Abstract
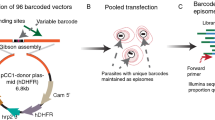
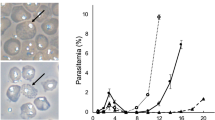
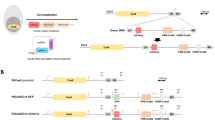
This protocol describes a method of genetic transformation for the rodent malaria parasite Plasmodium berghei with a high transfection efficiency of 10−3–10−4. It provides methods for: (i) in vitro cultivation and purification of the schizont stage;(ii) transfection of DNA constructs containing drug-selectable markers into schizonts using the nonviral Nucleofector technology; and (iii) injection of transfected parasites into mice and subsequent selection of mutants by drug treatment in vivo. Drug selection is described for two (antimalarial) drugs, pyrimethamine and WR92210. The drug-selectable markers currently in use are the pyrimethamine-resistant dihydrofolate reductase (dhfr) gene of Plasmodium or Toxoplasma gondii and the DHFR gene of humans that confer resistance to pyrimethamine and WR92210, respectively. This protocol enables the generation of transformed parasites within 10–15 d. Genetic modification of P. berghei is widely used to investigate gene function in Plasmodium, and this protocol for high-efficiency transformation will enable the application of large-scale functional genomics approaches.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cowman, A.F. & Crabb, B.S. in Molecular Approaches to Malaria (Sherman, I.W. ed.) 50–67 (ASM Press, Washington, DC, 2005).
Carvalho, T.G. & Menard, R. Manipulating the Plasmodium genome. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 7, 39–55 (2005).
Koning-Ward, T.F., Janse, C.J. & Waters, A.P. The development of genetic tools for dissecting the biology of malaria parasites. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 54, 157–185 (2000).
Janse, C.J. et al. High efficiency transfection of Plasmodium berghei facilitates novel selection procedures. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 145, 60–70 (2006).
van Dijk, M.R., McConkey, G.A., Vinkenoog, R., Waters, A.P. & Janse, C.J. Mechanisms of pyrimethamine resistance in two different strains of Plasmodium berghei. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 68, 167–171 (1994).
van Dijk, M.R., Waters, A.P. & Janse, C.J. Stable transfection of malaria parasite blood stages. Science 268, 1358–1362 (1995).
Waters, A.P., Thomas, A.W., van Dijk, M.R. & Janse, C.J. Transfection of malaria parasites. Methods 13, 134–147 (1997).
Menard, R. & Janse, C. Gene targeting in malaria parasites. Methods 13, 148–157 (1997).
Sakamoto, H. et al. Towards systematic identification of Plasmodium essential genes by transposon shuttle mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, e174 (2005).
Ecker, A., Moon, R., Sinden, R.E. & Billker, O. Generation of gene targeting constructs for Plasmodium berghei by a PCR-based method amenable to high throughput applications. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 145, 265–268 (2006).
Maasho, K., Marusina, A., Reynolds, N.M., Coligan, J.E. & Borrego, F. Efficient gene transfer into the human natural killer cell line, NKL, using the Amaxa nucleofection system. J. Immunol. Methods 284, 133–140 (2004).
Gresch, O. et al. New non-viral method for gene transfer into primary cells. Methods 33, 151–163 (2004).
Leclere, P.G. et al. Effective gene delivery to adult neurons by a modified form of electroporation. J. Neurosci. Methods 142, 137–143 (2005).
Jongco, A.M., Ting, L.M., Thathy, V., Mota, M.M. & Kim, K. Improved transfection and new selectable markers for the rodent malaria parasite Plasmodium yoelii. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 146, 242–250 (2006).
Koning-Ward, T.F. et al. The selectable marker human dihydrofolate reductase enables sequential genetic manipulation of the Plasmodium berghei genome. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 106, 199–212 (2000).
Gilks, C.F., Jarra, W., Harvey-Wood, K., McLean, S.A. & Schetters, T. Host diet in experimental rodent malaria: a variable which can compromise experimental design and interpretation. Parasitology 98, 175–177 (1989).
Deitsch, K., Driskill, C. & Wellems, T. Transformation of malaria parasites by the spontaneous uptake and expression of DNA from human erythrocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 29, 850–853 (2001).
Mamoun, C.B. et al. Transfer of genes into Plasmodium falciparum by polyamidoamine dendrimers. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 103, 117–121 (1999).
Gardiner, D.L., Skinner-Adams, T.S., Spielmann, T. & Trenholme, K.R. Malaria transfection and transfection vectors. Trends Parasitol. 19, 381–383 (2003).
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank B. Franke-Fayard, H. Kroeze and S. Khan for their critical comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Video 1
Purification of cultured, mature schizonts of P. berghei by Nycodenz density-gradient centrifugation. (MOV 2727 kb)
Supplementary Video 2
Transfection of schizonts of P. berghei using the Amaxa Nucleofector device and injection of transfected schizonts into a mouse. (MOV 3048 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Janse, C., Ramesar, J. & Waters, A. High-efficiency transfection and drug selection of genetically transformed blood stages of the rodent malaria parasite Plasmodium berghei. Nat Protoc 1, 346–356 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.53
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.53