Abstract
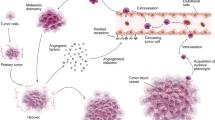
We have shown that a soluble receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor (sVEGFR), which adsorbs VEGF and may function as a dominant-negative receptor, suppresses tumor angiogenesis and enhances apoptosis of cancer cells, thereby inhibiting tumor growth [Cancer Res 60 (2000) 2169–2177]. In the present study, using as many as 11 cancer cell lines, we tested two hypotheses: (a) that a soluble fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 (sFGFR1) might inhibit tumor angiogenesis and growth in sVEGFR-resistant cancers, and (b) that combining sFGFR1 with sVEGFR might produce an enhanced inhibitory effect. In two cell lines derived from human lung cancer, H460 and A549, both of which produce a considerable amount of FGF-2, sVEGFR and a soluble receptor for angiopoietin-1 were both ineffective; however, sFGFR1 inhibited tumor angiogenesis and growth, demonstrating the critical role that FGFs play in some cancers. In three cell lines (QG56 from lung cancer, T3M4 and Panc1 from pancreatic cancer), which produced both VEGF and FGF-2 at detectable levels, combined sVEGFR and sFGFR1 produced an enhanced inhibitory effect compared to their individual effects. The combined usage of sVEGFR plus sFGFR1 suppressed tumor growth in all cancer cell lines tested, suggesting possible effectiveness of this strategy against a wide range of cancers.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saaristo A, Karpanen T, Alitalo K . Mechanisms of angiogenesis and their use in the inhibition of tumor growth and metastasis Oncogene 2000 19: 6122–6129
Folkman J . Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease Nat Med 1995 1: 27–31
Shibuya M . Role of VEGF–flt receptor system in normal and tumor angiogenesis Adv Cancer Res 1995 67: 281–316
Siemeister G, Martiny BG, Marme D . The pivotal role of VEGF in tumor angiogenesis: molecular facts and therapeutic opportunities Cancer Metastasis Rev 1998 17: 241–248
Kendall RL, Wang G, Thomas KA . Identification of a natural soluble form of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor, FLT-1, and its heterodimerization with KDR Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1996 226: 324–328
Takayama K, Ueno H, Nakanishi Y et al. Suppression of tumor angiogenesis and growth by gene transfer of a soluble form of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor into a remote organ Cancer Res 2000 60: 2169–2177
Yamanaka Y, Friess H, Buchler M et al. Overexpression of acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors in human pancreatic cancer correlates with advanced tumor stage Cancer Res 1993 53: 5289–5296
Yamazaki K, Nagao T, Yamaguchi T et al. Expression of basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2)-associated with tumour proliferation in human pancreatic carcinoma Virchows Arch 1997 431: 95–101
Guddo F, Fontanini G, Reina C et al. The expression of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) in tumor-associated stromal cells and vessels is inversely correlated with non-small cell lung cancer progression Hum Pathol 1999 30: 788–794
Lin P, Sankar S, Shan S et al. Inhibition of tumor growth by targeting tumor endothelium using a soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Cell Growth Differ 1998 9: 49–58
Kong H-L, Hecht D, Song W et al. Regional suppression of tumor growth by in vivo transfer of a cDNA encoding a secreted form of the extracellular domain of the flt-1 vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Hum Gene Ther 1998 9: 823–833
Ueno H, Gunn M, Dell K et al. A truncated form of FGF receptor 1 inhibits signal transduction by multiple types of FGF receptor J Biol Chem 1992 267: 1470–1476
Zimmer Y, Givol D, Yayon A . Multiple structural elements determine ligand binding of fibroblast growth factor receptors. Evidence that both Ig domain 2 and 3 define receptor specificity J Biol Chem 1993 268: 7899–7903
Ueno H, Li J-J, Tomita H et al. Quantitative analysis of repeated adenovirus-mediated gene transfer into injured canine femoral arteries Arterioscler, Thromb, Vasc Biol 1995 15: 2246–2253
Ueno H, Li J-J, Masuda S et al. Adenovirus-mediated expression of the secreted form of basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2) induces cellular proliferation and angiogenesis in vivo Arterioscler, Thromb, Vasc Biol 1997 17: 2453–2460
Miyake S, Makimura M, Kanegae Y et al. Efficient generation of recombinant adenoviruses using adenovirus DNA-terminal protein complex and a cosmid bearing the full-length virus genome Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996 93: 1320–1324
Niwa H, Yamamura K, Miyazaki J . Efficient selection for high-expression transfectants with a novel eukaryotic vector Gene 1991 108: 193–199
Johnson DE, Williams LT . Structural and functional diversity in the FGF receptor multigene family Adv Cancer Res 1993 60: 1–40
Takakura N, Huang XL, Naruse T et al. Critical role of the TIE2 endothelial cell receptor in the development of definitive hematopoiesis Immunity 1998 9: 677–686
Takayama K, Ueno H, Pei XH et al. The levels of integrin α v β 5 may predict the susceptibility to adenovirus-mediated gene transfer in human lung cancer cells Gene Ther 1998 5: 361–368
Majima M, Hayashi I, Muramatsu M et al. Cyclo-oxygenase-2 enhances basic fibroblast growth factor–induced angiogenesis through induction of vascular endothelial growth factor in rat sponge implants Br J Pharmacol 2000 130: 641–649
Takahashi JA, Fukumoto M, Kozai Y et al. Inhibition of cell growth and tumorigenesis of human glioblastoma cells by a neutralizing antibody against human basic fibroblast growth factor FEBS Lett 1991 288: 65–71
Ogasawara S, Yano H, Iemura A et al. Expressions of basic fibroblast growth factor and its receptors and their relationship to proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines Hepatology 1996 24: 198–205
Ensoli B, Markham P, Kao V et al. Block of AIDS–Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) cell growth, angiogenesis, and lesion formation in nude mice by antisense oligonucleotide targeting basic fibroblast growth factor. A novel strategy for the therapy of KS J Clin Invest 1994 94: 1736–1746
Maret A, Galy B, Arnaud E et al. Inhibition of fibroblast growth factor 2 expression by antisense RNA induced a loss of the transformed phenotype in a human hepatoma cell line Cancer Res 1995 55: 5075–5079
Wang Y, Becker D . Antisense targeting of basic fibroblast growth factor and fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 in human melanomas blocks intratumoral angiogenesis and tumor growth Nat Med 1997 3: 887–893
Bagheri-Yarmand R, Kourbali Y, Mabilat C et al. The suppression of fibroblast growth factor 2/fibroblast growth factor 4–dependent tumour angiogenesis and growth by the anti-growth factor activity of dextran derivative (CMDB7) Br J Cancer 1998 78: 111–118
Westphal JR, Van't Hullenaar R, Peek R et al. Angiogenic balance in human melanoma: expression of VEGF, bFGF, IL-8, PDGF and angiostatin in relation to vascular density of xenografts in vivo Int J Cancer 2000 86: 768–776
Eggert A, Ikegaki N, Kwiatkowski J et al. High-level expression of angiogenic factors is associated with advanced tumor stage in human neuroblastomas Clin Cancer Res 2000 6: 1900–1908
Volm M, Koomagi R, Mattern J . PD-ECGF, bFGF, and VEGF expression in non-small cell lung carcinomas and their association with lymph node metastasis Anticancer Res 1999 19: 651–655
Schmidt NO, Westphal M, Hagel C et al. Levels of vascular endothelial growth factor, hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in human gliomas and their relation to angiogenesis Int J Cancer 1999 84: 10–18
Pepper MS, Ferrara N, Orci L et al. Potent synergism between vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in the induction of angiogenesis in vitro Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1992 189: 824–831
Pepper MS, Mandriota SJ, Jeltsch M et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C synergizes with basic fibroblast growth factor and VEGF in the induction of angiogenesis in vitro and alters endothelial cell extracellular proteolytic activity J Cell Physiol 1998 177: 439–452
Pepper MS, Mandriota SJ . Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (Flk-1) expression in vascular endothelial cells Exp Cell Res 1998 241: 414–425
Saadeh PB, Mehrara BJ, Steinbrech DS et al. Mechanisms of fibroblast growth factor-2 modulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression by osteoblastic cells Endocrinology 2000 141: 2075–2083
Guerrin M, Scotet E, Malecaze F et al. Overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor induces cell transformation in cooperation with fibroblast growth factor 2 Oncogene 1997 14: 463–471
Hanahan D . Heritable formation of pancreatic β-cell tumours in transgenic mice expressing recombinant insulin/simian virus 40 oncogenes Nature 1985 315: 115–122
Compagni A, Wilgenbus P, Impagnatiello MA et al. Fibroblast growth factors are required for efficient tumor angiogenesis Cancer Res 2000 60: 7163–7169
Bergers G, Brekken R, McMahon G et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 triggers the angiogenic switch during carcinogenesis Nat Cell Biol 2000 2: 737–744
Parsons-Wingerter P, Elliott KE, Clark JI et al. Fibroblast growth factor-2 selectively stimulates angiogenesis of small vessels in arterial tree Arterioscler, Thromb, Vasc Biol 2000 20: 1250–1256
Zhou M, Sutliff RL, Paul RJ et al. Fibroblast growth factor 2 control of vascular tone Nat Med 1998 4: 201–207
Ortega S, Ittmann M, Tsang SH et al. Neuronal defects and delayed wound healing in mice lacking fibroblast growth factor 2 Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998 95: 5672–5677
Ferrara N, Carver-Moore K, Chen H et al. Heterozygous embryonic lethality induced by targeted inactivation of the VEGF gene Nature 1996 380: 439–442
Yoshida A, Anand-Apte B, Zetter BR . Differential endothelial migration and proliferation to basic fibroblast growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor Growth Factors 1996 13: 57–64
Gross JL, Herblin WF, Dusak BA et al. Effects of modulation of basic fibroblast growth factor on tumor growth in vivo J Natl Cancer Inst 1993 85: 121–131
Saiki M, Mima T, Takahashi JC et al. Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of a truncated form of fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibits growth of glioma cells both in vitro and in vivo J Neuro-Oncol 1999 44: 195–203
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports Science, and Technology, and by grants from Fukuoka Cancer Society, Mitsukoshi Medical Foundation, YASUDA Medical Research Foundation, and the Princess Takamatsu Cancer Research Fund (00-23202) (to HU).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogawa, T., Takayama, K., Takakura, N. et al. Anti-tumor angiogenesis therapy using soluble receptors: enhanced inhibition of tumor growth when soluble fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 is used with soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor. Cancer Gene Ther 9, 633–640 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700478
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700478
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Markers of pancreatic cancer stem cells and their clinical and therapeutic implications
Molecular Biology Reports (2019)
-
Angiosarcome du sein : à propos de deux cas
Journal Africain du Cancer / African Journal of Cancer (2011)
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFR) as possible therapeutic targets in human non-small cell lung cancer
memo - Magazine of European Medical Oncology (2010)
-
A phase II study evaluating bevacizumab in combination with fixed-dose rate gemcitabine and low-dose cisplatin for metastatic pancreatic cancer: is an anti-VEGF strategy still applicable?
Investigational New Drugs (2008)
-
Evaluation of the fibroblast growth factor system as a potential target for therapy in human prostate cancer
British Journal of Cancer (2005)