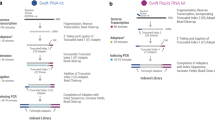
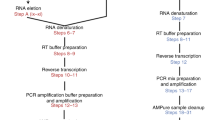
Abstract
The unifying feature of second-generation sequencing technologies is that single template strands are amplified clonally onto a solid surface prior to the sequencing reaction. To convert template strands into a compatible state for attachment to this surface, a multistep library preparation is required, which typically culminates in amplification by the PCR. PCR is an inherently biased process, which decreases the efficiency of data acquisition. Flowcell reverse transcription sequencing is a method of transcriptome sequencing for Illumina sequencers in which the reverse transcription reaction is performed on the flowcell by using unamplified, adapter-ligated mRNA as a template. This approach removes PCR biases and duplicates, generates strand-specific paired-end data and is highly reproducible. The procedure can be performed quickly, taking 2 d to generate clusters from mRNA.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, Z., Gerstein, M. & Snyder, M. RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 10, 57–63 (2009).
Wu, J.Q., Du, J. & Rozowsky, J. et al. Systematic analysis of transcribed loci in ENCODE regions using RACE sequencing reveals extensive transcription in the human genome. Genome Biol. 9, R3 (2008).
Marioni, J.C., Mason, C.E., Mane, S.M., Stephens, M. & Gilad, Y. RNA-seq: an assessment of technical reproducibility and comparison with gene expression arrays. Genome Res. 18, 1509–1517 (2008).
David, L., Huber, W. & Granovskaia, M. et al. A high-resolution map of transcription in the yeast genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 5320–5325 (2006).
Wilhelm, B.T., Marguerat, S. & Watt, S. et al. Dynamic repertoire of a eukaryotic transcriptome surveyed at single-nucleotide resolution. Nature 453, 1239–1243 (2008).
Dutrow, N., Nix, D.A. & Holt, D. et al. Dynamic transcriptome of Schizosaccharomyces pombe shown by RNA-DNA hybrid mapping. Nat. Genet. 40, 977–986 (2008).
Carninci, P., Kasukawa, T. & Katayama, S. et al. The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. Science 309, 1559–1563 (2005).
Katayama, S., Tomaru, Y. & Kasukawa, T. et al. Antisense transcription in the mammalian transcriptome. Science 309, 1564–1566 (2005).
Cloonan, N., Forrest, A.R. & Kolle, G. et al. Stem cell transcriptome profiling via massive-scale mRNA sequencing. Nat. Methods 5, 613–619 (2008).
Croucher, N.J., Fookes, M.C. & Perkins, T.T. et al. A simple method for directional transcriptome sequencing using Illumina technology. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, e148 (2009).
He, Y., Vogelstein, B., Velculescu, V.E., Papadopoulos, N. & Kinzler, K.W. The antisense transcriptomes of human cells. Science 322, 1855–1857 (2008).
Lister, R., O'Malley, R.C. & Tonti-Filippini, J. et al. Highly integrated single-base resolution maps of the epigenome in Arabidopsis. Cell 133, 523–536 (2008).
Ozsolak, F., Platt, A.R. & Jones, D.R. et al. Direct RNA sequencing. Nature 461, 814–818 (2009).
Parkhomchuk, D., Borodina, T. & Amstislavskiy, V. et al. Transcriptome analysis by strand-specific sequencing of complementary DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, e123 (2009).
Vivancos, A.P., Guell, M., Dohm, J.C., Serrano, L. & Himmelbauer, H. Strand-specific deep sequencing of the transcriptome. Genome Res. 20, 989–999 (2010).
Kozarewa, I., Ning, Z. & Quail, M.A. et al. Amplification-free Illumina sequencing-library preparation facilitates improved mapping and assembly of (G+C)-biased genomes. Nat. Methods 6, 291–295 (2009).
Lipson, D., Raz, T. & Kieu, A. et al. Quantification of the yeast transcriptome by single-molecule sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 27, 652–658 (2009).
Mamanova, L., Andrews, R.M. & James, K.D. et al. FRT-seq: amplification-free, strand-specific transcriptome sequencing. Nat. Methods 7, 130–132 (2010).
Chen, D. & Patton, J.T. Reverse transcriptase adds nontemplated nucleotides to cDNAs during 5′-RACE and primer extension. Biotechniques 30, 574–580, 582 (2001).
Acknowledgements
We thank R. Andrews, K. James, L. Sheridan, P. Ellis, C. Langford, T. Ost and J. Collins, who co-authored the primary paper, and M. Gibbs, who helped with the cBot recipes. This work was supported by the Wellcome Trust, grant no. WT079643.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.J.T. designed the study; L.M. developed protocols and conducted the experiments; D.J.T. and L.M. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Method 1
cBot_FRTseq_amp_v7.0.txt — recipe for reverse transcription and cluster amplification for both single and paired end flowcells on cBot (XML 3 kb)
Supplementary Method 2
cBot_PE_Destain_Lin_Block_Hyb_v7.0.txt — recipe for paired end read flowcells, destain, linearization and blocking on cBot (XML 5 kb)
Supplementary Method 3
cBot_SR_Destain_Lin_Block_Hyb_v7.0.txt — recipe for single read flowcells, destain, linearization and blocking on cBot (XML 5 kb)
Supplementary Method 4
CS_FRTseq_amp_v5.0.txt — recipe for reverse transcription and cluster amplification on Cluster Station (XML 10 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mamanova, L., Turner, D. Low-bias, strand-specific transcriptome Illumina sequencing by on-flowcell reverse transcription (FRT-seq). Nat Protoc 6, 1736–1747 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2011.399
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2011.399
This article is cited by
-
The Antisense Transcriptome and the Human Brain
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2016)
-
RNA-seq analysis of the influence of anaerobiosis and FNR on Shigella flexneri
BMC Genomics (2014)