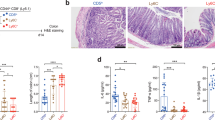
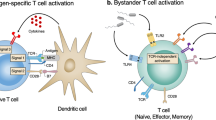
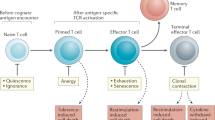
Abstract
The regulation of immune responses to self-antigens is a complex process that involves maintaining self-tolerance while retaining the capacity to mount robust immune responses against invading microorganisms. Over the past few years, many new insights into this process have been gained, leading to the re-emergence of the idea that regulatory T (TReg) cells are a central mechanism of immune regulation. These insights have raised fundamental questions concerning what constitutes a TReg cell, where they develop and what signals maintain TReg-cell populations in a functional state. Here, we propose the existence of two subsets of CD4+ TReg cells — natural and adaptive — that differ in terms of their development, specificity, mechanism of action and dependence on T-cell receptor and co-stimulatory signalling.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sakaguchi, S., Sakaguchi, N., Asano, M., Itoh, M. & Toda, M. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor α-chains. J. Immunol. 155, 1151–1164 (1995).
Asano, M., Toda, M., Sakaguchi, N. & Sakaguchi, S. Autoimmune disease as a consequence of developmental abnormality of a T-cell subpopulation. J. Exp. Med. 184, 387–396 (1996).
Shevach, E. M. CD4+CD25+ suppressor T cells: more questions than answers. Nature Rev. Immunol. 2, 389–400 (2002).
Jordan, M. S. et al. Thymic selection of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells induced by an agonist self-peptide. Nature Immunol. 2, 301–306 (2001).
Barrat, F. J. et al. In vitro generation of interleukin-10-producing regulatory CD4+ T cells is induced by immunosuppressive drugs and inhibited by T helper type 1 (TH1)- and TH2-inducing cytokines. J. Exp. Med. 195, 603–616 (2002).
Chatenoud, L., Primo, J. & Bach, J. F. CD3 antibody-induced dominant self-tolerance in overtly diabetic NOD mice. J. Immunol. 158, 2947–2954 (1997).
Sakaguchi, S. et al. Immunologic tolerance maintained by CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells: their common role in controlling autoimmunity, tumor immunity and transplantation tolerance. Immunol. Rev. 182, 18–32 (2001).
Derbinski, J., Schulte, A., Kyewski, B. & Klein, L. Promiscuous gene expression in medullary thymic epithelial cells mirrors the peripheral self. Nature Immunol. 2, 1032–1039 (2001).
Salomon, B. et al. B7/CD28 costimulation is essential for the homeostasis of the CD4+CD25+ immunoregulatory T cells that control autoimmune diabetes. Immunity 12, 431–440 (2000).
Shimizu, J., Yamazaki, S., Takahashi, T., Ishida, Y. & Sakaguchi, S. Stimulation of CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells through GITR breaks immunological self-tolerance. Nature Immunol. 3, 135–142 (2002).
Malek, T. R., Yu, A., Vincek, V., Scibelli, P. & Kong, L. CD4 regulatory T cells prevent lethal autoimmunity in IL-2Rβ-deficient mice. Implications for the nonredundant function of IL-2. Immunity 17, 167–178 (2002).
Seddon, B. & Mason, D. Peripheral autoantigen induces regulatory T cells that prevent autoimmunity. J. Exp. Med. 189, 877–882 (1999).
Boden, E., Tang, Q., Bour-Jordan, H. & Bluestone, J. A. in Novartis Foundation Symposium 252. Generation and Effector Functions of Regulatory Lymphocytes (Wiley, Europe) (in the press).
Bensinger, S. J., Bandeira, A., Jordan, M. S., Caton, A. J. & Laufer, T. M. Major histocompatibility complex class-II-positive cortical epithelium mediates the selection of CD4+CD25+ immunoregulatory T cells. J. Exp. Med. 194, 427–438 (2001).
Lenschow, D. et al. CD28/B7 regulation of TH1 and TH2 subsets in the development of autoimmune diabetes. Immunity 5, 285–293 (1996).
Sharif, S. et al. Activation of natural killer T cells by α-galactosylceramide treatment prevents the onset and recurrence of autoimmune type 1 diabetes. Nature Med. 7, 1057–1062 (2001).
Bach, J. F. Regulatory T cells under scrutiny. Nature Rev. Immunol. 3, 189–198 (2003).
Maloy, K. J. & Powrie, F. Regulatory T cells in the control of immune pathology. Nature Immunol. 2, 816–822 (2001).
Kingsley, C. I., Karim, M., Bushell, A. R. & Wood, K. J. CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells prevent graft rejection: CTLA-4- and IL-10-dependent immunoregulation of alloresponses. J. Immunol. 168, 1080–1086 (2002).
Nakamura, K., Kitani, A. & Strober, W. Cell contact-dependent immunosuppression by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells is mediated by cell surface-bound transforming growth factor-β. J. Exp. Med. 194, 629–644 (2001).
Chen, Y., Kuchroo, V. K., Inobe, J. -I., Hafler, D. A. & Weiner, H. L. Regulatory T-cell clones induced by oral tolerance: suppression of autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Science 265, 1237–1240 (1994).
Levings, M. K., Sangregorio, R. & Roncarolo, M. -G. Human CD25+CD4+ T cells suppress naive and memory T-cell proliferation and can be expanded in vitro without loss of suppressor function. J. Exp. Med. 193, 1295–1302 (2001).
Gonzalez, A., Andre-Schmutz, I., Carnaud, C., Mathis, D. & Benoist, C. Damage control, rather than unresponsiveness, effected by protective DX5+ T cells in autoimmune diabetes. Nature Immunol. 2, 1117–1125 (2001).
Chatenoud, L., Salomon, B. & Bluestone, J. A. Suppressor T cells — they're back and critical for regulation of autoimmunity! Immunol. Rev. 182, 149–163 (2001).
Khanna, A., Kapur, S., Sharma, V., Li, B. & Suthanthiran, M. In vivohyperexpression of transforming growth factor-β1 in mice: stimulation by cyclosporine. Transplantation 63, 1037–1039 (1997).
Apostolou, I., Sarukhan, A., Klein, L. & von Boehmer, H. Origin of regulatory T cells with known specificity for antigen. Nature Immunol. 3, 756–763 (2002).
Belkaid, Y., Piccirillo, C. A., Mendez, S., Shevach, E. M. & Sacks, D. L. CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells control Leishmania major persistence and immunity. Nature 420, 502–507 (2002).
Fuss, I. J., Boirivant, M., Lacy, B. & Strober, W. The interrelated roles of TGF-β and IL-10 in the regulation of experimental colitis. J. Immunol. 168, 900–908 (2002).
Powrie, F. in Novartis Foundation Symposium 252. Generation and Effector Functions of Regulatory Lymphocytes (Wiley, Europe) (in the press).
Taylor, P. A., Friedman, T. M., Korngold, R., Noelle, R. J. & Blazar, B. R. Tolerance induction of alloreactive T cells via ex vivo blockade of the CD40–CD40L costimulatory pathway results in the generation of a potent immune regulatory cell. Blood 99, 4601–4609 (2002).
Furtado, G. C., de Lafaille, M. A., Kutchukhidze, N. & Lafaille, J. J. Interleukin-2 signaling is required for CD4+ regulatory T-cell function. J. Exp. Med. 196, 851–857 (2002).
Nakamura, K., Kitani, A. & Strober, W. Cell contact-dependent immunosuppression by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells is mediated by cell surface-bound transforming growth factor-β. J. Exp. Med. 194, 629–644 (2001).
Bach, J. F. & Chatenoud, L. Tolerance to islet autoantigens and type I diabetes. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 19, 131–161 (2001).
Jonuleit, H. et al. Infectious tolerance: human CD25+ regulatory T cells convey suppressor activity to conventional CD4+ T helper cells. J. Exp. Med. 196, 255–260 (2002).
Dieckmann, D., Bruett, C. H., Ploettner, H., Lutz, M. B. & Schuler, G. Human CD4+CD25+ regulatory, contact-dependent T cells induce interleukin-10-producing, contact-independent type-1-like regulatory T cells. J. Exp. Med. 196, 247–253 (2002).
Kukreja, A. et al. Multiple immuno-regulatory defects in type-1 diabetes. J. Clin. Invest. 109, 131–140 (2002).
Inaba, K. et al. Expression of B7 costimulator molecules on mouse dendritic cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 378, 65–70 (1995).
Acknowledgements
We thank L. Chatenoud and J. F. Bach for helpful discussions and sharing of unpublished data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bluestone, J., Abbas, A. Natural versus adaptive regulatory T cells. Nat Rev Immunol 3, 253–257 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nri1032
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nri1032
This article is cited by
-
Macrophage and T cell networks in adipose tissue
Nature Reviews Endocrinology (2023)
-
Immunological effect of irreversible electroporation on hepatocellular carcinoma
BMC Cancer (2021)
-
Allergoonkologie: was Allergologen und Onkologen voneinander lernen können
HNO (2020)
-
Association between Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and papillary thyroid carcinoma: a retrospective analysis of 305 patients
BMC Endocrine Disorders (2019)
-
Regulatory T Cells Could Improve Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction in Heatstroke
Inflammation (2019)