108: 1167–1174.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by INSERM, a grant from Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer (grant# 3701); Association pour la Recherche sur les tumeurs de la Prostate (ARTP). We thank Dan Mercola for the cells, Gilles Ponzio for scientific discussions, V Corcelle for reading the manuscript. F Bost and JF Tanti are CNRS investigators.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahra, I., Laurent, K., Loubat, A. et al. The antidiabetic drug metformin exerts an antitumoral effect in vitro and in vivo through a decrease of cyclin D1 level. Oncogene 27, 3576–3586 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1211024
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1211024
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Enhancement of targeted therapy in combination with metformin on human breast cancer cell lines
Cell Communication and Signaling (2024)
-
Metformin regulates multiple signaling pathways within castration-resistant human prostate cancer cells
BMC Cancer (2022)
-
A functional screen with metformin identifies microRNAs that regulate metabolism in colorectal cancer cells
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Metformin inhibits the development and metastasis of colorectal cancer
Medical Oncology (2022)
-
The role of AMPK-dependent pathways in cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin: a new perspective for treatment and prevention of diseases
Inflammopharmacology (2022)