Abstract
Objective: The purpose of present study is to investigate small intestinal trehalase activity and the ability to utilize trehalose in healthy Japanese subjects.
Design: First, transitory laxative thresholds of trehalose and lactulose were estimated for each of 20 Japanese female subjects. Then, according to the difference between two relative laxative thresholds, small intestinal trehalase activity was estimated for each individual subject. Trehalose tolerance tests were then carried out on two groups with lower or higher trehalase activity.
Setting: Department of Nutrition, Faculty of Medicine, University of Tokyo.
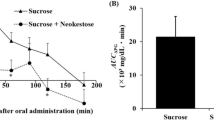
Results: When 30 g of trehalose were administered orally to six subjects with the low trehalase activity, blood glucose and insulin levels scarcely elevated after loading. In contrast, when 50 g of trehalose were administered orally to six subjects with high trehalase activity, blood glucose levels quickly and significantly increased 30 min after loading (P<0.01) and slightly decreased after 60 min, reducing quickly to a fasting level 90 min after loading. Blood insulin levels also peaked 30 min after administration. Yet, decreases in blood insulin levels in the trehalose loading experiment were delayed in comparison with the same amount of glucose ingestion, and peak insulin levels were significantly lower than those with glucose ingestion (P<0.01).
Conclusion: We conclude that subjects with high trehalase activity can effectively utilize trehalose which is ingested from the diet, and when a subject with low trehalase activity ingests a large amount of trehalose, a portion of the trehalose might pass through the small intestine and reach the large intestine where it is fermented completely by colonic bacteria. Therefore, the apparent digestibility of trehalose is similar in both subjects with low and high trehalase activities.
Sponsorship: This study was supported partly by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Basic Area B (no. 10470104) from the Ministry of Education.
European Journal Of Clinical Nutrition (2000) 24, 783–788
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oku, T., Nakamura, S. Estimation of intestinal trehalase activity from a laxative threshold of trehalose and lactulose on healthy female subjects. Eur J Clin Nutr 54, 783–788 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601091
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601091