Abstract
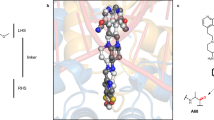
Quinolone antibacterials have been used to treat bacterial infections for over 40 years. A crystal structure of moxifloxacin in complex with Acinetobacter baumannii topoisomerase IV now shows the wedge-shaped quinolone stacking between base pairs at the DNA cleavage site and binding conserved residues in the DNA cleavage domain through chelation of a noncatalytic magnesium ion. This provides a molecular basis for the quinolone inhibition mechanism, resistance mutations and invariant quinolone antibacterial structural features.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boucher, H.W. et al. Clin. Infect. Dis. 48, 1–12 (2009).
Payne, D.J., Gwynn, M.N., Holmes, D.J. & Pompliano, D.L. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 6, 29–40 (2007).
Hooper, D.C. in Quinolone Antimicrobial Agents 3rd edn. (eds. Hooper, D.C. & Rubinstein, E.) 41–67 (ASM Press, Washington, USA, 2003).
Bax, B.D. et al. Nature doi:10.1038/nature09197, published online 04 August 2010.
Dong, K.C. & Berger, J.M. Nature 450, 1201–1205 (2007).
Laponogov, I. et al. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 16, 667–669 (2009).
Bock, C.W., Katz, A.K., Markham, G.D. & Glusker, J.P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121, 7360–7372 (1999).
Drevensek, P. et al. J. Inorg. Biochem. 100, 1755–1763 (2006).
Sissi, C. et al. J. Mol. Biol. 311, 195–203 (2001).
Mitscher, L.A. Chem. Rev. 105, 559–592 (2005).
Richter, S.N. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, 6075–6085 (2007).
Yoshida, H., Bogaki, M., Nakamura, M., Yamanaka, L.M. & Nakamura, S. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 35, 1647–1650 (1991).
Laponogov et al. PloS ONE 5, e11388 (2010).
Acknowledgements
We thank D. Payne for discussions. A.W. was funded and supported by the Wellcome Trust Seeding Drug Discovery Initiative and contract HDTRA1-07-9-0002 with the US Department of Defense Joint Science and Technology Office for Chemical and Biological Defense and the Defense Threat Reduction Agency's Transformational Medical Technologies. The views expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the US Department of Defense or the US Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.D.B. and M.N.G. designed experiments; A.P.F., P.H., V.R.L., R.L.P. and A.J.S. cloned, expressed and isolated ParE28–ParC58; P.F.C. and J.H. performed enzyme assays; A.W. crystallized the complex, and A.W. and B.D.B. determined its structure; T.J.M. and N.D.P. interpreted SAR; M.K. ran ab initio calculations and analyzed structures from the CSD; A.W., B.D.B. and M.N.G. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Table 1, Supplementary Figures 1–11 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 2561 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wohlkonig, A., Chan, P., Fosberry, A. et al. Structural basis of quinolone inhibition of type IIA topoisomerases and target-mediated resistance. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17, 1152–1153 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1892
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1892