Abstract
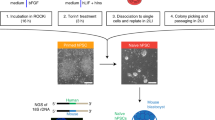
Here we describe a simple and efficient protocol for derivation of germline chimera-competent mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) from embryonic day 3.5 (E3.5) blastocysts. The protocol involves the use of early-passage mouse embryonic fibroblast feeders (MEF) and the alternation of fetal bovine serum– and serum replacement (SR)–containing media. As compared to other available protocols for mESCs derivation, our protocol differs in the combination of commercial availability of all reagents, technical simplicity and high efficiency. mESC lines are derived with approximately 50% efficiency (50 independent mESC lines derived from 96 blastocysts). We believe that this protocol could be a good starting point for (i) setting up the derivation of mESC lines in a laboratory and (ii) incorporating further steps to improve efficiency or adapt the protocol to other applications. The whole process (from blastocyst extraction to the freezing of mESC line) usually takes between 15 and 20 d.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Evans, M.J. & Kaufman, M.H. Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature 292, 154–156 (1981).
Martin, G.R. Isolation of a pluripotent cell line from early mouse embryos cultured in medium conditioned by teratocarcinoma stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78, 7634–7638 (1981).
Thomson, J.A. et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 282, 1145–1147 (1998).
Bongso, A., Fong, C.Y., Ng, S.C. & Ratnam, S. Isolation and culture of inner cell mass cells from human blastocysts. Hum. Reprod. 9, 2110–2117 (1994).
Bradley, A., Evans, M., Kaufman, M.H. & Robertson, E. Formation of germ-line chimaeras from embryo-derived teratocarcinoma cell lines. Nature 309, 255–256 (1984).
Smith, A.G. et al. Inhibition of pluripotential embryonic stem cell differentiation by purified polypeptides. Nature 336, 688–690 (1988).
Williams, R.L. et al. Myeloid leukaemia inhibitory factor maintains the developmental potential of embryonic stem cells. Nature 336, 684–687 (1988).
Miura, T., Mattson, M.P. & Rao, M.S. Cellular lifespan and senescence signaling in embryonic stem cells. Aging Cell 3, 333–343 (2004).
Robertson, E.J. Embryo-derived stem cell lines. in Teratocarcinomas and Embryonic Stem Cells: A Practical Approach (ed. Robertson, E.J.) pp 71–112 (IRL Press, Oxford, 1987).
Hogan, B. Manipulating the Mouse Embryo: A Laboratory Manual (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Plainview, NY, USA, 1994).
Nagy, A. Manipulating the Mouse Embryo: A Laboratory Manual Edn. 3 (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2003).
Abbondanzo, S.J., Gadi, I. & Stewart, C.L. Derivation of embryonic stem cell lines. Methods Enzymol. 225, 803–823 (1993).
Schoonjans, L. et al. Improved generation of germline-competent embryonic stem cell lines from inbred mouse strains. Stem Cells 21, 90–97 (2003).
McWhir, J. et al. Selective ablation of differentiated cells permits isolation of embryonic stem cell lines from murine embryos with a non-permissive genetic background. Nat. Genet. 14, 223–226 (1996).
Brook, F.A. & Gardner, R.L. The origin and efficient derivation of embryonic stem cells in the mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 5709–5712 (1997).
Bryja, V. et al. An efficient method for the derivation of mouse embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 24, 844–849 (2006).
Ying, Q.L., Nichols, J., Chambers, I. & Smith, A. BMP induction of Id proteins suppresses differentiation and sustains embryonic stem cell self-renewal in collaboration with STAT3. Cell 115, 281–292 (2003).
Tanigaki, K. et al. Notch-RBP-J signaling is involved in cell fate determination of marginal zone B cells. Nat. Immunol. 3, 443–450 (2002).
Kawase, E. et al. Strain difference in establishment of mouse embryonic stem (ES) cell lines. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 38, 385–390 (1994).
Auerbach, W. et al. Establishment and chimera analysis of 129/SvEv- and C57BL/6-derived mouse embryonic stem cell lines. Biotechniques 29, 1024–1028, 1030, 1032 (2000).
Cheng, J., Dutra, A., Takesono, A., Garrett-Beal, L. & Schwartzberg, P.L. Improved generation of C57BL/6J mouse embryonic stem cells in a defined serum-free media. Genesis 39, 100–104 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank J. Wilbertz and his team from Karolinska Center for Transgene Technologies for ESC microinjections, C. Tello, J. Söderlund and L. Bryjová for excellent technical assistance, P. Sacchetti for critical reading of the manuscript, C. Collstam and C. Olsson for extraordinary animal maintenance, and members of the Arenas laboratory for assistance and stimulating discussions. Financial support was obtained from the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research, Swedish Royal Academy of Sciences, Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, European Commission (EuroStemCell), Swedish MRC, Karolinska Institutet and Lars Hiertas Minnesfond. S.B. is the recipient of a postdoctoral fellowship from the Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia (Spain).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bryja, V., Bonilla, S. & Arenas, E. Derivation of mouse embryonic stem cells. Nat Protoc 1, 2082–2087 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.355
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.355