Abstract
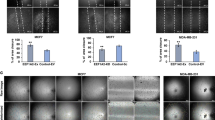
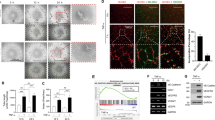
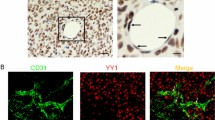
Recently, we found that mutation of the C-terminus of transcription factor hexamethylene bisacetamide-inducible protein 1 (HEXIM1) in mice leads to abnormalities in cardiovascular development because of aberrant vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression. HEXIM1 regulation of some genes has also been shown to be positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) dependent. However, it is not known whether HEXIM1 regulates VEGF in the mammary gland. We demonstrate that HEXIM1 regulates estrogen-induced VEGF transcription through inhibition of estrogen receptor-α recruitment to the VEGF promoter in a P-TEFb-independent manner in MCF-7 cells. Under hypoxic conditions, HEXIM1 inhibits estrogen-induced hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α) protein expression and recruitment of HIF-1α to the hypoxia-response element in the VEGF promoter. In the mouse mammary gland, increased HEXIM1 expression decreased estrogen-driven VEGF and HIF-1α expression. Conversely, a mutation in the C-terminus of HEXIM1 (HEXIM11−312) led to increased VEGF and HIF-1α expression and vascularization in mammary glands of heterozygous HEXIM11−312 mice when compared with their wild-type littermates. In addition, HEXIM11−312 mice have a higher incidence of carcinogen-induced mammary tumors with increased vascularization, suggesting an inhibitory role for HEXIM1 during angiogenesis. Taken together, our data provide evidence to suggest a novel role for HEXIM1 in cancer progression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bogin L, Degani H . (2002). Hormonal regulation of VEGF in orthotopic MCF7 human breast cancer. Cancer Res 62: 1948–1951.
Bos R, van Diest PJ, van der Groep P, Shvarts A, Greijer AE, van der Wall E . (2004). Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and cell cycle proteins in invasive breast cancer are estrogen receptor related. Breast Cancer Res 6: R450–R459.
Buteau-Lozano H, Ancelin M, Lardeux B, Milanini J, Perrot-Applanat M . (2002). Transcriptional regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor by estradiol and tamoxifen in breast cancer cells: a complex interplay between estrogen receptors alpha and beta. Cancer Res 62: 4977–4984.
Cho J, Kim D, Lee S, Lee Y . (2005). Cobalt chloride-induced estrogen receptor alpha down-regulation involves hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol 19: 1191–1199.
Deroo BJ, Korach KS . (2006). Estrogen receptors and human disease. J Clin Invest 116: 561–570.
Ellis LM, Hicklin DJ . (2008). VEGF-targeted therapy: mechanisms of anti-tumour activity. Nat Rev Cancer 8: 579–591.
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J . (2003). The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med 9: 669–676.
Garvin S, Nilsson UW, Dabrosin C . (2005). Effects of oestradiol and tamoxifen on VEGF, soluble VEGFR-1, and VEGFR-2 in breast cancer and endothelial cells. Br J Cancer 93: 1005–1010.
Higgins KJ, Liu S, Abdelrahim M, Yoon K, Vanderlaag K, Porter W et al. (2006). Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 expression is induced by 17beta-estradiol in ZR-75 breast cancer cells by estrogen receptor alpha/Sp proteins. Endocrinology 147: 3285–3295.
Hyder SM . (2006). Sex-steroid regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 13: 667–687.
Kawai H, Li H, Chun P, Avraham S, Avraham HK . (2002). Direct interaction between BRCA1 and the estrogen receptor regulates vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) transcription and secretion in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 21: 7730–7739.
Kazi AA, Jones JM, Koos RD . (2005). Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis of gene expression in the rat uterus in vivo: estrogen-induced recruitment of both estrogen receptor alpha and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 to the vascular endothelial growth factor promoter. Mol Endocrinol 19: 2006–2019.
Kazi AA, Koos RD . (2007). Estrogen-induced activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, vascular endothelial growth factor expression, and edema in the uterus are mediated by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Endocrinology 148: 2363–2374.
Kazi AA, Molitoris KH, Koos RD . (2009). Estrogen rapidly activates the PI3K/AKT pathway and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and induces vascular endothelial growth factor A expression in luminal epithelial cells of the rat uterus. Biol Reprod 81: 378–387.
Kimbro KS, Simons JW . (2006). Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in human breast and prostate cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 13: 739–749.
Kushner PJ, Agard DA, Greene GL, Scanlan TS, Shiau AK, Uht RM et al. (2000). Estrogen receptor pathways to AP-1. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 74: 311–317.
Li B, Kittrell FS, Medina D, Rosen JM . (1995). Delay of dimethylbenz[a]anthracene-induced mammary tumorigenesis in transgenic mice by apoptosis induced by an unusual mutant p53 protein. Mol Carcinog 14: 75–83.
Liao D, Corle C, Seagroves TN, Johnson RS . (2007). Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha is a key regulator of metastasis in a transgenic model of cancer initiation and progression. Cancer Res 67: 563–572.
Lydon JP, Ge G, Kittrell FS, Medina D, O'Malley BW . (1999). Murine mammary gland carcinogenesis is critically dependent on progesterone receptor function. Cancer Res 59: 4276–4284.
Maity A, Sall W, Koch CJ, Oprysko PR, Evans SM . (2001). Low pO2 and beta-estradiol induce VEGF in MCF-7 and MCF-7-5C cells: relationship to in vivo hypoxia. Breast Cancer Res Treat 67: 51–60.
Molitoris KH, Kazi AA, Koos RD . (2009). Inhibition of oxygen-induced hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha degradation unmasks estradiol induction of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in ECC-1 cancer cells in vitro. Endocrinology 150: 5405–5414.
Montano MM, Doughman YQ, Deng H, Chaplin L, Yang J, Wang N et al. (2008). Mutation of the HEXIM1 gene results in defects during heart and vascular development partly through downregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor. Circ Res 102: 415–422.
Ogba N, Chaplin LJ, Doughman YQ, Fujinaga K, Montano MM . (2008). HEXIM1 regulates 17beta-estradiol/estrogen receptor-alpha-mediated expression of cyclin D1 in mammary cells via modulation of P-TEFb. Cancer Res 68: 7015–7024.
Rossiter H, Barresi C, Ghannadan M, Gruber F, Mildner M, Fodinger D et al. (2007). Inactivation of VEGF in mammary gland epithelium severely compromises mammary gland development and function. FASEB J 21: 3994–4004.
Rugo HS . (2004). Bevacizumab in the treatment of breast cancer: rationale and current data. Oncologist 9 (Suppl 1): 43–49.
Seifeddine R, Dreiem A, Tomkiewicz C, Fulchignoni-Lataud MC, Brito I, Danan JL et al. (2007). Hypoxia and estrogen co-operate to regulate gene expression in T-47D human breast cancer cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 104: 169–179.
Shimizu N, Ouchida R, Yoshikawa N, Hisada T, Watanabe H, Okamoto K et al. (2005). HEXIM1 forms a transcriptionally abortive complex with glucocorticoid receptor without involving 7SK RNA and positive transcription elongation factor b. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 8555–8560.
Sims 3rd RJ, Belotserkovskaya R, Reinberg D . (2004). Elongation by RNA polymerase II: the short and long of it. Genes Dev 18: 2437–2468.
Stoner M, Wormke M, Saville B, Samudio I, Qin C, Abdelrahim M et al. (2004). Estrogen regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor gene expression in ZR-75 breast cancer cells through interaction of estrogen receptor alpha and SP proteins. Oncogene 23: 1052–1063.
Wittmann BM, Fujinaga K, Deng H, Ogba N, Montano MM . (2005). The breast cell growth inhibitor, estrogen down regulated gene 1, modulates a novel functional interaction between estrogen receptor alpha and transcriptional elongation factor cyclin T1. Oncogene 24: 5576–5588.
Wittmann BM, Wang N, Montano MM . (2003). Identification of a novel inhibitor of breast cell growth that is down-regulated by estrogens and decreased in breast tumors. Cancer Res 63: 5151–5158.
Woodfin A, Voisin MB, Nourshargh S . (2007). PECAM-1: a multi-functional molecule in inflammation and vascular biology. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27: 2514–2523.
Zhou Q, Yik JH . (2006). The Yin and Yang of P-TEFb regulation: implications for human immunodeficiency virus gene expression and global control of cell growth and differentiation. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 70: 646–659.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs Anthony J Berdis and Jay Prendergast for reagents and their help with kinase and ELISA assays. This work was supported by the National Institute of Health Grant CA92440 and the American Heart Association Grant to MMM and a Department of Defense predoctoral Fellowship W81XWH-06-1-0426 to NO.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogba, N., Doughman, Y., Chaplin, L. et al. HEXIM1 modulates vascular endothelial growth factor expression and function in breast epithelial cells and mammary gland. Oncogene 29, 3639–3649 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.110
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.110
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Non-epigenetic induction of HEXIM1 by DNMT1 inhibitors and functional relevance
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Inhibition of the histone demethylase, KDM5B, directly induces re-expression of tumor suppressor protein HEXIM1 in cancer cells
Breast Cancer Research (2019)
-
Inhibition of metastasis by HEXIM1 through effects on cell invasion and angiogenesis
Oncogene (2013)
-
The Mammary Gland Vasculature Revisited
Journal of Mammary Gland Biology and Neoplasia (2010)