Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To study the relation of fibrinogen and C-reactive protein (CRP) to various measures of body fat and body fat distribution and to investigate whether these relations were explained by differences in insulin sensitivity.
DESIGN AND SUBJECTS: Cross-sectional analysis of the IRAS (Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study), a large (n=1559) tri-ethnic population (non-Hispanic whites, African-Americans and Mexican-Americans) across different states of glucose tolerance.
MEASUREMENTS: Glucose tolerance (oral glucose tolerance test), insulin sensitivity (frequently sampled intravenous glucose tolerance test and minimal model analysis), assessment of body fat mass and distribution (weight, girths, bioelectrical impedance), subclinical atherosclerosis (B-mode ultrasonography of carotid artery intima-media thickness, IMT), CRP (highly sensitive immunoassay), fibrinogen (standard assay).
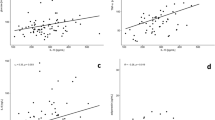
RESULTS: Both CRP and fibrinogen were related to all measures of body fat. Strong correlations (correlation coefficient r≥0.35) were found between CRP and body mass index (BMI), waist circumference and adipose body mass, respectively. The associations were consistent in non-diabetic and type-2 diabetic subjects, were generally stronger in women, and were only moderately attenuated by the prevailing insulin sensitivity (SI). In a multivariate linear regression model waist circumference explained 14.5% of the variability of circulating CRP levels (P=0.0001), BMI 0.4% (P=0.0067), and SI 1.7% (P=0.0001). Common carotid artery IMT was related to CRP and fibrinogen in men, but not in women, and was attenuated after adjusting for BMI or waist.
CONCLUSION: Our findings show that measures of body fat are strongly associated with circulating levels of CRP and fibrinogen. These associations were not explained by lower SI in obese subjects. Chronic, subclinical inflammation may be one pathophysiological mechanism explaining the increased risk of atherosclerotic disease associated with adiposity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kissebah AH, Krakower GR . Regional adiposity and morbidity Physiol Rev 1994 74: 761–811.
Björntorp P . ‘Portal’ adipose tissue as a generator of risk factors for cardiovascular disease and diabetes Arteriosclerosis 1990 10: 493–496.
Lapidus L, Bengtsson C, Larsson B, Pennert K, Rybo E, Sjöström L . Distribution of adipose tissue and risk of cardiovascular disease and death: 12 y follow-up of participants in the population study of women in Gothenburg, Sweden Br Med J 1984 289: 1257–1261.
Larsson B, Svärdsud DK, Welin L, Wilhelmsen L, Björntorp P, Tibbin G . Abdominal adipose tissue distribution, obesity and risk of cardiovascular disease and death: 13 y follow-up of participants in the study of men born in 1913 Br Med J 1984 288: 1401–1404.
Mohamed-Ali V, Pinkney JH, Coppack SW . Adipose tissue as an endocrine and paracrine organ Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1998 22: 1145–1158.
Juhan-Vague I, Alessi MC . PAI-1, obesity, insulin resistance and risk of cardiovascular events Thromb Haemostas 1997 78: 656–660.
Tracy RP . Inflammation in cardiovascular disease: cart, horse, or both? Circulation 1998 97: 2000–2002.
Maresca G, Di Blasio A, Marchioli R, Di Minno G . Measuring plasma fibrinogen to predict stroke and myocardial infarction Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1999 19: 1368–1377.
Haverkate F, Thompson SG, Pyke SDM, Gallimore JR, Pepys MB, for the European Concerted Action on Thrombosis and Disabilities Angina Pectoris Study Group . Production of C-reactive protein and risk of coronary events in stable and unstable angina Lancet 1997 349: 462–466.
Koenig W, Sund M, Fröhlich M, Fischer H-G, Löwel H, Döring A, Hutchinson WL, Pepys MB . C-reactive protein, a sensitive marker of inflammation, predicts future risk of coronary heart disease in initially healthy middle-aged men Circulation 1999 99: 237–242.
Ridker PM, Cushman M, Stampfer MJ, Tracy R, Hennekens CH . Inflammation, aspirin, and the risk of cardiovascular disease in apparently healthy men New Engl J Med 1997 336: 973–979.
Tracy RP, Lemaitre RN, Psaty BM, Ives DG, Evans RW, Cushman M, Meilahn EN, Kuller LH . Relationship of C-reactive protein to risk of cardiovascular disease in the elderly: results from the Cardiovascular Health Study and the Rural Health Promotion Prodject. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1997 17: 1121–1127.
Mendall MA, Patel P, Ballam L, Strachan D, Northfield TC . C-Reactive protein and it relation to cardiovasular risk factors: a population based cross sectional study. Br Med J 1996 312: 1061–1065.
Tracy RP, Psaty BM, Macy E, Bovill EG, Cushman M, Cornell ES, Kuller LH . Lifetime smoking exposure affects the association of C-reactive protein with cardiovascular disease risk factors and subclinical disease in healthy elderly subjects. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1997 17: 2167–2176.
Yudkin JS, Stehouwer CDA, Emeis JJ, Coppack SW . C-reactive protein in healthy subjects: associations with obesity, insulin resistance, and endothelial dysfunction. Aterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1999 19: 972–978.
Festa A, D'Agostino R Jr, Mykkänen, Tracy RP, Zaccaro DJ, Hales CN, Haffner SM . Relative contribution of insulin and its precursors to fibrinogen and PAI-1 in a large population with different states of glucose tolerance—the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study (IRAS). Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1999 19: 562–568.
Howard G, Tracy R, Wagenknecht L, Macy E . Predictors of inflammatory status in a middle-aged population Circulation 1999 99: A1108.
Eliasson M, Røder ME, Dinesen B, Evrin PE, Lindahl B . Proinsulin, intact insulin, and fibrinolytic variables and fibrinogen in healthy subjects. Diabetes Care 1997 20: 1252–1255.
Folsom AR, Qamhieh HT, Wing RR, Jeffery RW, Stinson VL, Kuller LH, Wu KK . Impact of weight loss on plasinogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1), factor VII, and other hemostatic factors in moderately overweight adults. Arteroscler Thromb 1993 13: 162–169.
Eliasson M, Evrin PE, Lindblad D . Fibrinogen and fibrinolytic variables in relation to anthropometry, lipids and blood pressure. The Northern Sweden MONICA Study. J Clin Epidemiol 1994 47: 513–524.
Wagenknecht LE, Mayer EJ, Rewers M, Haffner SM, Selby J, Borok GM, Henkin L, Howard G, Savage PJ, Saad MF, Bergman RN, Hamman R . The Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study (IRAS): objectives, design and recruitment results Ann Epidemiol 1995 5: 464–471.
World Health Organization . Diabetes mellitus Report of a WHO Study Group. Technical Report Series no. 727 WHO: Geneva 1985
Bergman RN, Finegood DT, Ader M . Assessment of insulin sensitivity in vivo Endocr Rev 1985 6: 45–86.
Pacini G, Bergman RN . MINMOD: a computer program to calculate insulin sensitivity and pancreatic responsivity from the frequently sampled intravenous glucose tolerance test Comput Meth Programs Biomed 1986 23: 113–122.
Lukaski HC, Bolonchuk WW, Hall CB, Siders WA . Validation of tetrapolar bioelectrical impedance method to assess human body composition J Appl Physiol 1986 60: 1327–1332.
Macy E, Hayes T, Tracy R . Variability in the measurement of C-reactive protein in healthy subjects: implications for reference interval and epidemiological applications Clin Chem 1997 43: 52–58.
Geffken D, Keating F, Kennedy M, Cornell E, Bovill E, Tracy R . The measurement of fibrinogen in population-based research: studies on instrumentation and methodology Arch Pathol Lab Med 1994 118: 1106–1109.
Clauss A . Gerinnungsphysiologische Schnellmethode zur Bestimmung des Fibrinogens Acta Haematol 1957 17: 237–246.
Ford ES . Body mass index, diabetes, and c-reactive protein among U.S. adults Diabetes Care 1999 22: 1971–1977.
Karter AJ, Mayer-Davis EJ, Selby JV, D'Agostino RB Jr, Haffner SM, Sholinsky P, Bergman R, Saad MF, Hamman RF . Insulin sensitivity and abdominal obesity in African-American, Hispanic, and Non-Hispanic White men and women Diabetes 1996 45: 1547–1555.
DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E . Insulin resistance: a multifaceted syndrome responsible for NIDDM, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease Diabetes Care 1991 14: 173–194.
Festa A, D'Agostino R Jr, Howard G, Mykkänen L, Tracy RP, Haffner SM . Chronic subclinical inflammation as part of the insulin resistance syndrome Circulation 2000 102: 42–47.
Endres S, Ghorbani R, Kelley VE, Georgilis K, Lonnemann G, van der Meer JW, Cannon JG, Rogers TS, Klempner MS, Weber PC . The effect of dietary supplementation with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on the synthesis of interleukin-1 and tumour necrosis factor by mononuclear cells New Engl J Med 1989 320: 265–271.
Hotamisligil GS, Arner P, Caro JF, Atkinson RL, Spiegelman BM . Increased adipose tissue expression of tumour necrosis factor-α in human obesity and insulin resistance J Clin Invest 1995 95: 2409–2415.
Mohamed-Ali V, Goodrick S, Rawesh A, Katz DR, Miles JM, Yudkin JS, Klein S, Coppack SW . Subcutaneous adipose tissue release interleukin-6, but not tumor necrosis factor-α, in vivo J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997 82: 4196–4200.
Stephens JM, Butts MD, Pekala PH . Regulation of transcription factor mRNA accumulation during 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation by tumor necrosis factor-alpha J Mol Endocrinol 1992 9: 61–72.
Berg M, Fraker DL, Alexander HR . Characterisation of differentiation factor/leukaemia inhibitory factor effect on lipoprotein lipase activity and mRNA in 3T3-L1 adipocytes Cytokine 1994 6: 425–432.
Feingold KR, Grunfeld C . Role of cytokines in inducing hyperlipidaemia Diabetes 1992 41: (Suppl 2): 97–101.
Ridker PM, Hennekens CH, Buring JE, Rifai N . C-reactive protein and other markers of inflammation in the prediction of cardiovascular disease in women New Engl J Med 2000 342: 836–843.
Huber SA, Sakkinen P, Conze D, Hardin N, Tracy R . Interleukin-6 exacerbates early atherosclerosis in mice Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1999 19: 2364–2367.
Seidell JC, Oosterlee A, Thijssen MAO, Burema J, Deurenberg P, Hautvast JGAJ, Ruijs JHJ . Assessment of intra-abdominal and subcutaneous abdominal fat: relation between anthropometry and computed tomography Am J Clin Nutr 1987 45: 7–13.
Pouliot M-C, Després J-P, Lemieux S, Moorjani S, Bouchard C, Tremblay A, Nadeau A, Lupien PJ . Waist circumference and abdominal sagittal diameter: best simple anthropometric indexes of abdominal visceral adipose tissue accumulation and related cardiovascular risk in men and women Am J Cardiol 1994 73: 460–468.
Duncan BB, Chambless LE, Schmidt MI, Szklo M, Folsom AR, Carpenter MA, Crouse JR III for the ARIC study investigators . Correlates of body fat distribution. Variation across categories of race, sex, and body mass in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study Ann Epidemiol 1995 5: 192–200.
Kvist H, Chowdhury B, Grangård U, Tylén U, Sjöström L . Predictive equations of total and visceral adipose tissue volumes derived from measurements with computed tomography in adult men and women Am J Clin Nutr 1988 48: 1351–1361.
Ridker PM, Hennekens CH, Rifai N, Buring JE, Manson JE . Hormone replacement therapy and increased plasma concentration of C-reactive protein Circulation 1999 100: 713–716.
Cushman M, Legault C, Barrett-Connor E, Stefanick ML, Kessler C, Judd HL, Sakkinen PA, Tracy RP . Effect of postmenopausal hormones on inflammation-sensitive proteins Circulation 1999 100: 717–722.
Stenvinkel P, Heimbürger O, Paultre F, Diczfalusy U, Wang T, Berglund L, Jogestrand T . Strong association between malnutrition, inflammation, and atherosclerosis in chronic renal failure Kidney Int 1999 55: 1899–1911.
Hak AE, Stehouwer CDA, Bots ML, Polderman KH, Schalkwijk CG, Westendorp ICD, Hofman A, Witteman JCM . Association of C-reactive protein with measures of obesity, insulin resistance, and subclinical atherosclerosis in healthy, middle-aged women Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1999 19: 1986–1991.
Sattar N, Tan CE, Han TS, Forster L, Lean MEJ, Shepherd J, Packard CJ . Association of indices of adiposity with atherogenic lipoprotein subfractions Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1998 22: 432–439.
Lean MEJ, Han TS, Seidell JC . Impairment of health and quality of life in people with large waist circumference Lancet 1998 351: 853–856.
Laakso M, Lehto S . Epidemiology of macrovascular disease in diabetes Diabetes Rev 1997 5: 294–315.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (grants HL47887, HL47889, HL47890, HL47892, HL47902, HL55208 and R01 HL58329) and the General Clinic Research Centers Program (grants NCRR GCRC, M01 RR431 and M01 RR01346).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Festa, A., D'Agostino Jr, R., Williams, K. et al. The relation of body fat mass and distribution to markers of chronic inflammation. Int J Obes 25, 1407–1415 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801792
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801792