Abstract
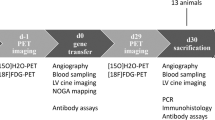
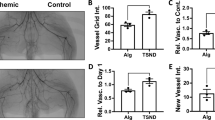
Although clinical trials of stimulation of angiogenesis by transfection of angiogenic growth factors using naked plasmid DNA or adenoviral vector have been successful, there are still unresolved problems for human gene therapy such as low transfection efficiency and safety. From this viewpoint, it is necessary to develop safe and efficient novel nonviral gene transfer methods. As therapeutic ultrasound induces cell membrane permeabilization, ultrasound irradiation might increase the transfection efficiency of naked plasmid DNA into skeletal muscle. Thus, we examined the transfection efficiency of naked plasmid DNA using ultrasound irradiation with echo contrast microbubble (Optison) in vitro and in vivo experiments. First, we examined the feasibility of ultrasound-mediated transfection of naked plasmid DNA into skeletal muscle cells. Luciferase plasmid mixed with or without Optison was transfected into cultured human skeletal muscle cells using ultrasound (1 MHz; 0.4 W2) for 30 s. Interestingly, luciferase activity was markedly increased in cells treated with Optison, while little luciferase activity could be detected without Optison (P < 0.01). Electron microscopy demonstrated the transient formation of holes (less than 5 μM) in the cell surface, which could possibly explain the rapid migration of the transgene into the cells. Next, we studied the in vivo transfection efficiency of naked plasmid DNA using ultrasound with Optison into skeletal muscle. Two days after transfection, luciferase activity in skeletal muscle transfected with Optison using ultrasound was significantly increased about 10-fold as compared with plasmid alone. Successful transfection was also confirmed by β-galactosidase staining. Finally, we examined the feasibility of therapeutic angiogenesis using naked hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) plasmid in a rabbit ischemia model using the ultrasound–Optison method. Five weeks after transfection, the angiographic score and the number of capillary density in rabbits transfected with Optison using ultrasound was significantly increased as compared with HGF plasmid alone (P < 0.01), accompanied by a significant increase in blood flow and blood pressure ratio (P < 0.01). Overall, the ultrasound transfection method with Optison enhanced the transfection efficiency of naked plasmid DNA in vivo as well as in vitro. Transfection of HGF plasmid by the ultrasound-Optison method could be useful for safe clinical gene therapy to treat peripheral arterial disease without a viral vector system.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Second European Consensus Document on Chronic Critical Leg Ischemia. Circulation 1991; 84 (4 Suppl.): 1–26
Dormandy J. et al. Fate of the patient with chronic leg ischaemia. A review article J Cardiovasc Surg Torino 1989 30: 50 50
Rutherford R.B. et al. Suggested standards for reports dealing with lower extremity ischemia. Ad Hoc Committee on Reporting Standards. Society for Vascular Surgery/North American Chapter, International Society for Cardiovascular Surgery J Vasc Surg 1986 4: 80 80
Isner J.M. et al. Clinical evidence of angiogenesis after arterial gene transfer of ph VEGF165 in patient with ischaemic limb Lancet 1996 348: 370 370
Baumgartner I. et al. Constitutive expression of phVEGF165 after intramuscular gene transfer promotes collateral vessel development in patients with critical limb ischemia Circulation 1998 97: 1114 1114
Isner J.M. et al. Treatment of thromboangiitis obliterans (Buerger's disease) by intramuscular gene transfer of vascular endothelial growth factor: preliminary clinical results J Vasc Surg 1998 28: 964 964
Baumgartner I. et al. Lower-extremity edema associated with gene transfer of naked DNA encoding vascular endothelial growth factor Ann Intern Med 2000 132: 880 880
Losordo D.W. et al. Gene therapy for myocardial angiogenesis: initial clinical results with direct myocardial injection of phVEGF165 as sole therapy for myocardial ischemia Circulation 1998 98: 2800 2800
Vale P.R. et al. Left ventricular electromechanical mapping to assess efficacy of phVEGF165 gene transfer for therapeutic angiogenesis in chronic myocardial ischemia Circulation 2000 102: 965 965
Rosengart T.K. et al. Angiogenesis gene therapy: phase 1 assessment of direct intramyocardial administration of an adenovirus vector expressing VEGF121 cDNA to individuals with clinically significant severe coronary artery disease Circulation 1999 100: 468 468
Rosengart T.K. et al. Six-month assessment of a phase 1 trial of angiogenic gene therapy for the treatment of coronary artery disease using direct intramyocardial administration of an adenovirus vector expressing the VEGF121 cDNA Ann Surg 1999 230: 466 466
Taniyama Y. et al. Therapeutic angiogenesis induced by human hepatocyte growth factor gene in rat and rabbit hind limb ischemia models: preclinical study for treatment of peripheral arterial disease Gene Therapy 2000 8: 181 181
Tabata H., Silver M., Isner J.M. . Arterial gene transfer of acidic fibroblast growth factor for therapeutic angiogenesis in vivo: critical role of secretion signal in use of naked DNA Cardiovasc Res 1997 35: 470 470
Ueno H. et al. Adenovirus-mediated expression of the secreted form of basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2) induces cellular proliferation and angiogenesis in vivo Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1997 17: 2453 2453
Takahashi J.C. et al. Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of basic fibroblast growth factor induces in vitro angiogenesis Atherosclerosis 1997 132: 199 199
Vincent K.A. et al. Angiogenesis is induced in a rabbit model of hindlimb ischemia by naked DNA encoding an HIF-1alpha/VP16 hybrid transcription factor Circulation 2000 102: 2255 2255
Giordano F.J. et al. Intracoronary gene transfer of fibroblast growth factor-5 increases blood flow and contractile function in an ischemic region of the heart Nat Med 1996 2: 534 534
Aoki M. et al. Angiogenesis induced by hepatocyte growth factor in non-infarcted myocardium and infarcted myocardium: up-regulation of essential transcription factor for angiogenesis, ets Gene Therapy 2000 7: 417 417
Ueda H. et al. Gene transfection of hepatocyte growth factor attenuates reperfusion injury in the heart Ann Thorac Surg 1999 67: 1726 1726
Safi J. Jr. et al. Adenovirus-mediated acidic fibroblast growth factor gene transfer induces angiogenesis in the nonischemic rabbit heart Microvasc Res 1999 58: 238 238
Schwarz E.R. et al. Evaluation of the effects of intramyocardial injection of DNA expressing vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in a myocardial infarction model in the rat – angiogenesis and angioma formation J Am Coll Cardiol 2000 35: 1323 1323
Lazarous D.F. et al. Adenoviral-mediated gene transfer induces sustained pericardial VEGF expression in dogs: effect on myocardial angiogenesis Cardiovasc Res 1999 44: 294 294
Lee L.Y. et al. Focal angiogen therapy using intramyocardial delivery of an adenovirus vector coding for vascular endothelial growth factor 121 Ann Thorac Surg 2000 69: 14 14
Gowdak L.H. et al. Adenovirus-mediated VEGF(121) gene transfer stimulates angiogenesis in normoperfused skeletal muscle and preserves tissue perfusion after induction of ischemia Circulation 2000 102: 565 565
Varenne O. et al. Percutaneous adenoviral gene transfer into porcine coronary arteries: is catheter-based gene delivery adapted to coronary circulation? Hum Gene Ther 1999 10: 1105 1105
Barr E. et al. Efficient catheter-mediated gene transfer into the heart using replication-defective adenovirus Gene Therapy 1994 1: 51 51
Dzau V.J., Mann M.J., Morishita R., Kaneda Y. . Fusigenic viral liposome for gene therapy in cardiovascular diseases Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996 93: 11421 11421
Marshall E. . Gene therapy death prompts review of adenovirus vector Science 1999 286: 2244 2244
Aoki M. et al. Survival of grafts of genetically modified cardiac myocytes transfected with FITC-labeled oligodeoxynucleotides and β-galactosidase gene in non-infarcted area, but not myocardial infarcted area Gene Therapy 1997 4: 120 120
Tyrrell M.R., Wolfe J.H. . Critical leg ischaemia: an appraisal of clinical definitions. Joint Vascular Research Group Br J Surg 1993 80: 177 177
Eneroth M., Persson B.M. . Amputation for occlusive arterial disease. A prospective multicentre study of 177 amputees Int Orthop 1992 16: 383 383
Dawson I. et al. Late outcomes of limb loss after failed infrainguinal bypass J Vasc Surg 1995 21: 613 613
Losordo D.W. et al. Use of the rabbit ear artery to serially assess foreign protein secretion after site specific arterial gene transfer in vivo: evidence that anatomic identification of successful gene transfer may underestimate the potential magnitude of transgene expression Circulation 1994 89: 785 785
Huber P.E., Pfisterer P. . In vitro and in vivo transfection of plasmid DNA in the Dunning prostate tumor R3327-AT1 is enhanced by focused ultrasound Gene Therapy 2000 7: 1516 1516
Greenleaf W.J. et al. Artificial cavitation nuclei significantly enhance acoustically induced cell transfection Ultrasound Med Biol 1998 24: 587 587
Manome Y., Nakamura M., Ohno T., Furuhata H. . Ultrasound facilitates transduction of naked plasmid DNA into colon carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo Hum Gene Ther 2000 11: 1521 1521
Tachibana K. et al. Induction of cell-membrane porosity by ultrasound Lancet 1999 353: 1409 1409
Lawrie A. et al. Microbubble-enhanced ultrasound for vascular gene delivery Gene Therapy 2000 7: 2023 2023
Tachibana K., Tachibana S. . Albumin microbubble echo-contrast material as an enhancer for ultrasound accelerated thrombolysis Circulation 1995 92: 1148 1148
Podell S. et al. Physical and biochemical stability of Optison, an injectable ultrasound contrast agent Biotechnol Appl Biochem 1999 30: 213 213
Aoki M. et al. Efficient in vivo gene transfer into heart in rat myocardial infarction model using HVJ (hemagglutinating virus of Japan)–liposome method J Mol Cell Cardiol 1997 29: 949 949
Morishita R. et al. Therapeutic angiogenesis induced by human recombinant hepatocyte growth factor in rabbit hind limb ischemia model as ‘cytokine supplement therapy’ Hypertension 1999 33: 1379 1379
Hayashi S. et al. Potential role of hepatocyte growth factor, a novel angiogenic growth factor, in peripheral arterial disease: down-regulation of HGF in response to hypoxia in vascular cells Circulation 1999 100: II301 II301
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by grants from the Japan Health Sciences Foundation, a Grant-in-Aid from The Ministry of Public Health and Welfare, a Grant-in-Aid for the Development of Innovative Technology, a Grant-in-Aid from Japan Promotion of Science, and through Special Coordination Funds of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, the Japanese Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taniyama, Y., Tachibana, K., Hiraoka, K. et al. Development of safe and efficient novel nonviral gene transfer using ultrasound: enhancement of transfection efficiency of naked plasmid DNA in skeletal muscle. Gene Ther 9, 372–380 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301678
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301678
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Enhancement of astaxanthin incorporation by pulsed high-intensity ultrasound in LPS-stimulated macrophages
Journal of Medical Ultrasonics (2022)
-
Ultrasonic microbubble VEGF gene delivery improves angiogenesis of senescent endothelial progenitor cells
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Enhanced effect of recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin by ultrasound irradiation in acute liver failure
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Acoustic Emission-Feedback Planar Ultrasound System for Localized Blood–Brain Barrier Opening Monitoring
Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering (2019)
-
Current therapies and investigational drugs for peripheral arterial disease
Hypertension Research (2016)