Key Points
-
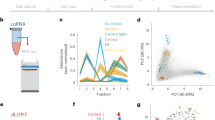
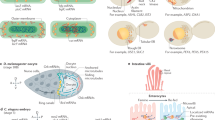
Ribosomes bound to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane translate a large and diverse population of mRNAs.
-
Many mechanisms, including ribosome and mRNA binding, contribute to the recruitment of translation to the ER.
-
Ribosomes and mRNAs associate with the ER over many successive rounds of protein synthesis.
-
The ER and cytosol are distinct compartments for protein translation and post-transcriptional gene regulation.
-
Localization of an mRNA can be an important regulatory variable during cell stress.
Abstract
Pioneering electron microscopy studies defined two primary populations of ribosomes in eukaryotic cells: one freely dispersed through the cytoplasm and the other bound to the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Subsequent investigations revealed a specialized function for each population, with secretory and integral membrane protein-encoding mRNAs translated on ER-bound ribosomes, and cytosolic protein synthesis was widely attributed to free ribosomes. Recent findings have challenged this view, and transcriptome-scale studies of mRNA distribution and translation have now demonstrated that ER-bound ribosomes also function in the translation of a large fraction of mRNAs that encode cytosolic proteins. These studies suggest a far more expansive role for the ER in transcriptome expression, where membrane and secretory protein synthesis represents one element of a multifaceted and dynamic contribution to post-transcriptional gene expression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caro, L. G. & Palade, G. E. Protein synthesis, storage, and discharge in the pancreatic exocrine cell. An. Autoradiogr. Study. J. Cell Biol. 20, 473–495 (1964).
Johnson, A. E. & van Waes, M. A. The translocon: a dynamic gateway at the ER membrane. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 15, 799–842 (1999).
Palade, G. Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science 189, 347–358 (1975). This paper provides an important overview of the early understanding of the field and a summary of outstanding questions.
Rapoport, T. A. Protein translocation across the eukaryotic endoplasmic reticulum and bacterial plasma membranes. Nature 450, 663–669 (2007).
Blobel, G. Protein targeting (Nobel lecture). Chembiochem 1, 86–102 (2000).
Walter, P. & Johnson, A. E. Signal sequence recognition and protein targeting to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 10, 87–119 (1994).
Cross, B. C., Sinning, I., Luirink, J. & High, S. Delivering proteins for export from the cytosol. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10, 255–264 (2009).
Walter, P. & Blobel, G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum. II. Signal recognition protein (SRP) mediates the selective binding to microsomal membranes of in-vitro-assembled polysomes synthesizing secretory protein. J. Cell Biol. 91, 551–556 (1981). This landmark study reports the discovery of the SRP mechanism of cytosol-to-ER mRNA localization.
Walter, P., Ibrahimi, I. & Blobel, G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum. I. Signal recognition protein (SRP) binds to in-vitro-assembled polysomes synthesizing secretory protein. J. Cell Biol. 91, 545–550 (1981).
Noriega, T. R., Chen, J., Walter, P. & Puglisi, J. D. Real-time observation of signal recognition particle binding to actively translating ribosomes. Elife 3, e04418 (2014).
Gilmore, R., Blobel, G. & Walter, P. Protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. I. Detection in the microsomal membrane of a receptor for the signal recognition particle. J. Cell Biol. 95, 461–469 (1982).
Meyer, D. I., Krause, E. & Dobberstein, B. Secretory protein translocation across membranes-the role of the 'docking protein'. Nature 297, 647–650 (1982).
Blobel, G. & Dobberstein, B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J. Cell Biol. 67, 835–851 (1975).
Siekevitz, P. & Palade, G. E. A cytochemical study on the pancreas of the guinea pig. 5. In vivo incorporation of leucine-1-C14 into the chymotrypsinogen of various cell fractions. J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 7, 619–630 (1960).
Potter, M. D., Seiser, R. M. & Nicchitta, C. V. Ribosome exchange revisited: a mechanism for translation-coupled ribosome detachment from the ER membrane. Trends Cell Biol. 11, 112–115 (2001).
Seiser, R. M. & Nicchitta, C. V. The fate of membrane-bound ribosomes following the termination of protein synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 33820–33827 (2000).
Potter, M. D. & Nicchitta, C. V. Regulation of ribosome detachment from the mammalian endoplasmic reticulum membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 33828–33835 (2000).
Reid, D. W., Chen, Q., Tay, A. S., Shenolikar, S. & Nicchitta, C. V. The unfolded protein response triggers selective mRNA release from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell 158, 1362–1374 (2014). This study identifies a role for dynamic ER mRNA localization in cellular stress responses.
Palade, G. E. A small particulate component of the cytoplasm. J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 1, 59–68 (1955).
Hicks, S. J., Drysdale, J. W. & Munro, H. N. Preferential synthesis of ferritin and albumin by different populations of liver polysomes. Science 164, 584–585 (1969).
Mueckler, M. M. & Pitot, H. C. Structure and function of rat liver polysome populations. I. Complexity, frequency distribution, and degree of uniqueness of free and membrane-bound polysomal polyadenylate-containing RNA populations. J. Cell Biol. 90, 495–506 (1981).
Mechler, B. & Vassalli, P. Membrane-bound ribosomes of myeloma cells. III. The role of the messenger RNA and the nascent polypeptide chain in the binding of ribosomes to membranes. J. Cell Biol. 67, 25–37 (1975).
Mechler, B. & Vassalli, P. Membrane-bound ribosomes of myeloma cells. II. Kinetic studies on the entry of newly made ribosomal subunits into the free and the membrane-bound ribosomal particles. J. Cell Biol. 67, 16–24 (1975).
Kopczynski, C. C. et al. A high throughput screen to identify secreted and transmembrane proteins involved in Drosophila embryogenesis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 9973–9978 (1998).
Diehn, M., Eisen, M. B., Botstein, D. & Brown, P. O. Large-scale identification of secreted and membrane-associated gene products using DNA microarrays. Nature Genet. 25, 58–62 (2000).
Diehn, M., Bhattacharya, R., Botstein, D. & Brown, P. O. Genome-scale identification of membrane-associated human mRNAs. PLoS Genet. 2, e11 (2006).
Lerner, R. S. et al. Partitioning and translation of mRNAs encoding soluble proteins on membrane-bound ribosomes. RNA 9, 1123–1137 (2003).
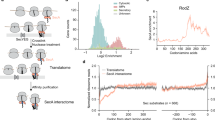
Reid, D. W. & Nicchitta, C. V. Primary role for endoplasmic reticulum-bound ribosomes in cellular translation identified by ribosome profiling. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 5518–5527 (2012). This report defines the translation that occurs on cytosolic and ER-bound ribosomes during homeostasis and cell stress.
Stephens, S. B., Dodd, R. D., Lerner, R. S., Pyhtila, B. M. & Nicchitta, C. V. Analysis of mRNA partitioning between the cytosol and endoplasmic reticulum compartments of mammalian cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 419, 197–214 (2008).
Jagannathan, S., Nwosu, C. & Nicchitta, C. V. Analyzing mRNA localization to the endoplasmic reticulum via cell fractionation. Methods Mol. Biol. 714, 301–321 (2011).
Jagannathan, S., Reid, D. W., Cox, A. H. & Nicchitta, C. V. De novo translation initiation on membrane-bound ribosomes as a mechanism for localization of cytosolic protein mRNAs to the endoplasmic reticulum. RNA 120, 489–498 (2014). This paper presents findings that translation initiation occurs on the ER.
Martin, K. C. & Ephrussi, A. mRNA localization: gene expression in the spatial dimension. Cell 136, 719–730 (2009).
Palacios, I. M. & Johnston, D. S. Getting the message across: the intracellular localization of mRNAs in higher eukaryotes. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 17, 569–614 (2001).
Cui, X. A., Zhang, Y., Hong, S. J. & Palazzo, A. F. Identification of a region within the placental alkaline phosphatase mRNA that mediates p180-dependent targeting to the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 29633–29641 (2013).
Loya, A. et al. The 3′-UTR mediates the cellular localization of an mRNA encoding a short plasma membrane protein. RNA 14, 1352–1365 (2008).
Nicchitta, C. V., Lerner, R. S., Stephens, S. B., Dodd, R. D. & Pyhtila, B. Pathways for compartmentalizing protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells: the template-partitioning model. Biochem. Cell Biol. 83, 687–695 (2005).
Pyhtila, B. et al. Signal sequence- and translation-independent mRNA localization to the endoplasmic reticulum. RNA 14, 445–453 (2008).
Zhou, C. et al. Organelle-based aggregation and retention of damaged proteins in asymmetrically dividing cells. Cell 159, 530–542 (2014). This study identifies a distinct protein folding and aggregation environment on the ER.
Krogh, A., Larsson, B., von Heijne, G. & Sonnhammer, E. L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 305, 567–580 (2001).
Mueckler, M. M. & Pitot, H. C. Structure and function of rat liver polysome populations. II. Characterization of polyadenylate-containing mRNA associated with subpopulations of membrane-bound particles. J. Cell Biol. 94, 297–307 (1982).
Mechler, B. & Rabbitts, T. H. Membrane-bound ribosomes of myeloma cells. IV. mRNA complexity of free and membrane-bound polysomes. J. Cell Biol. 88, 29–36 (1981).
Chen, Q., Jagannathan, S., Reid, D. W., Zheng, T. & Nicchitta, C. V. Hierarchical regulation of mRNA partitioning between the cytoplasm and the endoplasmic reticulum of mammalian cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 22, 2646–2658 (2011).
Jagannathan, S. et al. Multifunctional roles for the protein translocation machinery in RNA anchoring to the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 25907–25924 (2014).
Unsworth, H., Raguz, S., Edwards, H. J., Higgins, C. F. & Yague, E. mRNA escape from stress granule sequestration is dictated by localization to the endoplasmic reticulum. FASEB J. 24, 3370–3380 (2010).
Williams, C. C., Jan, C. H. & Weissman, J. S. Targeting and plasticity of mitochondrial proteins revealed by proximity-specific ribosome profiling. Science 346, 748–751 (2014).
Dudek, J., Rehling, P. & van der Laan, M. Mitochondrial protein import: common principles and physiological networks. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1833, 274–285 (2013).
Johnson, N., Powis, K. & High, S. Post-translational translocation into the endoplasmic reticulum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1833, 2403–2409 (2013).
Zhou, W., Brush, M. H., Choy, M. S. & Shenolikar, S. Association with endoplasmic reticulum promotes proteasomal degradation of GADD34 protein. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 21687–21696 (2011).
Brush, M. H., Weiser, D. C. & Shenolikar, S. Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein GADD34 targets protein phosphatase 1α to the endoplasmic reticulum and promotes dephosphorylation of the α subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23, 1292–1303 (2003).
Jousse, C. et al. Inhibition of a constitutive translation initiation factor 2α phosphatase, CReP, promotes survival of stressed cells. J. Cell Biol. 163, 767–775 (2003).
Li, S. et al. MicroRNAs inhibit the translation of target mRNAs on the endoplasmic reticulum in Arabidopsis. Cell 153, 562–574 (2013).
Schwarz, D. S. & Blower, M. D. The calcium-dependent ribonuclease XendoU promotes ER network formation through local RNA degradation. J. Cell Biol. 207, 41–57 (2014).
Hollien, J. & Weissman, J. S. Decay of endoplasmic reticulum-localized mRNAs during the unfolded protein response. Science 313, 104–107 (2006).
Yoshida, H., Matsui, T., Yamamoto, A., Okada, T. & Mori, K. XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription factor. Cell 107, 881–891 (2001).
Batlle, M., Marsellach, F. X., Huertas, D. & Azorin, F. Drosophila vigilin, DDP1, localises to the cytoplasm and associates to the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1809, 46–55 (2011).
Stalder, L. et al. The rough endoplasmatic reticulum is a central nucleation site of siRNA-mediated RNA silencing. EMBO J. 32, 1115–1127 (2013). This report defines the ER as essential for the execution of siRNA function.
O'Brien, E. P., Vendruscolo, M. & Dobson, C. M. Kinetic modelling indicates that fast-translating codons can coordinate cotranslational protein folding by avoiding misfolded intermediates. Nature Commun. 5, 2988 (2014).
Fedorov, A. N. & Baldwin, T. O. Contribution of cotranslational folding to the rate of formation of native protein structure. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 1227–1231 (1995).
Negrutskii, B. S. & Deutscher, M. P. Channeling of aminoacyl-tRNA for protein synthesis in vivo. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 88, 4991–4995 (1991).
Negrutskii, B. S. & Deutscher, M. P. A sequestered pool of aminoacyl-tRNA in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 89, 3601–3604 (1992).
Stephens, S. B. & Nicchitta, C. V. Divergent regulation of protein synthesis in the cytosol and endoplasmic reticulum compartments of mammalian cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 19, 623–632 (2008).
David, A. et al. RNA binding targets aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases to translating ribosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 20688–20700 (2011).
McCloskey, M. A. & Poo, M. M. Rates of membrane-associated reactions: reduction of dimensionality revisited. J. Cell Biol. 102, 88–96 (1986).
Saks, V., Beraud, N. & Wallimann, T. Metabolic compartmentation — a system level property of muscle cells: real problems of diffusion in living cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 9, 751–767 (2008).
Hudder, A., Nathanson, L. & Deutscher, M. P. Organization of mammalian cytoplasm. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23, 9318–9326 (2003).
Walter, P. & Blobel, G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum III. Signal recognition protein (SRP) causes signal sequence-dependent and site-specific arrest of chain elongation that is released by microsomal membranes. J. Cell Biol. 91, 557–561 (1981).
Walter, P. & Blobel, G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 4, 137–146 (1982).
Rapoport, T. A. Protein transport across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. FEBS J. 275, 4471–4478 (2008).
Zimmermann, R., Eyrisch, S., Ahmad, M. & Helms, V. Protein translocation across the ER membrane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1808, 912–924 (2011).
Stephens, S. B. et al. Stable ribosome binding to the endoplasmic reticulum enables compartment-specific regulation of mRNA translation. Mol. Biol. Cell 16, 5819–5831 (2005).
Beckmann, R. et al. Architecture of the protein-conducting channel associated with the translating 80S ribosome. Cell 107, 361–372 (2001).
Gorlich, D. & Rapoport, T. A. Protein translocation into proteoliposomes reconstituted from purified components of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Cell 75, 615–630 (1993).
Menetret, J. F. et al. Single copies of Sec61 and TRAP associate with a nontranslating mammalian ribosome. Structure 16, 1126–1137 (2008).
Voorhees, R. M., Fernandez, I. S., Scheres, S. H. & Hegde, R. S. Structure of the mammalian ribosome-Sec61 complex to 3.4 Å resolution. Cell 157, 1632–1643 (2014).
Simon, S. M. & Blobel, G. A protein-conducting channel in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell 65, 371–380 (1991).
Borgese, D., Blobel, G. & Sabatini, D. D. In vitro exchange of ribosomal subunits between free and membrane-bound ribosomes. J. Mol. Biol. 74, 415–438 (1973).
Borgese, N., Mok, W., Kreibich, G. & Sabatini, D. D. Ribosomal-membrane interaction: in vitro binding of ribosomes to microsomal membranes. J. Mol. Biol. 88, 559–580 (1974).
Savitz, A. J. & Meyer, D. I. Identification of a ribosome receptor in the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Nature 346, 540–544 (1990).
Savitz, A. J. & Meyer, D. I. 180 kD ribosome receptor is essential for both ribosome binding and protein translocation. J. Cell Biol. 120, 853–863 (1993).
Collins, P. G. & Gilmore, R. Ribosome binding to the endoplasmic reticulum — a 180 kD protein identified by crosslinking to membrane-bound ribosomes is not required for ribosome binding activity. J. Cell Biol. 114, 639–649 (1991).
Nunnari, J. M., Zimmerman, D. L., Ogg, S. C. & Walter, P. Characterization of the rough endoplasmic reticulum ribosome-binding activity. Nature 352, 638–640 (1991).
Prinz, A., Behrens, C., Rapoport, T. A., Hartmann, E. & Kalies, K. U. Evolutionarily conserved binding of ribosomes to the translocation channel via the large ribosomal RNA. EMBO J. 19, 1900–1906 (2000).
Görlich, D., Prehn, S., Hartmann, E., Kalies, K.-U. & Rapoport, T. A. A mammalian homolog of Sec61p and SecYp is associated with ribosomes and nascent polypeptides during translocation. Cell 71, 489–503 (1992).
Kalies, K. U., Gorlich, D. & Rapoport, T. A. Binding of ribosomes to the rough endoplasmic reticulum mediated by the Sec61p-complex. J. Cell Biol. 126, 925–934 (1994).
Schaletzky, J. & Rapoport, T. A. Ribosome binding to and dissociation from translocation sites of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Mol. Biol. Cell 17, 3860–3869 (2006).
Murphy, E. C. I., Zheng, T. & Nicchitta, C. V. Identification of a novel stage of ribosome/nascent chain association with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. J. Cell Biol. 136, 1213–1226 (1997).
Kreibich, G., Freienstein, C. M., Pereyra, B. N., Ulrich, B. L. & Sabatini, D. D. Proteins of rough microsomal membranes related to ribosome binding. II. Cross-linking of bound ribosomes to specific membrane proteins exposed at the binding sites. J. Cell Biol. 77, 488–506 (1978).
Kreibich, G., Ulrich, B. L. & Sabatini, D. D. Proteins of rough microsomal membranes related to ribosome binding. I. Identification of ribophorins I and II, membrane proteins characteristics of rough microsomes. J. Cell Biol. 77, 464–487 (1978).
Harada, Y., Li, H., Li, H. & Lennarz, W. J. Oligosaccharyltransferase directly binds to ribosome at a location near the translocon-binding site. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106, 6945–6949 (2009).
Yu, Y. H., Sabatini, D. D. & Kreibich, G. Antiribophorin antibodies inhibit the targeting to the ER membrane of ribosomes containing nascent secretory polypeptides. J. Cell Biol. 111, 1335–1342 (1990).
Levy, R., Wiedmann, M. & Kreibich, G. In vitro binding of ribosomes to the β subunit of the Sec61p protein translocation complex. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 2340–2346 (2001).
Muller, L. et al. Evolutionary gain of function for the ER membrane protein Sec62 from yeast to humans. Mol. Biol. Cell 21, 691–703 (2010).
Blau, M. et al. ERj1p uses a universal ribosomal adaptor site to coordinate the 80S ribosome at the membrane. Nature Struct. Mol. Biol. 12, 1015–1016 (2005).
Ueno, T., Kaneko, K., Sata, T., Hattori, S. & Ogawa-Goto, K. Regulation of polysome assembly on the endoplasmic reticulum by a coiled-coil protein, 180. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, 3006–3017 (2012). This paper provides a thorough analysis of the potential impact of p180 in regulating ribosome binding to the ER.
Mauro, V. P. & Edelman, G. M. The ribosome filter hypothesis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99, 12031–12036 (2002).
Potter, M. D. & Nicchitta, C. V. Endoplasmic reticulum ribosomes reside in stable association with the translocon following termination of protein synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 23314–23320 (2002).
Jan, C. H., Williams, C. C. & Weissman, J. S. Principles of ER cotranslational translocation revealed by proximity-specific ribosome profiling. Science 346, 1257521 (2014).
Kraut-Cohen, J. et al. Translation- and SRP-independent mRNA targeting to the endoplasmic reticulum in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Biol. Cell 24, 3069–3084 (2013).
Decatur, W. A. & Fournier, M. J. rRNA modifications and ribosome function. Trends Biochem. Sci. 27, 344–351 (2002).
Ovodov, SYu. & Alakhov, YuB. mRNA acetylated at 2′-OH-groups of ribose residues is functionally active in the cell-free translation system from wheat embryos. FEBS Lett. 270, 111–114 (1990).
Cui, X. A., Zhang, H. & Palazzo, A. F. p180 promotes the ribosome-independent localization of a subset of mRNA to the endoplasmic reticulum. PLoS Biol. 10, e1001336 (2012). This report identifies a role for p180 in promoting selective mRNA localization.
Hortsch, M., Avossa, D. & Meyer, D. I. Characterization of secretory protein translocation: ribosome-membrane interaction in endoplasmic reticulum. J. Cell Biol. 103, 241–253 (1986).
Ueno, T. et al. Enhancement of procollagen biosynthesis by p180 through augmented ribosome association on the endoplasmic reticulum in response to stimulated secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 29941–29950 (2010).
Wang, H. & Stefanovic, B. Role of LARP6 and nonmuscle myosin in partitioning of collagen mRNAs to the ER membrane. PLoS ONE 9, e108870 (2014).
Polyansky, A. A., Hlevnjak, M. & Zagrovic, B. Analogue encoding of physicochemical properties of proteins in their cognate messenger RNAs. Nature Commun. 4, 2784 (2013). This paper provides a statistical approach that links the chemical properties of mRNAs and their encoded proteins to ER localization.
Prilusky, J. & Bibi, E. Studying membrane proteins through the eyes of the genetic code revealed a strong uracil bias in their coding mRNAs. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106, 6662–6666 (2009).
del Alamo, M. et al. Defining the specificity of cotranslationally acting chaperones by systematic analysis of mRNAs associated with ribosome-nascent chain complexes. PLoS Biol. 9, e1001100 (2011). This report demonstrates that loss of the SRP does not compromise mRNA localization at a transcriptome scale.
Mutka, S. C. & Walter, P. Multifaceted physiological response allows yeast to adapt to the loss of the signal recognition particle-dependent protein-targeting pathway. Mol. Biol. Cell 12, 577–588 (2001).
Ren, Y. G. et al. Differential regulation of the TRAIL death receptors DR4 and DR5 by the signal recognition particle. Mol. Biol. Cell 15, 5064–5074 (2004).
Walter, P. & Ron, D. The unfolded protein response: from stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science 334, 1081–1086 (2011).
Lee, K. et al. IRE1-mediated unconventional mRNA splicing and S2P-mediated ATF6 cleavage merge to regulate XBP1 in signaling the unfolded protein response. Genes Dev. 16, 452–466 (2002).
Aragon, T. et al. Messenger RNA targeting to endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling sites. Nature 457, 736–740 (2009).
Yanagitani, K. et al. Cotranslational targeting of XBP1 protein to the membrane promotes cytoplasmic splicing of its own mRNA. Mol. Cell 34, 191–200 (2009).
Gaddam, D., Stevens, N. & Hollien, J. Comparison of mRNA localization and regulation during endoplasmic reticulum stress in Drosophila cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 24, 14–20 (2013).
Risco, C. et al. Endoplasmic reticulum–Golgi intermediate compartment membranes and vimentin filaments participate in vaccinia virus assembly. J. Virol. 76, 1839–1855 (2002).
Sodeik, B. et al. Assembly of vaccinia virus: role of the intermediate compartment between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi stacks. J. Cell Biol. 121, 521–541 (1993).
Desmet, E. A., Anguish, L. J. & Parker, J. S. Virus-mediated compartmentalization of the host translational machinery. mBio 5, e01463-14 (2014).
Wiest, D. L. et al. Membrane biogenesis during B cell differentiation: most endoplasmic reticulum proteins are expressed coordinately. J. Cell Biol. 110, 1501–1511 (1990).
Blobel, G. et al. Translocation of proteins across membranes: the signal hypothesis and beyond. Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol. 33, 9–36 (1979).
Walter, P. & Blobel, G. Purification of a membrane-associated protein complex required for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 77, 7112–7116 (1980).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank former members of C.V.N.'s laboratory, in particular M. Potter, R. Seiser, S. Stephens, R. Lerner and S. Jagannathan, for their many contributions to the concepts proposed in this Review, and current laboratory members, in particular J. C.-C. Hsu and A. Hoffman, for their critical feedback and contributions. They also thank S. Shenolikar for his ongoing contribution to the introduction and maturation of these ideas. Work in C.V.N.'s laboratory is supported by a grant from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the US National Institutes of Health (GM101533 to C.V.N.). D.W.R. is funded by a Translational Clinical Research Flagship Award entitled 'National Parkinson's Disease Translational Clinical Research Programme' from National Medical Research Council Singapore.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Glossary
- Topogenic signal
-
A hydrophobic region of a protein that is targeted to the endoplasmic reticulum.
- Signal recognition particle
-
(SRP). A ribonucleoprotein complex that targets nascent secretory and membrane proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum as they emerge from the ribosomes.
- Microsomal vesicles
-
Vesicles that are derived from the endoplasmic reticulum and that are commonly used for in vitro studies of translation and protein translocation.
- Multi-tRNA synthetase
-
An assembly of many tRNA synthetases that serves to concentrate the charging of tRNAs with amino acids.
- Rough microsomes
-
Highly purified, translation-competent endoplasmic reticulum, generally obtained from canine pancreas.
- Proteostasis
-
The status and health of protein folding in the cell.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reid, D., Nicchitta, C. Diversity and selectivity in mRNA translation on the endoplasmic reticulum. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 16, 221–231 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3958
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3958
This article is cited by
-
Toxoplasma gondii dense granule protein 3 promotes endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis by activating the PERK pathway
Parasites & Vectors (2022)
-
ATase inhibition rescues age-associated proteotoxicity of the secretory pathway
Communications Biology (2022)
-
PlantMWpIDB: a database for the molecular weight and isoelectric points of the plant proteomes
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Membrane surfaces regulate assembly of ribonucleoprotein condensates
Nature Cell Biology (2022)
-
Dynamic changes in the association between maternal mRNAs and endoplasmic reticulum during ascidian early embryogenesis
Development Genes and Evolution (2022)