Abstract
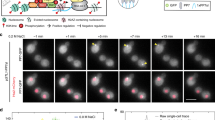
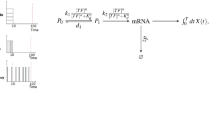
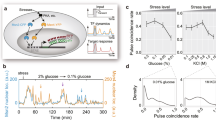
Information about environmental stimuli is often transmitted using common signaling molecules, but the mechanisms that ensure signaling specificity are not entirely known. Here we show that the identities and intensities of different stresses are transmitted by modulation of the amplitude, duration or frequency of nuclear translocation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae general stress response transcription factor Msn2. Through artificial control of the dynamics of Msn2 translocation, we reveal how distinct dynamical schemes differentially affect reporter gene expression. Using a simple model, we predict stress-induced reporter gene expression from single-cell translocation dynamics. We then demonstrate that the response of natural target genes to dynamical modulation of Msn2 translocation is influenced by differences in the kinetics of promoter transitions and transcription factor binding properties. Thus, multiple environmental signals can trigger qualitatively different dynamics of a single transcription factor and influence gene expression patterns.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Shaywitz, A.J. & Greenberg, M.E. CREB: a stimulus-induced transcription factor activated by a diverse array of extracellular signals. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 68, 821–861 (1999).
Hao, N., Zeng, Y., Elston, T.C. & Dohlman, H.G. Control of MAPK specificity by feedback phosphorylation of shared adaptor protein Ste50. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 33798–33802 (2008).
Skalhegg, B.S. & Tasken, K. Specificity in the cAMP/PKA signaling pathway. Differential expression, regulation, and subcellular localization of subunits of PKA. Front. Biosci. 5, D678–D693 (2000).
Behar, M. & Hoffmann, A. Understanding the temporal codes of intra-cellular signals. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 20, 684–693 (2010).
Hoffmann, A., Levchenko, A., Scott, M.L. & Baltimore, D. The IkappaB-NF-kappaB signaling module: temporal control and selective gene activation. Science 298, 1241–1245 (2002).
Lee, T.K. et al. A noisy paracrine signal determines the cellular NF-kappaB response to lipopolysaccharide. Sci. Signal. 2, ra65 (2009).
Ashall, L. et al. Pulsatile stimulation determines timing and specificity of NF-kappaB-dependent transcription. Science 324, 242–246 (2009).
Tay, S. et al. Single-cell NF-kappaB dynamics reveal digital activation and analogue information processing. Nature 466, 267–271 (2010).
Cai, L., Dalal, C.K. & Elowitz, M.B. Frequency-modulated nuclear localization bursts coordinate gene regulation. Nature 455, 485–490 (2008).
Martínez-Pastor, M.T. et al. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae zinc finger proteins Msn2p and Msn4p are required for transcriptional induction through the stress response element (STRE). EMBO J. 15, 2227–2235 (1996).
Schmitt, A.P. & McEntee, K. Msn2p, a zinc finger DNA-binding protein, is the transcriptional activator of the multistress response in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 5777–5782 (1996).
Görner, W. et al. Nuclear localization of the C2H2 zinc finger protein Msn2p is regulated by stress and protein kinase A activity. Genes Dev. 12, 586–597 (1998).
Görner, W. et al. Acute glucose starvation activates the nuclear localization signal of a stress-specific yeast transcription factor. EMBO J. 21, 135–144 (2002).
Hersen, P., McClean, M.N., Mahadevan, L. & Ramanathan, S. Signal processing by the HOG MAP kinase pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 7165–7170 (2008).
Jacquet, M., Renault, G., Lallet, S., De Mey, J. & Goldbeter, A. Oscillatory nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of the general stress response transcriptional activators Msn2 and Msn4 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Cell Biol. 161, 497–505 (2003).
Medvedik, O., Lamming, D.W., Kim, K.D. & Sinclair, D.A. MSN2 and MSN4 link calorie restriction and TOR to sirtuin-mediated lifespan extension in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS Biol. 5, e261 (2007).
Bishop, A.C. et al. A chemical switch for inhibitor-sensitive alleles of any protein kinase. Nature 407, 395–401 (2000).
Sheff, M.A. & Thorn, K.S. Optimized cassettes for fluorescent protein tagging in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 21, 661–670 (2004).
Shenton, D. et al. Global translational responses to oxidative stress impact upon multiple levels of protein synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 29011–29021 (2006).
Kim, H.D. & O'Shea, E.K. A quantitative model of transcription factor-activated gene expression. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 15, 1192–1198 (2008).
Jessen, W.J., Hoose, S.A., Kilgore, J.A. & Kladde, M.P. Active PHO5 chromatin encompasses variable numbers of nucleosomes at individual promoters. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 13, 256–263 (2006).
Lam, F.H., Steger, D.J. & O'Shea, E.K. Chromatin decouples promoter threshold from dynamic range. Nature 453, 246–250 (2008).
Marshall, C.J. Specificity of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling: transient versus sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Cell 80, 179–185 (1995).
Giorgetti, L. et al. Noncooperative interactions between transcription factors and clustered DNA binding sites enable graded transcriptional responses to environmental inputs. Mol. Cell 37, 418–428 (2010).
Geva-Zatorsky, N. et al. Oscillations and variability in the p53 system. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2, 2006.0033 (2006).
Loewer, A., Batchelor, E., Gaglia, G. & Lahav, G. Basal dynamics of p53 reveal transcriptionally attenuated pulses in cycling cells. Cell 142, 89–100 (2010).
Werner, S.L., Barken, D. & Hoffmann, A. Stimulus specificity of gene expression programs determined by temporal control of IKK activity. Science 309, 1857–1861 (2005).
Hao, N. et al. Regulation of cell signaling dynamics by the protein kinase-scaffold Ste5. Mol. Cell 30, 649–656 (2008).
Capaldi, A.P. et al. Structure and function of a transcriptional network activated by the MAPK Hog1. Nat. Genet. 40, 1300–1306 (2008).
Zhou, X. & O'Shea, E.K. Integrated approaches reveal determinants of genome-wide binding and function of the transcription factor Pho4. Mol. Cell 42, 826–836 (2011).
Gasch, A.P. et al. Genomic expression programs in the response of yeast cells to environmental changes. Mol. Biol. Cell 11, 4241–4257 (2000).
Acknowledgements
We thank S. Ramanathan for help with the microfluidics devices. We thank P. Cluzel, V. Denic, G. Lahav, M. Springer, B. Stern, H. Dohlman, T. Elston and M. Behar for critical comments on the manuscript. We thank X. Zhou in the O'Shea lab for generously providing the unpublished nucleosome profile data, M. Rust and S. Mukherji for insightful suggestions, and other members of the O'Shea lab for helpful discussions. E.K.O. is a Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N.H. and E.K.O. designed the project. N.H. carried out the experiments and analyzed the data. N.H. and E.K.O. wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–15, Supplementary Results and Supplementary Methods (PDF 6869 kb)
Supplementary Video 1
Time-lapse video of Msn2-YFP in response to 0.1% glucose limitation. (MP4 3256 kb)
Supplementary Video 2
Time-lapse video of Msn2-YFP in response to 0.375 M KCl. (MP4 3297 kb)
Supplementary Video 3
Time-lapse video of Msn2-YFP in response to 0.01 mM H2O2. (MP4 2853 kb)
Supplementary Video 4
Time-lapse video of Msn2-YFP in response to oscillatory 1-NM-PP1 treatment. (MP4 1837 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, N., O'Shea, E. Signal-dependent dynamics of transcription factor translocation controls gene expression. Nat Struct Mol Biol 19, 31–39 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2192
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2192
This article is cited by
-
FOXO transcription factors as mediators of stress adaptation
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2024)
-
Optogenetic control of YAP reveals a dynamic communication code for stem cell fate and proliferation
Nature Communications (2023)
-
BioNetGMMFit: estimating parameters of a BioNetGen model from time-stamped snapshots of single cells
npj Systems Biology and Applications (2023)
-
Modulation of transcription factor dynamics allows versatile information transmission
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Frequency modulation of a bacterial quorum sensing response
Nature Communications (2022)