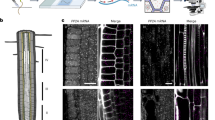
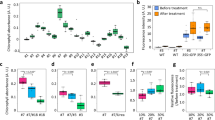
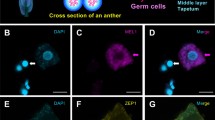
Abstract
As the field of plant molecular biology is swiftly advancing, a need has been created for methods that allow rapid and reliable in situ localization of proteins in plant cells. Here we describe a whole-mount 'immunolocalization' technique for various plant tissues, including roots, hypocotyls, cotyledons, young primary leaves and embryos of Arabidopsis thaliana and other species. The detailed protocol, recommended controls and troubleshooting are presented, along with examples of applications. The protocol consists of five main procedures: tissue fixation, tissue permeation, blocking, primary and secondary antibody incubation. Notably, the first procedure (tissue fixation) includes several steps (4–12) that are absolutely necessary for protein localization in hypocotyls, cotyledons and young primary leaves but should be omitted for other tissues. The protocol is usually done in 3 days, but could also be completed in 2 days.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brandizzi, F., Fricker, M. & Hawes, C. A greener world: The revolution in plant bioimaging. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 520–530 (2002).
Lauber, M.H. et al. The Arabidopsis KNOLLE protein is a cytokinesis-specific syntaxin. J. Cell Biol. 139, 1485–1493 (1997).
Friml, J., Benková, E., Mayer, U., Palme, K. & Muster, G. Automated whole-mount localization techniques for plant seedlings. Plant J. 34, 115–124 (2003).
Paciorek, T., Sauer, M., Balla, J., Wisniewska, J. & Friml, J. Immunocytochemical technique for protein localization in sections of plant tissues. Nat. Protocols doi:10.1038/nprot.2006.16.
Pimpl, P., Movafeghi, A ., Coughlan, S., Denecke, J., Hilmer, S. & Robinson, D.G. In situ localization and in vitro induction of plant COPI-coated vesicles. Plant Cell 11, 2213–2236 (2000).
Paciorek, T. et al. Auxin inhibits endocytosis and promotes its own efflux from cells. Nature 435, 1251–1256 (2005).
Swarup, R. et al. Structure-function analysis of the presumptive Arabidopsis auxin permease AUX1. Plant Cell 16, 3069–3083 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to C. Luschnig, W. Michalke, D. Robinson and R. Swarup for sharing material, and we thank P. Brewer for critical reading of the manuscript and discussions. M.S. and J.F. were supported by VolkswagenStiftung and the European Molecular Biology Organization Young Investigator Program; T.P. was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB 446); and E.B. was supported by the Margarete von Wrangell-Habilitationsprogramm.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sauer, M., Paciorek, T., Benková, E. et al. Immunocytochemical techniques for whole-mount in situ protein localization in plants. Nat Protoc 1, 98–103 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.15
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.15
This article is cited by
-
Adaptor protein complex interaction map in Arabidopsis identifies P34 as a common stability regulator
Nature Plants (2023)
-
Genome-wide identification of AP2/EREBP in Fragaria vesca and expression pattern analysis of the FvDREB subfamily under drought stress
BMC Plant Biology (2021)
-
PHYTOCHROME-INTERACTING FACTORs trigger environmentally responsive chromatin dynamics in plants
Nature Genetics (2021)
-
Arabidopsis antibody resources for functional studies in plants
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Protein trafficking in plant cells: Tools and markers
Science China Life Sciences (2020)