Abstract
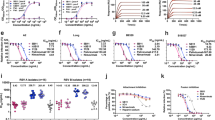
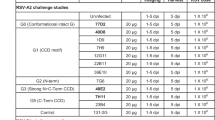
Motavizumab is ∼tenfold more potent than its predecessor, palivizumab (Synagis), the FDA-approved monoclonal antibody used to prevent respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection. The structure of motavizumab in complex with a 24-residue peptide corresponding to its epitope on the RSV fusion (F) glycoprotein reveals the structural basis for this greater potency. Modeling suggests that motavizumab recognizes a different quaternary configuration of the F glycoprotein than that observed in a homologous structure.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
World Health Organization. Acute respiratory infection (World Health Organization, Geneva, 2009; accessed 6 January 2010). <http://www.who.int/vaccine_research/diseases/ari/en/index.html>
Thompson, W.W. et al. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 289, 179–186 (2003).
Groothuis, J.R., Simoes, E.A. & Hemming, V.G. Pediatrics 95, 463–467 (1995).
Johnson, S. et al. J. Infect. Dis. 176, 1215–1224 (1997).
Beeler, J.A. & van Wyke Coelingh, K. J. Virol. 63, 2941–2950 (1989).
Arbiza, J. et al. J. Gen. Virol. 73, 2225–2234 (1992).
Lopez, J.A. et al. J. Gen. Virol. 74, 2567–2577 (1993).
The IMpact-RSV Study Group. Pediatrics 102, 531–537 (1998).
Wu, H. et al. J. Mol. Biol. 368, 652–665 (2007).
Wu, H. et al. J. Mol. Biol. 350, 126–144 (2005).
Johnson, L.S. & Braden, B. USPTO Patent 7229618 (2007).
Smith, B.J., Lawrence, M.C. & Colman, P.M. Protein Eng. 15, 365–371 (2002).
Krissinel, E. & Henrick, K. J. Mol. Biol. 372, 774–797 (2007).
Lawrence, M.C. & Colman, P.M. J. Mol. Biol. 234, 946–950 (1993).
Zhao, X., Chen, F.-P., Megaw, A.G. & Sullender, W.M. J. Infect. Dis. 190, 1941–1946 (2004).
Tous, G.I., Schenerman, M.A., Casas-Finet, J., Wei, Z. & Pfarr, D.S. USPTO Patent application 11/230,593 (2006).
Yin, H.S., Wen, X., Paterson, R.G., Lamb, R.A. & Jardetzky, T.S. Nature 439, 38–44 (2006).
Tao, Y., Strelkov, S.V., Mesyanzhinov, V.V. & Rossmann, M.G. Structure 5, 789–798 (1997).
Lok, S.-M. et al. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 15, 312–317 (2008).
Liu, J., Bartesaghi, A., Borgnia, M.J., Sapiro, G. & Subramaniam, S. Nature 455, 109–113 (2008).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank L. Shapiro and members of the Structural Biology Section, Vaccine Research Center, for helpful comments, and J. Gonczy and the staff at SER-CAT (Southeast Regional Collaborative Access Team) for help with X-ray diffraction data collection. Support for this work was provided by the Intramural Research Program (US National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases). Use of insertion device 22 (SER-CAT) at the Advanced Photon Source was supported by the US Department of Energy, Basic Energy Sciences, Office of Science, under contract W-31-109-Eng-38.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.S.M., B.S.G. and P.D.K. designed experiments and analyzed data; J.S.M. also prepared, crystallized and solved the structure of the motavizumab–peptide complex and performed the biochemical and biophysical experiments; M.C. performed the neutralization experiments; Y.Y. and A.K. expressed and purified the RSV F0 Fd glycoprotein and motavizumab IgG, respectively.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Methods, Supplementary Figues 1–4 and Supplementary Table 1 (PDF 912 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McLellan, J., Chen, M., Kim, A. et al. Structural basis of respiratory syncytial virus neutralization by motavizumab. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17, 248–250 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1723
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1723
This article is cited by
-
Genomic characterization of human respiratory syncytial virus circulating in Islamabad, Pakistan, during an outbreak in 2022-2023
Archives of Virology (2024)
-
A human antibody potently neutralizes RSV by targeting the conserved hydrophobic region of prefusion F
Science China Life Sciences (2023)
-
CAF08 adjuvant enables single dose protection against respiratory syncytial virus infection in murine newborns
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Backbone and side-chain resonance assignments of the NISTmAb-scFv and antigen-binding study
Biomolecular NMR Assignments (2022)
-
Bottom-up de novo design of functional proteins with complex structural features
Nature Chemical Biology (2021)