Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
Use the meta-analytic approach to examine the effects of aerobic exercise on lipids and lipoproteins in overweight and obese adults.
DATA SOURCES:
(1) Computerized literature searches, (2) cross-referencing from review and original articles, (3) hand searching, and (4) expert review of reference list.
STUDY SELECTION:
(1) randomized controlled trials, (2) aerobic exercise ≥8 weeks, (3) adult humans ≥18 y of age, (4) all subjects overweight or obese (BMI ≥25 kg/m2), (5) studies published in journal, dissertation, or master's thesis format, (6) studies published in the English-language, (7) studies published between 1 January 1955 and 1 January 2003, (8) assessment of one or more of the following lipid and/or lipoprotein variables: total cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL), and triglycerides (TG).
DATA ABSTRACTION:
Dual-coding by the first two authors (inter-rater agreement=0.96).
RESULTS:
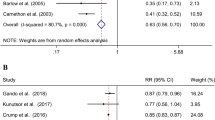
In total, 13 studies representing 31 groups (17 exercise, 14 control), 613 subjects (348 exercise, 265 control), and up to 17 outcomes were available for pooling. Across all categories, random-effects modeling resulted in statistically significant improvements for TC (X̄±s.e.m., − 3.4±1.7 mg/dl, 95% CI, − 6.7 to − 0.2 mg/dl) and TG (X̄±s.e.m., − 16.1±7.3 mg/dl, 95% CI, − 30.2 to − 2.1 mg/dl) but not HDL (X̄±s.e.m., 1.6±0.8 mg/dl, 95% CI, − 0.02 to 3.2 mg/dl) or LDL (X̄±s.e.m., − 0.5±1.3 mg/dl, 95% CI, − 3.0 to 2.0 mg/dl). Changes were equivalent to improvements of 2% (TC), 11% (TG), 3% (HDL), and 0.3% (LDL). After conducting sensitivity analyses (each study deleted from the model once), only decreases in TG remained statistically significant. Increases in HDL were associated with increases in maximum oxygen consumption (VO2 max in ml/kg/min, r=0.75, P=0.002) and decreases in body weight (r=0.77, P<0.001), while decreases in LDL were associated with decreases in body weight (r=0.75, P=0.009).
CONCLUSIONS:
Aerobic exercise decreases TG in overweight and obese adults. However, a need exists for additional randomized controlled trials in various overweight and/or obese populations above and beyond those included in our analysis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Johnson CL . Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2000. JAMA 2002; 288: 1723–1727.
Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Executive summary of the third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 2001; 285: 2486–2497.
Campbell DE . Effect of controlled running on serum cholesterol of young adult males of varying morphological constitutions. Res Q 1968; 39: 47–53.
Gillett PA, Caserta MS, White AT, Martinson L . Responses of 49- to 59-year old sedentary, overweight women to four months of exercise conditioning and/or fitness education. Activities Adaptation Aging 1995; 19: 13–32.
Hagan RD, Upton SJ, Wong L, Whittam J . The effects of aerobic conditioning and/or caloric restriction in overweight men and women. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1986; 18: 87–94.
Hinkleman LL, Nieman DC . The effects of a walking program on body composition and serum lipids and lipoproteins in overweight women. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 1993; 33: 49–58.
Hopewell R . The effect of fiber and exercise on weight loss and blood lipids in moderately overweight women 1989. West Virginia University: Morgantown, West Virginia.
Kaplan RM, Wilson DK, Hartwell SL, Merino KL, Wallace JP . Prospective evaluation of HDL cholesterol changes after diet and physical conditioning programs for patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 1985; 8: 343–348.
Keller C, Trevino RP . Effects of two frequencies of walking on cardiovascular risk factor reduction in Mexican American women. Res Nurs Health 2001; 24: 390–401.
Kraus WE, Houmard JA, Duscha BD, Knetzger KJ, Wharton MB, McCartney JS, Bales CW, Henes S, Samsa GP, Otvos JD, Kulkarni KR, Slentz CA . Effects of the amount and intensity of exercise on plasma lipoproteins. N Engl J Med 2002; 347: 1483–1492.
Leon AS, Casal D, Jacobs D . Effects of 2,000 kcal per week of walking and stair climbing on physical fitness and risk factors for coronary heart disease. J Cardiopulm Rehabil 1996; 16: 183–192.
Ligtenberg PC, Hoekstra JB, Bol E, Zonderland ML, Erkelens DW . Effects of physical training on metabolic control in elderly type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Clin Sci (London) 1997; 93: 127–135.
Nieman DC, Brock DW, Butterworth D, Utter AC, Nieman CC . Reducing diet and/or exercise training decreases the lipid and lipoprotein risk factors of moderately obese women. J Am Coll Nutr 2002; 21: 344–350.
Sopko G, Leon AS, Jacobs DR, Foster N, Moy J, Kuba K, Anderson JT, Casal D, McNally C, Frantz I . The effects of exercise and weight loss on plasma lipids in young obese men. Metabolism 1985; 34: 227–236.
Verity LS, Ismail AH . Effects of exercise on cardiovascular disease risk in women with NIDDM. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 1989; 6: 27–35.
Wood PD, Stefanick ML, Dreon DM, Frey-Hewitt B, Garay SG, Williams PT, Superko HR, Fortmann SP, Albers JJ, Vranizan KM, Ellsworth NM, Terry RB, Haskell WL . Changes in plasma lipids and lipoproteins in overweight men during weight loss through dieting as compared with exercise. N Engl J Med 1988; 319: 1173–1179.
Hedges LV, Olkin I . Vote-counting methods in research synthesis. Psychol Bull 1980; 88: 359–369.
Durstine JL, Grandjean PW, Davis PG, Ferguson MA, Alderson NL, DuBose KD . Blood lipid and lipoprotein adaptations to exercise: a quantitative analysis. Sports Med 2001; 31: 1033–1062.
Halbert JA, Silagy CA, Finucane P, Withers RT, Hamdorf PA . Exercise training and blood lipids in hyperlipidemic and normolipidemic adults: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Eur J Clin Nutr 1999; 53: 514–522.
Kelley GA, Kelley KS, Tran ZV . Walking, lipids, and lipoproteins: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Prev Med 2004; 38: 651–661.
Leon AS, Sanchez OA . Response of blood lipids to exercise training alone or combined with dietary intervention. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2001; 33: S502–S515.
Lokey EA, Tran ZV . Effects of exercise training on serum lipid and lipoprotein concentration in women: a meta-analysis. Int J Sports Med 1989; 10: 424–429.
Tran ZV, Weltman A . Differential effects of exercise on serum lipid and lipoprotein levels seen with changes in body weight: a meta-analysis. JAMA 1985; 254: 919–924.
Tran ZV, Weltman AW, Glass GV, Mood DF . The effects of exercise on blood lipids and lipoproteins: a meta-analysis of studies. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1983; 15: 393–402.
Dersimonian R, Laird N . Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 1986; 7: 177–188.
Cochran WG . The combination of estimates from different experiments. Biometrics 1954; 10: 101–129.
Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG . Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. Br Med J 2003; 327: 557–560.
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C . Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple graphical test. Br Med J 1997; 315: 629–634.
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJM, Gavaghan DJ, McQuay HJ . Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: Is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials 1996; 17: 1–12.
West S, King V, Carey T, Lohr K, McKoy N, Sutton S, Lux L . Systems to rate the strength of scientific evidence, Evidence Report/Technology Assessment No. 47 AHRQ (Publication No. 02-E016) [Prepared by Research Triangle Institute-University of North Carolina Evidenced-Based Practice Center under Contract No. 290-97-0011] Agency of Healthcare Research and Quality: Rockville, MD; 2002.
Alderson P, Green S, Higgins JPT . Cochrane Reviewers' Handbook 4.2.1, [updated December 2003] 2004. http://www.cochrane.org/resources/handbook/hbook.htm.
Lipsey MW, Wilson DB . Practical meta-analysis. Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA; 2001.
American College of Sports Medicine. The recommended quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory and muscular fitness, and flexibility in healthy adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1998; 30: 975–991.
Booth FW, Chakravarthy MV, Gordon SE, Spangenburg EE . Waging war on physical inactivity: using modern molecular ammunition against an ancient enemy. J Appl Physiol 2002; 93: 3–30.
Acknowledgements
We thank William Haskell, PhD, Stanford University, for reviewing our reference list and providing suggestions for the coding of studies. This study was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health-National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, Award #R01-HL069802 (GA Kelley, Principal Investigator).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kelley, G., Kelley, K. & Vu Tran, Z. Aerobic exercise, lipids and lipoproteins in overweight and obese adults: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Obes 29, 881–893 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802959
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802959