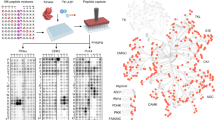
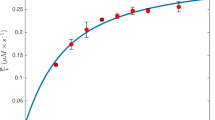
Abstract
Protein kinase activity results in the incorporation of radiolabeled phosphate from [γ-32P]ATP into a peptide or protein substrate. The measurement of the amount of radioactivity incorporated into a substrate as a function of time and enzyme concentration allows enzyme activity to be quantified. The activity is expressed as a 'unit', where 1 unit corresponds to the amount of protein kinase that catalyzes the incorporation of 1 nanomole of phosphate into the standard substrate in 1 minute. Specific activity is defined as units of activity per milligram protein. The assay format described here is quick, simple, inexpensive, sensitive and accurate, provides a direct measurement of activity and remains the 'gold standard' for the quantification of protein kinase activity. Up to 40 samples can be assayed manually at one time, and the assay takes one person less than 1 hour to complete.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohen, P. Protein kinases, the major drug targets of the 21st century? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 1, 309–316 (2002).
Witt, J.J. & Roskoski, R., Jr. Rapid protein kinase assay using phosphocellulose-paper absorption. Anal. Biochem. 66, 253–258 (1975).
Glass, D.B., Masaracchia, R.A., Feramisco, J.R. & Kemp, B.E. Isolation of phosphorylated peptides and proteins on ion exchange papers. Anal. Biochem. 87, 566–575 (1978).
Roskoski, R., Jr. Assays of protein kinase. Methods Enzymol. 99, 3–6 (1983).
Wei, Y.F. & Matthews, H.R. A filter-based protein kinase assay selective for alkali-stable protein phosphorylation and suitable for acid-labile protein phosphorylation. Anal. Biochem. 190, 188–192 (1990).
Tan, E., Lin Zu, X., Yeoh, G.C., Besant, P.G. & Attwood, P.V. Detection of histidine kinases via a filter-based assay and reverse-phase thin-layer chromatographic phosphoamino acid analysis. Anal. Biochem. 323, 122–126 (2003).
Park, Y.W. et al. Homogeneous proximity tyrosine kinase assays: scintillation proximity assay versus homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence. Anal. Biochem. 269, 94–104 (1999).
Wu, J.J. Comparison of SPA, FRET and FP for kinase assays. Methods Mol. Biol. 190, 65–85 (2002).
Seethala, R. & Menzel, R. A homogeneous, fluorescence polarization assay for src-family tyrosine kinases. Anal. Biochem. 253, 210–218 (1997).
Turek-Etienne, T.C. et al. Evaluation of fluorescent compound interference in 4 fluorescence polarization assays: 2 kinases, 1 protease, and 1 phosphatase. J. Biomol. Screen. 8, 176–184 (2003).
Davies, S.P., Reddy, H., Caivano, M. & Cohen, P. Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem. J. 351, 95–105 (2000).
Bain, J., McLauchlan, H., Elliott, M. & Cohen, P. The specificities of protein kinase inhibitors: an update. Biochem. J. 371, 199–204 (2003).
Acknowledgements
We thank the UK Medical Research Council, The Royal Society, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck and Co., Merck KGaA and Pfizer for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hastie, C., McLauchlan, H. & Cohen, P. Assay of protein kinases using radiolabeled ATP: a protocol. Nat Protoc 1, 968–971 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.149
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.149