Abstract
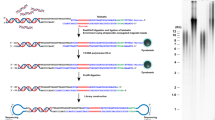
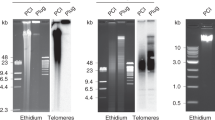
The telomeric repeat amplification protocol (TRAP) is a two-step process for analyzing telomerase activity in cell or tissue extracts. Recent modifications of this sensitive assay include elimination of radioactivity by using a fluorescently labeled primer instead of a radiolabeled primer. In addition, the TRAP assay has been modified for real-time, quantitative PCR analysis. Here, we describe cost-effective procedures for detection of telomerase activity using a fluorescent-based assay as well as by using real-time PCR. These modified TRAP assays can be accomplished within 4 h (from lysis of samples to analysis of telomerase products).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greider, C.W. & Blackburn, E.H. Identification of a specific telomere terminal transferase activity in Tetrahymena extracts. Cell 43, 405–413 (1985).
Kim, N.-W. et al. Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal cells and cancer. Science 266, 2011–2015 (1994).
Norton, J.C., Holt, S.E., Wright, W.E. & Shay, J.W. Enhanced detection of human telomerase activity. DNA Cell Biol. 17, 217–219 (1998).
Wright, W.E., Shay, J.W. & Piatyszek, M.A. Modifications of a telomeric repeat amplification protocol (TRAP) result in increased reliability, linearity and sensitivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 23, 3794–3795 (1995).
Kim, N.W. & Wu, F. Advances in quantification and characterization of telomerase activity by the telomeric repeat amplification protocol (TRAP). Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 2595–2597 (1997).
Norton, J.C., Holt, S.E., Wright, W.E. & Shay, J.W. Enhanced detection of human telomerase activity. DNA Cell Biol. 17, 217–219 (1998).
Elmore, L.W. et al. Real-time quantitative analysis of telomerase activity in breast tumor specimens using a highly specific and sensitive fluorescent-based assay. Diagn. Mol. Pathol. 11, 177–185 (2002).
Gollahon, L.S. & Holt, S.E. Alternative methods of extracting telomerase activity from human tumor samples. Cancer Lett. 159, 141–149 (2000).
Piatyszek, M.A. et al. Detection of telomerase activity in human cells and tumors by a telomeric repeat amplification protocol (TRAP). Methods Cell Sci. 17, 1–15 (1995).
Saldanha, S.N., Andrews, L.G. & Tollefsbol, T.O. Analysis of telomerase activity and detection of its catalytic subunit, hTERT. Anal. Biochem. 315, 1–21 (2003).
Fajkus, J. Detection of telomerase activity by the TRAP assay and its variants and alternatives. Clin. Chim. Acta 371, 25–31 (2006).
Huang, Y.P., Liu, Z.S., Tang, H., Liu, M. & Li, X. Real-time telomeric repeat amplification protocol using the duplex scorpion and two reverse primers system: the high sensitive and accurate method for quantification of telomerase activity. Clin. Chim. Acta 372, 112–119 (2006).
Hou, M., Xu, D., Bjorkholm, M. & Gruber, A. Real-time quantitative telomeric repeat amplification protocol assay for the detection of telomerase activity. Clin. Chem. 47, 519–524 (2001).
Jakupciak, J.P. Real-time telomerase activity measurements for detection of cancer. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 5, 745–753 (2005).
Jakupciak, J.P., Barker, P.E., Wang, W., Srivastava, S. & Atha, D.H. Preparation and characterization of candidate reference materials for telomerase assays. Clin. Chem. 51, 1443–1450 (2005).
Wege, H., Chui, M.S., Le, H.T., Tran, J.M. & Zern, M.A. SYBR Green real-time telomeric repeat amplification protocol for the rapid quantification of telomerase activity. Nucleic Acids Res. Methods Online 31, E3 (2003).
Acknowledgements
We thank P. Erickson and E. Badenhop for technical assistance. This work was supported by the Indiana University Cancer Center and the Indiana Genomics Initiative (INGEN). INGEN of Indiana University is supported in part by Lilly Endowment Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
JWS and WEW consult for, hold stock in, and are members of the scientific advisory board of Geron Corporation. Other authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herbert, BS., Hochreiter, A., Wright, W. et al. Nonradioactive detection of telomerase activity using the telomeric repeat amplification protocol. Nat Protoc 1, 1583–1590 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.239
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.239