Abstract
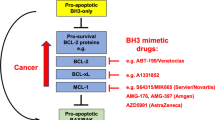
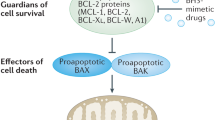
Impaired apoptosis is both critical in cancer development and a major barrier to effective treatment. In response to diverse intracellular damage signals, including those evoked by cancer therapy, the cell's decision to undergo apoptosis is determined by interactions between three factions of the Bcl-2 protein family. The damage signals are transduced by the diverse ‘BH3-only’ proteins, distinguished by the BH3 domain used to engage their pro-survival relatives: Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, Bcl-w, Mcl-1 and A1. This interaction ablates pro-survival function and allows activation of Bax and Bak, which commit the cell to apoptosis by permeabilizing the outer membrane of the mitochondrion. Certain BH3-only proteins (e.g. Bim, Puma) can engage all the pro-survival proteins, but others (e.g. Bad, Noxa) engage only subsets. Activation of Bax and Bak appears to require that the BH3-only proteins engage the multiple pro-survival proteins guarding Bax and Bak, rather than binding to the latter. The balance between the pro-survival proteins and their BH3 ligands regulates tissue homeostasis, and either overexpression of a pro-survival family member or loss of a proapoptotic relative can be oncogenic. Better understanding of the Bcl-2 family is clarifying its role in cancer development, revealing how conventional therapy works and stimulating the search for ‘BH3 mimetics’ as a novel class of anticancer drugs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JM . (2003). Ways of dying: multiple pathways to apoptosis. Genes Dev 17: 2481–2495.
Akiyama T, Bouillet P, Miyazaki T, Kadono Y, Chikuda H, Chung UI et al. (2003). Regulation of osteoclast apoptosis by ubiquitylation of proapoptotic BH3-only Bcl-2 family member Bim. EMBO J 22: 6653–6664.
Amundson SA, Myers TG, Scudiero D, Kitada S, Reed JC, Fornace Jr AJ . (2000). An informatics approach identifying markers of chemosensitivity in human cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 60: 6101–6110.
Annis MG, Soucie EL, Dlugosz PJ, Cruz-Aguado JA, Penn LZ, Leber B et al. (2005). Bax forms multispanning monomers that oligomerize to permeabilize membranes during apoptosis. EMBO J 24: 2096–2103.
Bellot G, Cartron PF, Er E, Oliver L, Juin P, Armstrong LC et al. (2006). TOM22, a core component of the mitochondria outer membrane protein translocation pore, is a mitochondrial receptor for the proapoptotic protein Bax. Cell Death Differ [Epub ahead of print].
Bouillet P, Cory S, Zhang L-C, Strasser A, Adams JM . (2001). Degenerative disorders caused by Bcl-2 deficiency are prevented by loss of its BH3-only antagonist Bim. Dev Cell 1: 645–653.
Bouillet P, Metcalf D, Huang DCS, Tarlinton DM, Kay TWH, Köntgen F et al. (1999). Proapoptotic Bcl-2 relative Bim required for certain apoptotic responses, leukocyte homeostasis, and to preclude autoimmunity. Science 286: 1735–1738.
Bouillet P, Purton JF, Godfrey DI, Zhang L-C, Coultas L, Puthalakath H et al. (2002). BH3-only Bcl-2 family member Bim is required for apoptosis of autoreactive thymocytes. Nature 415: 922–926.
Cartron PF, Gallenne T, Bougras G, Gautier F, Manero F, Vusio P et al. (2004). The first alpha helix of Bax plays a necessary role in its ligand-induced activation by the BH3-only proteins Bid and PUMA. Mol Cell 16: 807–818.
Certo M, Moore Vdel G, Nishino M, Wei G, Korsmeyer S, Armstrong SA et al. (2006). Mitochondria primed by death signals determine cellular addiction to antiapoptotic BCL-2 family members. Cancer Cell 9: 351–365.
Chauhan D, Velankar M, Brahmandam M, Hideshima T, Podar K, Richardson P et al. (2006). A novel Bcl-2/Bcl-X(L)/Bcl-w inhibitor ABT-737 as therapy in multiple myeloma. Oncogene [Epub ahead of print].
Chen L, Willis SN, Wei A, Smith BJ, Fletcher JI, Hinds MG et al. (2005). Differential targeting of pro-survival Bcl-2 proteins by their BH3-only ligands allows complementary apoptotic function. Mol Cell 17: 393–403.
Cheng EH, Sheiko TV, Fisher JK, Craigen WJ, Korsmeyer SJ . (2003). VDAC2 inhibits BAK activation and mitochondrial apoptosis. Science 301: 513–517.
Cheng EH, Wei MC, Weiler S, Flavell RA, Mak TW, Lindsten T et al. (2001). BCL-2, BCL-xL sequester BH3 domain-only molecules preventing BAX- and BAK-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis. Mol Cell 8: 705–711.
Chipuk JE, Kuwana T, Bouchier-Hayes L, Droin NM, Newmeyer DD, Schuler M et al. (2004). Direct activation of Bax by p53 mediates mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and apoptosis. Science 303: 1010–1014.
Chou CH, Lee RS, Yang-Yen HF . (2006). An internal EELD domain facilitates mitochondrial targeting of Mcl-1 via a Tom70-dependent pathway. Mol Biol Cell 17: 3952–3963.
Christophorou MA, Ringshausen I, Finch AJ, Swigart LB, Evan GI . (2006). The pathological response to DNA damage does not contribute to p53-mediated tumour suppression. Nature 443: 214–217.
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Shimizu M et al. (2005). miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 13944–13949.
Concannon CG, Koehler BF, Reimertz C, Murphy BM, Bonner C, Thurow N et al. (2006). Apoptosis induced by proteasome inhibition in cancer cells: predominant role of the p53/PUMA pathway. Oncogene [Epub ahead of print].
Cory S, Adams JM . (2002). The Bcl2 family: regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 647–656.
Cory S, Huang DCS, Adams JM . (2003). The Bcl-2 family: roles in cell survival and oncogenesis. Oncogene 22: 8590–8607.
Cuconati A, Mukherjee C, Perez D, White E . (2003). DNA damage response and MCL-1 destruction initiate apoptosis in adenovirus-infected cells. Genes Dev 17: 2922–2932.
Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ . (2004). Cell death: critical control points. Cell 116: 205–219.
Degenhardt K, Chen G, Lindsten T, White E . (2002). BAX and BAK mediate p53-independent suppression of tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2: 193–203.
Deng X, Gao F, Flagg T, May Jr WS . (2004). Mono- and multisite phosphorylation enhances Bcl2's antiapoptotic function and inhibition of cell cycle entry functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 153–158.
Deverman BE, Cook BL, Manson SR, Niederhoff RA, Langer EM, Rosová I et al. (2002). Bcl-xL deamidation is a critical switch in the regulation of the response to DNA damage. Cell 111: 51–62.
Deverman BE, Cook BL, Manson SR, Niederhoff RA, Langer EM, Rosová I et al. (2003). Bcl-xL deamidation is a critical switch in the regulation of the response to DNA damage. Cell 115: 503.
Dijkers PF, Medema RH, Lammers JJ, Koenderman L, Coffer PJ . (2000). Expression of the pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family member Bim is regulated by the forkhead transcription factor FKHR-L1. Curr Biol 10: 1201–1204.
Dzhagalov I, St John A, He YW . (2006). The anti-apoptotic protein Mcl-1 is essential for the survival of neutrophils but not macrophages. Blood [Epub ahead of print].
Egle A, Harris AW, Bath ML, O'Reilly L, Cory S . (2004a). VavP-Bcl2 transgenic mice develop follicular lymphoma preceded by germinal center hyperplasia. Blood 103: 2276–2283.
Egle A, Harris AW, Bouillet P, Cory S . (2004b). Bim is a suppressor of Myc-induced mouse B cell leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 6164–6169.
Eischen CM, Rehg JE, Korsmeyer SJ, Cleveland JL . (2002). Loss of Bax alters tumor spectrum and tumor numbers in ARF-deficient mice. Cancer Res 62: 2184–2191.
Eischen CM, Woo D, Roussel MF, Cleveland JL . (2001). Apoptosis triggered by myc-induced suppression of Bcl-XL or Bcl-2 Is bypassed during lymphomagenesis. Mol Cell Biol 21: 5063–5070.
Erlacher M, Michalak EM, Kelly PN, Labi V, Niederegger H, Coultas L et al. (2005). BH3-only proteins Puma and Bim are rate-limiting for {gamma}-radiation and glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis of lymphoid cells in vivo. Blood 106: 4131–4138.
Fernandez Y, Verhaegen M, Miller TP, Rush JL, Steiner P, Opipari Jr AW et al. (2005). Differential regulation of noxa in normal melanocytes and melanoma cells by proteasome inhibition: therapeutic implications. Cancer Res 65: 6294–6304.
Fesik SW . (2005). Promoting apoptosis as a strategy for cancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Cancer 5: 876–885.
Fribley AM, Evenchik B, Zeng Q, Park BK, Guan JY, Zhang H et al. (2006). Proteasome inhibitor PS-341 induces apoptosis in cisplatin-resistant squamous cell carcinoma cells by induction of Noxa. J Biol Chem 281: 31440–31447.
Gardai SJ, Hildeman DA, Frankel SK, Whitlock BB, Frasch SC, Borregaard N et al. (2004). Phosphorylation of Bax Ser184 by Akt regulates its activity and apoptosis in neutrophils. J Biol Chem 279: 21085–21095.
Green DR . (2005). Apoptotic pathways: ten minutes to dead. Cell 121: 671–674.
Hamasaki A, Sendo F, Nakayama K, Ishida N, Negishi I, Nakayama K-I et al. (1998). Accelerated neutrophil apoptosis in mice lacking A1-a, a subtype of the bcl-2-related A1 gene. J Exp Med 188: 1985–1992.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . (2000). The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100: 57–70.
Hemann MT, Bric A, Teruya-Feldstein J, Herbst A, Nilsson JA, Cordon-Cardo C et al. (2005). Evasion of the p53 tumour surveillance network by tumour-derived MYC mutants. Nature 436: 807–811.
Hemann MT, Zilfou JT, Zhao Z, Burgess DJ, Hannon GJ, Lowe SW . (2004). Suppression of tumorigenesis by the p53 target PUMA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 9333–9338.
Hildeman DA, Zhu Y, Mitchell TC, Bouillet P, Strasser A, Kappler J et al. (2002). Activated T cell death in vivo mediated by pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family member, Bim. Immunity 16: 759–767.
Hinds MG, Day CL . (2005). Regulation of apoptosis: uncovering the binding determinants. Curr Opin Struct Biol 15: 690–699.
Hsu YT, Youle RJ . (1997). Nonionic detergents induce dimerization among members of the Bcl-2 family. J Biol Chem 272: 13829–13834.
Hsu Y-T, Youle RJ . (1998). Bax in murine thymus is a soluble monomeric protein that displays differential detergent-induced conformations. J Biol Chem 273: 10777–10783.
Huang DC, Hahne M, Schroeter M, Frei K, Fontana A, Villunger A et al. (1999). Activation of Fas by FasL induces apoptosis by a mechanism that cannot be blocked by Bcl-2 or Bcl-xL . Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 14871–14876.
Huang DCS, Strasser A . (2000). BH3-only proteins – essential initiators of apoptotic cell death. Cell 103: 839–842.
Ionov Y, Yamamoto H, Krajewski S, Reed JC, Perucho M . (2000). Mutational inactivation of the proapoptotic gene BAX confers selective advantage during tumor clonal evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 10872–10877.
Jeffers JR, Parganas E, Lee Y, Yang C, Wang J, Brennan J et al. (2003). Puma is an essential mediator of p53-dependent and -independent apoptotic pathways. Cancer Cell 4: 321–328.
Johnstone RW, Ruefli AA, Lowe SW . (2002). Apoptosis: a link between cancer genetics and chemotherapy. Cell 108: 153–164.
Karbowski M, Norris KL, Cleland MM, Jeong SY, Youle RJ . (2006). Role of Bax and Bak in mitochondrial morphogenesis. Nature 443: 658–662.
Kim H, Rafiuddin-Shah M, Tu HC, Jeffers JR, Zambetti GP, Hsieh JJ et al. (2006a). Hierarchical regulation of mitochondrion-dependent apoptosis by BCL-2 subfamilies. Nat Cell Biol 8: 1348–1358.
Kim BJ, Ryu SW, Song BJ . (2006b). JNK- and p38 kinase-mediated phosphorylation of Bax leads to its activation, mitochondrial translocation and to apoptosis of human hepatoma HepG2 cells. J Biol Chem 281: 21256–21265.
Kim PK, Annis MG, Dlugosz PJ, Leber B, Andrews DW . (2004). During apoptosis bcl-2 changes membrane topology at both the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria. Mol Cell 14: 523–529.
Knudson CM, Johnson GM, Lin Y, Korsmeyer SJ . (2001). Bax accelerates tumorigenesis in p53-deficient mice. Cancer Res 61: 659–665.
Kondo S, Shinomura Y, Miyazaki Y, Kiyohara T, Tsutsui S, Kitamura S et al. (2000). Mutations of the bak gene in human gastric and colorectal cancers. Cancer Res 60: 4328–4330.
Konopleva M, Contractor R, Tsao T, Samudio I, Ruvolo PP, Kitada S et al. (2006). Mechanisms of apoptosis sensitivity and resistance to the BH3 mimetic ABT-737 in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 10: 375–388.
Kuribara R, Honda H, Matsui H, Shinjyo T, Inukai T, Sugita K et al. (2004). Roles of Bim in apoptosis of normal and Bcr-Abl-expressing hematopoietic progenitor. Mol Cell Biol 24: 6172–6183.
Kuroda J, Puthalakath H, Cragg MS, Kelly PN, Bouillet P, Huang DC et al. (2006). Bim and Bad mediate imatinib-induced killing of Bcr/Abl+ leukemic cells, and resistance due to their loss is overcome by a BH3 mimetic. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 14907–14912.
Kuwana T, Bouchier-Hayes L, Chipuk JE, Bonzon C, Sullivan BA, Green DR et al. (2005). BH3 domains of BH3-only proteins differentially regulate Bax-mediated mitochondrial membrane permeabilization both directly and indirectly. Mol Cell 17: 525–535.
Kuwana T, Mackey MR, Perkins G, Ellisman MH, Latterich M, Schneiter R et al. (2002). Bid, Bax, and lipids cooperate to form supramolecular openings in the outer mitochondrial membrane. Cell 111: 331–342.
Lakhani SA, Masud A, Kuida K, Porter Jr GA, Booth CJ, Mehal WZ et al. (2006). Caspases 3 and 7: key mediators of mitochondrial events of apoptosis. Science 311: 847–851.
Letai A, Bassik M, Walensky L, Sorcinelli M, Weiler S, Korsmeyer S . (2002). Distinct BH3 domains either sensitize or activate mitochondrial apoptosis, serving as prototype cancer therapeutics. Cancer Cell 2: 183–192.
Ley R, Balmanno K, Hadfield K, Weston C, Cook SJ . (2003). Activation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway promotes phosphorylation and proteasome-dependent degradation of the BH3-only protein, Bim. J Biol Chem 278: 18811–18816.
Lindsten T, Ross AJ, King A, Zong W, Rathmell JC, Shiels HA et al. (2000). The combined functions of proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members Bak and Bax are essential for normal development of multiple tissues. Mol Cell 6: 1389–1399.
Liu X, Dai S, Zhu Y, Marrack P, Kappler JW . (2003). The structure of a Bcl-xL/Bim fragment complex: implications for Bim function. Immunity 19: 341–352.
Luciano F, Jacquel A, Colosetti P, Herrant M, Cagnol S, Pages G et al. (2003). Phosphorylation of Bim-EL by Erk1/2 on serine 69 promotes its degradation via the proteasome pathway and regulates its proapoptotic function. Oncogene 22: 6785–6793.
Lucken-Ardjomande S, Martinou JC . (2005). Newcomers in the process of mitochondrial permeabilization. J Cell Sci 118: 473–483.
McDonnell TJ, Deane N, Platt FM, Nuñez G, Jaeger U, McKearn JP et al. (1989). bcl-2-immunoglobulin transgenic mice demonstrate extended B cell survival and follicular lymphoproliferation. Cell 57: 79–88.
McDonnell TJ, Korsmeyer SJ . (1991). Progression from lymphoid hyperplasia to high-grade malignant lymphoma in mice transgenic for the t(14;18). Nature 349: 254–256.
Meijerink JPP, Mensink EJBM, Wang K, Sedlak TW, Slöetjes AW, de Witte T et al. (1998). Hematopoietic malignancies demonstrate loss-of-function mutations of BAX. Blood 91: 2991–2997.
Mestre-Escorihuela C, Rubio-Moscardo F, Richter JA, Siebert R, Climent J, Fresquet V et al. (2006). Homozygous deletions localize novel tumor suppressor genes in B-cell lymphomas. Blood [Epub ahead of print].
Mihara M, Erster S, Zaika A, Petrenko O, Chittenden T, Pancoska P et al. (2003). p53 has a direct apoptogenic role at the mitochondria. Mol Cell 11: 577–590.
Ming L, Wang P, Bank A, Yu J, Zhang L . (2006). PUMA dissociates Bax and Bcl-XL to induce apoptosis in colon cancer cells. J Biol Chem 281: 16034–16042.
Miyashita T, Reed JC . (1995). Tumor suppressor p53 is a direct transcriptional activator of the human bax gene. Cell 80: 293–299.
Moldoveanu T, Liu Q, Tocilj A, Watson M, Shore G, Gehring K . (2006). The X-ray structure of a Bak homodimer reveals an inhibitory zinc binding site. Mol Cell 24: 677–688.
Motoyama N, Kimura T, Takahashi T, Watanabe T, Nakano T . (1999). bcl-x prevents apoptotic cell death of both primitive and definitive erythrocytes at the end of maturation. J Exp Med 189: 1691–1698.
Motoyama N, Wang FP, Roth KA, Sawa H, Nakayama K, Nakayama K et al. (1995). Massive cell death of immature hematopoietic cells and neurons in Bcl-x deficient mice. Science 267: 1506–1510.
Nakayama K, Nakayama K-I, Negishi I, Kuida K, Sawa H, Loh DY . (1994). Targeted disruption of bcl-2αβ in mice: occurrence of gray hair, polycystic kidney disease, and lymphocytopenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 3700–3704.
Nakayama K-I, Nakayama K, Izumi N, Kulda K, Shinkai Y, Louie MC et al. (1993). Disappearance of the lymphoid system in Bcl-2 homozygous mutant chimeric mice. Science 261: 1584–1588.
Newmeyer DD, Ferguson-Miller S . (2003). Mitochondria: releasing power for life and unleashing the machineries of death. Cell 112: 481–490.
Nijhawan D, Fang M, Traer E, Zhong Q, Gao W, Du F et al. (2003). Elimination of Mcl-1 is required for the initiation of apoptosis following ultraviolet irradiation. Genes Dev 17: 1475–1486.
Nikrad M, Johnson T, Puthalalath H, Coultas L, Adams J, Kraft AS . (2005). The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib sensitizes cells to killing by death receptor ligand TRAIL via BH3-only proteins Bik and Bim. Mol Cancer Ther 4: 443–449.
Ogilvy S, Metcalf D, Print CG, Bath ML, Harris AW, Adams JM . (1999). Constitutive bcl-2 expression throughout the hematopoietic compartment affects multiple lineages and enhances progenitor cell survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 14943–14948.
Oh KJ, Barbuto S, Pitter K, Morash J, Walensky LD, Korsmeyer SJ . (2006). A membrane-targeted BID BH3 peptide is sufficient for high potency activation of BAX in vitro. J Biol Chem 281: 36999–37008.
Oltersdorf T, Elmore SW, Shoemaker AR, Armstrong RC, Augeri DJ, Belli BA et al. (2005). An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces regression of solid tumours. Nature 435: 677–681.
Opferman J, Iwasaki H, Ong CC, Suh H, Mizuno S, Akashi K et al. (2005). Obligate role of anti-apoptotic MCL-1 in the survival of hematopoietic stem cells. Science 307: 1101–1104.
Opferman JT, Letai A, Beard C, Sorcinelli MD, Ong CC, Korsmeyer SJ . (2003). Development and maintenance of B and T lymphocytes requires antiapoptotic MCL-1. Nature 426: 671–676.
Parone PA, James DI, Da Cruz S, Mattenberger Y, Donze O, Barja F et al. (2006). Inhibiting the mitochondrial fission machinery does not prevent bax/bak-dependent apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 26: 7397–7408.
Patel JH, McMahon SB . (2006). BCL2 is a downstream effector of MIZ-1 essential for blocking c-MYC induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem [Epub ahead of print].
Pellegrini M, Belz G, Bouillet P, Strasser A . (2003). Shut down of an acute T cell immune response to viral infection is mediated by the pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 homology 3-only protein Bim. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 14175–14180.
Print CG, Loveland KL, Gibson L, Meehan T, Stylianou A, Wreford N et al. (1998). Apoptosis regulator Bcl-w is essential for spermatogenesis but appears otherwise redundant. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 12424–12431.
Putcha GV, Le S, Frank S, Besirli CG, Clark K, Chu B et al. (2003). JNK-mediated BIM phosphorylation potentiates BAX-dependent apoptosis. Neuron 38: 899–914.
Puthalakath H, Strasser A . (2002). Keeping killers on a tight leash: transcriptional and post-translational control of the pro-apoptotic activity of BH3-only proteins. Cell Death Differ 9: 505–512.
Puthalakath H, Huang DCS, O'Reilly LA, King SM, Strasser A . (1999). The pro-apoptotic activity of the Bcl-2 family member Bim is regulated by interaction with the dynein motor complex. Mol Cell 3: 287–296.
Puthalakath H, Villunger A, O'Reilly LA, Beaumont JG, Coultas L, Cheney RE et al. (2001). Bmf: a pro-apoptotic BH3-only protein regulated by interaction with the myosin V actin motor complex, activated by anoikis. Science 293: 1829–1832.
Qin JZ, Ziffra J, Stennett L, Bodner B, Bonish BK, Chaturvedi V et al. (2005). Proteasome inhibitors trigger NOXA-mediated apoptosis in melanoma and myeloma cells. Cancer Res 65: 6282–6293.
Rampino N, Yamamoto H, Ionov Y, Li Y, Sawai H, Reed JC et al. (1997). Somatic frameshift mutations in the bax gene in colon cancers of the microsatellite mutator phenotype. Science 275: 967–969.
Reginato MJ, Mills KR, Becker EB, Lynch DK, Bonni A, Muthuswamy SK et al. (2005). Bim regulation of lumen formation in cultured mammary epithelial acini is targeted by oncogenes. Mol Cell Biol 25: 4591–4601.
Reginato MJ, Mills KR, Paulus JK, Lynch DK, Sgroi DC, Debnath J et al. (2003). Integrins and EGFR coordinately regulate the pro-apoptotic protein Bim to prevent anoikis. Nat Cell Biol 5: 733–740.
Rinkenberger JL, Horning S, Klocke B, Roth K, Korsmeyer SJ . (2000). Mcl-1 deficiency results in peri-implantation embryonic lethality. Genes Dev 14: 23–27.
Ross AJ, Waymire KG, Moss JE, Parlow AF, Skinner MK, Russell LD et al. (1998). Testicular degeneration in Bclw-deficient mice. Nat Genet 18: 251–256.
Sadowsky JD, Fairlie WD, Hadley EB, Lee H-S, Umezawa N, Nikolovska-Coleska Z et al. (2006). Characterization of (a/b+a)-peptide antagonists of BH3 domain/Bcl-XLrecognition: toward general strategies for developing foldamer-based inhibitors of protein–protein interactions. J Am Chem Soc in press.
Sadowsky JD, Schmitt MA, Lee HS, Umezawa N, Wang S, Tomita Y et al. (2005). Chimeric (alpha/beta+alpha)-peptide ligands for the BH3-recognition cleft of Bcl-XL: critical role of the molecular scaffold in protein surface recognition. J Am Chem Soc 127: 11966–11968.
Sattler M, Liang H, Nettesheim D, Meadows RP, Harlan JE, Eberstadt M et al. (1997). Structure of Bcl-xL-Bak peptide complex: recognition between regulators of apoptosis. Science 275: 983–986.
Schmidt T, Korner K, Karsunky H, Korsmeyer S, Muller R, Moroy T . (1999). The activity of the murine bax promoter is regulated by Sp1/3 and E-box binding proteins but not by p53. Cell Death Differ 6: 873–882.
Schmitt CA, Rosenthal CT, Lowe SW . (2000). Genetic analysis of chemoresistance in primary murine lymphomas. Nat Med 6: 1029–1035.
Sentman CL, Shutter JR, Hockenbery D, Kanagawa O, Korsmeyer SJ . (1991). bcl-2 inhibits multiple forms of apoptosis but not negative selection in thymocytes. Cell 67: 879–888.
Shibata MA, Liu ML, Knudson MC, Shibata E, Yoshidome K, Bandey T et al. (1999). Haploid loss of bax leads to accelerated mammary tumor development in C3(1)/SV40-TAg transgenic mice: reduction in protective apoptotic response at the preneoplastic stage. EMBO J 18: 2692–2701.
Shoemaker AR, Oleksijew A, Bauch J, Belli BA, Borre T, Bruncko M et al. (2006). A small-molecule inhibitor of Bcl-XL potentiates the activity of cytotoxic drugs in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res 66: 8731–8739.
Strasser A, Harris AW, Bath ML, Cory S . (1990). Novel primitive lymphoid tumours induced in transgenic mice by cooperation between myc and bcl-2. Nature 348: 331–333.
Strasser A, Harris AW, Cory S . (1991a). Bcl-2 transgene inhibits T cell death and perturbs thymic self-censorship. Cell 67: 889–899.
Strasser A, Harris AW, Cory S . (1993). Eμ-bcl-2 transgene facilitates spontaneous transformation of early pre-B and immunoglobulin-secreting cells but not T cells. Oncogene 8: 1–9.
Strasser A, Harris AW, Huang DCS, Krammer PH, Cory S . (1995). Bcl-2 and Fas/APO-1 regulate distinct pathways to lymphocyte apoptosis. EMBO J 14: 6136–6147.
Strasser A, O'Connor L, Dixit VM . (2000). Apoptosis signaling. Ann Rev Biochem 69: 217–245.
Strasser A, Whittingham S, Vaux DL, Bath ML, Adams JM, Cory S et al. (1991b). Enforced BCL2 expression in B-lymphoid cells prolongs antibody responses and elicits autoimmune disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 8661–8665.
Strasser A . (2005). The role of BH3-only proteins in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 5: 189–200.
Suzuki M, Youle RJ, Tjandra N . (2000). Structure of Bax: coregulation of dimer formation and intracellular localization. Cell 103: 645–654.
Tagawa H, Karnan S, Suzuki R, Matsuo K, Zhang X, Ota A et al. (2005). Genome-wide array-based CGH for mantle cell lymphoma: identification of homozygous deletions of the proapoptotic gene BIM. Oncogene 24: 1348–1358.
Tan TT, Degenhardt K, Nelson DA, Beaudoin B, Nieves-Neira W, Bouillet P et al. (2005). Key roles of BIM-driven apoptosis in epithelial tumors and rational chemotherapy. Cancer Cell 7: 227–238.
van Delft MF, Wei AH, Mason KD, Vandenberg CJ, Chen L, Czabotar PE et al. (2006). The BH3 mimetic ABT-737 targets selective Bcl-2 proteins and efficiently induces apoptosis via Bak/Bax if Mcl-1 is neutralized. Cancer Cell 10: 389–399.
Vaux DL, Cory S, Adams JM . (1988). Bcl-2 gene promotes haemopoietic cell survival and cooperates with c-myc to immortalize pre-B cells. Nature 335: 440–442.
Veis DJ, Sorenson CM, Shutter JR, Korsmeyer SJ . (1993). Bcl-2-deficient mice demonstrate fulminant lymphoid apoptosis, polycystic kidneys, and hypopigmented hair. Cell 75: 229–240.
Villunger A, Michalak EM, Coultas L, Müllauer F, Böck G, Ausserlechner MJ et al. (2003). p53- and drug-induced apoptotic responses mediated by BH3-only proteins Puma and Noxa. Science 302: 1036–1038.
Vousden KH, Lu X . (2002). Live or let die: the cell's response to p53. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 594–604.
Wagner KU, Claudio E, Rucker III EB, Riedlinger G, Broussard C, Schwartzberg PL et al. (2000). Conditional deletion of the Bcl-x gene from erythroid cells results in hemolytic anemia and profound splenomegaly. Development 127: 4949–4958.
Walensky LD, Kung AL, Escher I, Malia TJ, Barbuto S, Wright RD et al. (2004). Activation of apoptosis in vivo by a hydrocarbon-stapled BH3 helix. Science 305: 1466–1470.
Walensky LD, Pitter K, Morash J, Oh KJ, Barbuto S, Fisher J et al. (2006). A stapled BID BH3 helix directly binds and activates BAX. Mol Cell 24: 199–210.
Wei MC, Zong WX, Cheng EH, Lindsten T, Panoutsakopoulou V, Ross AJ et al. (2001). Proapoptotic BAX and BAK: a requisite gateway to mitochondrial dysfunction and death. Science 292: 727–730.
Willis SN, Adams JM . (2005). Life in the balance: how BH3-only proteins induce apoptosis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17: 617–625.
Willis SN, Chen L, Dewson G, Wei A, Naik E, Fletcher JI et al. (2005). Pro-apoptotic Bak is sequestered by Mc1-1 and Bcl-xL, but not Bcl-2, until displaced by BH3-only proteins. Genes Dev 19: 1294–1305.
Willis SN, Fletcher JI, Kaufmann T, van Delft MF, Chen L, Czabotar PE et al. (2007). Apoptosis initiated when BH3 ligands engage multiple Bcl-2 homologs, not Bax or Bak. Science in press.
Wolter KG, Hsu YT, Smith CL, Nechushtan A, Xi XG, Youle RJ . (1997). Movement of Bax from the cytosol to mitochondria during apoptosis. J Cell Biol 139: 1281–1292.
Yin CY, Knudson CM, Korsmeyer SJ, Van Dyke T . (1997). Bax suppresses tumorigenesis and stimulates apoptosis in vivo. Nature 385: 637–640.
Zha J, Harada H, Yang E, Jockel J, Korsmeyer SJ . (1996). Serine phosphorylation of death agonist BAD in response to survival factor results in binding to 14-3-3 not Bcl-xL . Cell 87: 619–628.
Zha J, Weiler S, Oh KJ, Wei MC, Korsmeyer SJ . (2000). Posttranslational N-myristoylation of BID as a molecular switch for targeting mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 290: 1761–1765.
Zhang Y, Adachi M, Kawamura R, Imai K . (2005). Bmf is a possible mediator in histone deacetylase inhibitors FK228 and CBHA-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 13: 129–140.
Zhao Y, Tan J, Zhuang L, Jiang X, Liu ET, Yu Q . (2005). Inhibitors of histone deacetylases target the Rb-E2F1 pathway for apoptosis induction through activation of proapoptotic protein Bim. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 16090–16095.
Zhong Q, Gao W, Du F, Wang X . (2005). Mule/ARF-BP1, a BH3-Only E3 ubiquitin ligase, catalyzes the polyubiquitination of Mcl-1 and regulates apoptosis. Cell 121: 1085–1095.
Zhu Y, Liu X, Hildeman D, Peyerl FW, White J, Kushnir E et al. (2006). Bax does not have to adopt its final form to drive T cell death. J Exp Med 203: 1147–1152.
Zhu Y, Swanson BJ, Wang M, Hildeman DA, Schaefer BC, Liu X et al. (2004). Constitutive association of the proapoptotic protein Bim with Bcl-2-related proteins on mitochondria in T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 7681–7686.
Zong WX, Lindsten T, Ross AJ, MacGregor GR, Thompson CB . (2001). BH3-only proteins that bind pro-survival Bcl-2 family members fail to induce apoptosis in the absence of Bax and Bak. Genes Dev 15: 1481–1486.
Acknowledgements
The issues addressed here have benefited greatly from discussions with many colleagues, including in particular our senior colleagues Drs David Huang and Andreas Strasser, as well as Drs Simon Willis and Jamie Fletcher. This research is supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council (Program Grant 257502), the Leukmia and Lymphoma Society (SCOR Grant 7015-02) and the US National Cancer Institute (CA80188, CA43540).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adams, J., Cory, S. The Bcl-2 apoptotic switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene 26, 1324–1337 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210220
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210220
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Modulation of apoptosis and Inflammasome activation in chondrocytes: co-regulatory role of Chlorogenic acid
Cell Communication and Signaling (2024)
-
MicroRNA miR-20a-5p targets CYCS to inhibit apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma
Cell Death & Disease (2024)
-
BAX activation in mouse retinal ganglion cells occurs in two temporally and mechanistically distinct steps
Molecular Neurodegeneration (2023)
-
Aqueous extract of Platycodon grandiflorus attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis and inflammatory cell infiltration in mouse lungs by inhibiting PI3K/Akt signaling
Chinese Medicine (2023)
-
A literature review of microRNA and gene signaling pathways involved in the apoptosis pathway of lung cancer
Respiratory Research (2023)