Abstract
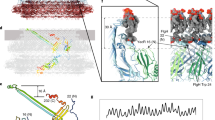
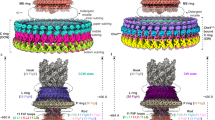
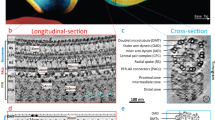
Outer and inner dynein arms generate force for the flagellar/ciliary bending motion. Although nucleotide-induced structural change of dynein heavy chains (the ATP-driven motor) was proven in vitro, our lack of knowledge in situ has precluded an understanding of the bending mechanism. Here we reveal nucleotide-induced global structural changes of the outer and inner dynein arms of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii flagella in situ using electron cryotomography. The ATPase domains of the dynein heavy chains move toward the distal end, and the N-terminal tail bends sharply during product release. This motion could drive the adjacent microtubule to cause a sliding motion. In contrast to in vitro results, in the presence of nucleotides, outer dynein arms coexist as clusters of apo or nucleotide-bound forms in situ. This implies a cooperative switching, which may be related to the mechanism of bending.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goodenough, U.W. & Heuser, J. Substructure of inner dynein arms, radial spokes, and the central pair/projection complex of cilia and flagella. J. Cell Biol. 100, 2008–2018 (1985).
Piperno, G., Ramanis, Z., Smith, E.F. & Sale, W.S. Three distinct inner dynein arms in Chlamydomonas flagella: molecular composition and location in the axoneme. J. Cell Biol. 110, 379–389 (1990).
Porter, M.E. Axonemal dyneins: assembly, organization, and regulation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 8, 10–17 (1996).
Kamiya, R. Functional diversity of axonemal dyneins as studied in Chlamydomonas mutants. Int. Rev. Cytol. 219, 115–155 (2002).
Bui, K.H., Sakakibara, H., Movassagh, T., Oiwa, K. & Ishikawa, T. Molecular architecture of inner dynein arms in situ in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii flagella. J. Cell Biol. 183, 923–932 (2008).
Fliegauf, M. et al. Mislocalization of DNAH5 and DNAH9 in respiratory cells from patients with primary ciliary dyskinesia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 171, 1343–1349 (2005).
Neuwald, A.F., Aravind, L., Spouge, J.L. & Koonin, E.V. AAA+: a class of chaperone-like ATPases associated with the assembly, operation, and disassembly of protein complexes. Genome Res. 9, 27–43 (1999).
Johnson, K.A. Pathway of the microtubule-dynein ATPase and the structure of dynein: a comparison with actomyosin. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 14, 161–188 (1985).
Burgess, S.A., Walker, M.L., Sakakibara, H., Knight, P.J. & Oiwa, K. Dynein structure and power stroke. Nature 421, 715–718 (2003).
Ishikawa, T., Sakakibara, H. & Oiwa, K. The architecture of outer dynein arms in situ. J. Mol. Biol. 368, 1249–1258 (2007).
Lupetti, P. et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction of axonemal outer dynein arms in situ by electron tomography. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 62, 69–83 (2005).
Nicastro, D. et al. The molecular architecture of axonemes revealed by cryoelectron tomography. Science 313, 944–948 (2006).
Porter, M.E., Knott, J.A., Myster, S.H. & Farlow, S.J. The dynein gene family in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Genetics 144, 569–585 (1996).
Ueno, H., Yasunaga, T., Shingyoji, C. & Hirose, K. Dynein pulls microtubules without rotating its stalk. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 19702–19707 (2008).
Burgess, S.A., Walker, M.L., Sakakibara, H., Oiwa, K. & Knight, P.J. The structure of dynein-c by negative stain electron microscopy. J. Struct. Biol. 146, 205–216 (2004).
Carter, A.P. et al. Structure and functional role of dynein′s microtubule-binding domain. Science 322, 1691–1695 (2008).
Gibbons, B.H. & Gibbons, I.R. Properties of flagellar “rigor waves” formed by abrupt removal of adenosine triphosphate from actively swimming sea urchin sperm. J. Cell Biol. 63, 970–985 (1974).
Bui, K.H., Sakakibara, H., Movassagh, T., Oiwa, K. & Ishikawa, T. Asymmetry of inner dynein arms and inter-doublet links in Chlamydomonas flagella. J. Cell Biol. 186, 437–446 (2009).
Roberts, A.J. et al. AAA+ ring and linker swing mechanism in the dynein motor. Cell 136, 485–495 (2009).
Gibbons, I.R. Dynein family of motor proteins: present status and future questions. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 32, 136–144 (1995).
Sakato, M., Sakakibara, H. & King, S.M. Chlamydomonas outer arm dynein alters conformation in response to Ca2+. Mol. Biol. Cell 18, 3620–3634 (2007).
Furuta, A., Yagi, T., Yanagisawa, H.A., Higuchi, H. & Kamiya, R. Systematic comparison of in vitro motile properties between Chlamydomonas wild-type and mutant outer arm dyneins each lacking one of the three heavy chains. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 5927–5935 (2009).
Goodenough, U.W. & Heuser, J.E. Substructure of the outer dynein arm. J. Cell Biol. 95, 798–815 (1982).
Kon, T., Mogami, T., Ohkura, R., Nishiura, M. & Sutoh, K. ATP hydrolysis cycle-dependent tail motions in cytoplasmic dynein. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 12, 513–519 (2005).
Hook, P. et al. Long range allosteric control of cytoplasmic dynein ATPase activity by the stalk and C-terminal domains. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 33045–33054 (2005).
Inoue, Y. & Shingyoji, C. The roles of noncatalytic ATP binding and ADP binding in the regulation of dynein motile activity in flagella. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 64, 690–704 (2007).
Takahashi, Y., Edamatsu, M. & Toyoshima, Y.Y. Multiple ATP-hydrolyzing sites that potentially function in cytoplasmic dynein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 12865–12869 (2004).
Holzbaur, E.L. & Johnson, K.A. ADP release is rate limiting in steady-state turnover by the dynein adenosinetriphosphatase. Biochemistry 28, 5577–5585 (1989).
Holzbaur, E.L. & Johnson, K.A. Microtubules accelerate ADP release by dynein. Biochemistry 28, 7010–7016 (1989).
Warner, F.D. & McIlvain, J.H. Kinetic properties of microtubule-activated 13 S and 21 S dynein ATPases. Evidence for allosteric behaviour associated with the inner row and outer row dynein arms. J. Cell Sci. 83, 251–267 (1986).
Seetharam, R.N. & Satir, P. Coordination of outer arm dynein activity along axonemal doublet microtubules. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 65, 572–580 (2008).
Haimo, L.T. & Rosenbaum, J.L. Dynein binding to microtubules containing microtubule-associated proteins. Cell Motil. 1, 499–515 (1981).
Moss, A.G., Sale, W.S., Fox, L.A. & Witman, G.B. The alpha subunit of sea urchin sperm outer arm dynein mediates structural and rigor binding to microtubules. J. Cell Biol. 118, 1189–1200 (1992).
Burgess, S.A. Rigor and relaxed outer dynein arms in replicas of cryofixed motile flagella. J. Mol. Biol. 250, 52–63 (1995).
Mallik, R., Carter, B.C., Lex, S.A., King, S.J. & Gross, S.P. Cytoplasmic dynein functions as a gear in response to load. Nature 427, 649–652 (2004).
Ishikawa, R. & Shingyoji, C. Induction of beating by imposed bending or mechanical pulse in demembranated, motionless sea urchin sperm flagella at very low ATP concentrations. Cell Struct. Funct. 32, 17–27 (2007).
Gorman, D.S. & Levine, R.P. Cytochrome f and plastocyanin: their sequence in the photosynthetic electron transport chain of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 54, 1665–1669 (1965).
Witman, G.B. Isolation of Chlamydomonas flagella and flagellar axonemes. Methods Enzymol. 134, 280–290 (1986).
Striebel, F. et al. Bacterial ubiquitin-like modifier Pup is deamidated and conjugated to substrates by distinct but homologous enzymes. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 16, 647–651 (2009).
Kremer, J.R., Mastronarde, D.N. & McIntosh, J.R. Computer visualization of three-dimensional image data using IMOD. J. Struct. Biol. 116, 71–76 (1996).
Mastronarde, D.N. Dual-axis tomography: an approach with alignment methods that preserve resolution. J. Struct. Biol. 120, 343–352 (1997).
Heymann, J.B. Bsoft: image and molecular processing in electron microscopy. J. Struct. Biol. 133, 156–169 (2001).
Frank, J. et al. SPIDER and WEB: processing and visualization of images in 3D electron microscopy and related fields. J. Struct. Biol. 116, 190–199 (1996).
Nickell, S. et al. TOM software toolbox: acquisition and analysis for electron tomography. J. Struct. Biol. 149, 227–234 (2005).
Bostina, M. et al. Single particle cryoelectron tomography characterization of the structure and structural variability of poliovirus-receptor-membrane complex at 30 Å resolution. J. Struct. Biol. 160, 200–210 (2007).
Pettersen, E.F. et al. UCSF Chimera - a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 25, 1605–1612 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We thank T.J. Richmond for the biochemical facility, D. Sargent and F. Damberger for critical reading of the manuscript, R. Wepf, P. Tittmann and F. Stribel for technical support, J.A. Parian for support on graphics, V.H. Bui for statistical calculation and S. Burgess for insightful discussion. This work was funded by grants from the Swiss National Science Foundation (NF3100A0-107540 and NF31003A-125131/1), a Swiss-Japan cooperative grant and NCCR Structural Biology to T.I., by Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology (16083207 to K.O.) and a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on the Priority Area “Regulation of Nano-systems in Cells” by the Japan Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (K.O.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.I. designed experiments; T.M. and H.S. prepared specimens and performed biochemical experiments; T.M. collected tomography data; K.H.B. developed algorithms of image alignment and classification and made programs; T.M. and K.H.B. performed image analysis of ODAs and IDAs, respectively; the mechanism of the power stroke was discussed by all the authors; the manuscript was written by T.I., T.M., K.O. and K.H.B.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Methods and Supplementary Figures 1–7 (PDF 968 kb)
Supplementary Video 1
Fitting a ring model to the density of the inner arm dynein c at various threshold levels and seen from different view angles (MOV 3126 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Movassagh, T., Bui, K., Sakakibara, H. et al. Nucleotide-induced global conformational changes of flagellar dynein arms revealed by in situ analysis. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17, 761–767 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1832
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1832